|
Martin Shpanberg
__NOTOC__ Martin Spanberg (d. 1761; russian: Мартын Петрович Шпанберг, ''Martyn Petrovich Shpanberg'') was a Danish naval officer in Russian service who took part with his compatriot Vitus Bering in both Kamchatka expeditions as second in command. He is best known for finding a sea route to Japan from Russian territory and for exploring the Kuril Islands. Shikotan, one of the Kurils, was renamed in his honor by the Russians in 1796. Spanberg led three voyages in 1738, 1739, and 1742. On the first of these voyages, Spanberg left 29 June 1738 aboard the ''Archangel Michael'' (, ''Arkhangel Mikhail'') with his own assistants William Walton ( or , ''Vilim Valton'') and Alexander Shelting (, ''Aleksey Yeleazarovich Shel'ting'') commanding the ''Sv.'' or ''St. Gabriel'' (, ''Sviatoi Gavriil'') and the ''Nadezhda'' () respectively. He charted 30 of the Kurils. On the second voyage, he gained a fourth shipthe ''Bolsheretsk'' ()and was the first Russian commander to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Presenting The Discoveries Of Russian Navigators In The Pacific Ocean, As Well As Those Of Captain Cook WDL127
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rica De Plata
The Anson Archipelago was a designation for a widely scattered group of purported islands in the Western North Pacific Ocean between Japan and Hawaii. The group was supposed to include Wake Island and Marcus Island, as well as many phantom islands such as Los Jardines, Ganges Island, Rica de Oro, and Rica de Plata (the latter two sometimes referred to as Roca de Oro and Roca de Plata). The archipelago was named after George Anson, who seized Spanish navigational charts of these waters during his voyage around the world. See also * Pedro de Unamuno * Chryse and Argyre Chryse and Argyre ( and ) were a pair of legendary islands, located in the Indian Ocean and said to be made of gold (''chrysos'' in Greek) and silver (''argyros''). In Book 6, chapter 23 of his '' Natural History'', concerning the regions near ... References Phantom islands Islands of the Pacific Ocean Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean Fictional archipelagoes {{oceania-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorers From The Russian Empire
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians. Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most of ''Human, Homo sapiens'' history, saw humans Recent African origin of modern humans, moving out of Africa, settling in new lands, and developing distinct cultures in relative isolation. Early explorers settled in Europe and Asia; 14,000 years ago, some crossed the Settlement of the Americas, Ice Age land bridge from Siberia to Alaska, and moved southbound to settle in the Americas. For the most part, these cultures were ignorant of each other's existence. The second period of exploration, occurring over the last 10,000 years, saw increased cross-cultural exchange through trade and exploration, and marked a new era of cultural intermingling, and more recently, convergence. Early writings about exploration date back to the 4th millennium B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1761 Deaths
Events January–March * January 14 – Third Battle of Panipat: Ahmad Shah Durrani and his coalition decisively defeat the Maratha Confederacy, and restore the Mughal Empire to Shah Alam II. * January 16 – Siege of Pondicherry (1760) ended: The British capture Pondichéry, India from the French. * February 8 – An earthquake in London breaks chimneys in Limehouse and Poplar. * March 8 – A second earthquake occurs in North London, Hampstead and Highgate. * March 31 – 1761 Portugal earthquake: A magnitude 8.5 earthquake strikes Lisbon, Portugal, with effects felt as far north as Scotland. April–June * April 1 – The Austrian Empire and the Russian Empire sign a new treaty of alliance. * April 4 – A severe epidemic of influenza breaks out in London and "practically the entire population of the city" is afflicted; particularly contagious to pregnant women, the disease causes an unusual number of miscarriages and prema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Fyodorov (navigator)
Ivan Fyodorov (russian: Ива́н Фёдоров; died ) was a Russian navigator and commanding officer of the expedition to northern Alaska in 1732. After the First Kamchatka expedition of Vitus Bering, Russian exploration efforts were continued by Bering's lieutenant Martin Spanberg and the navigator Fyodorov. In 1732, with participants of the First Kamchatka expedition, land-surveyor Mikhail Gvozdev, and the navigator K. Moshkov, Fyodorov sailed to Dezhnev Cape, the easternmost point of Asia, in the ''St. Gabriel'' (russian: Святой Гавриил, ''Sviatoi Gavriil''). From there, after having replenished the water supply on 5 August, they sailed east and soon came near the mainland at the Cape Prince of Wales. They charted the northwestern coast of Alaska and mapped their route. By doing this, Fyodorov and Gvozdev completed the discovery of the Bering Strait, once started by Semyon Dezhnyov and Fedot Alekseyev and continued by Bering. Their expedition also discove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerasim Izmailov
Gerasim Grigoryevich Izmaylov (russian: Герасим Григорьевич Измайлов; ''circa'' 1745 - ''after'' 1795) was a Russian navigator involved in the Russian colonization of the Americas and in the establishment of the colonies of Russian America in Alaska. He was responsible for the first detailed maps of the Aleutian Islands. A native of Yakutsk, Izmaylov attended a navigation school in Okhotsk with Dmitry Bocharov, who became his lifelong business companion. In 1771, both were caught up in the Benyovszky mutiny at Bolsheretsk on Kamchatka. Izmaylov attempted to break away from the mutineers but, after being flogged, was marooned on the isle of Simushir, one of the uninhabited Kuril Islands. For a year he subsisted on "scallops, grass, and roots" before being rescued by yasak gatherers. He was investigated in Irkutsk on account of his association with Benyovszky, but was eventually cleared of all charges in 1774. In 1775, Izmaylov assumed command of the boat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dembei
Dembei ( ja, 伝兵衛 ''Dembei'', russian: Дэмбэй) was a Japanese people, Japanese castaway who, through Vladimir Atlasov, provided Russia with some of its first knowledge of Japan. He was a merchant clerk accompanying a fleet of "thirty transports laden with goods for Edo," which had been caught in a storm; they found their way to Kamchatka Peninsula, Kamchatka and were found by Atlasov in 1701 or 1702. Despite pleading to be brought back to Japan, Dembei and another young Japanese person (who did not survive long) were instead brought to Saint Petersburg, where he told Peter I of Russia, Peter the Great what he could about Japan. He taught some of the Japanese language to a few Russians, making him the father of Japanese language education in Russia. He was baptized as Gabriel and spent the rest of his life in Saint Petersburg. Although it is unlikely that Dembei had any significant knowledge of Japan's politics or military organization or anything else that might prove pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordenskiöld Archipelago
The Nordenskiöld Archipelago or Nordenskjold Archipelago (russian: Архипелаг Норденшельда, Arkhipelag Nordenshel'da) is a large and complex cluster of islands in the eastern region of the Kara Sea. Its eastern limit lies west of the Taymyr Peninsula. There are about 90 cold, windswept and desolate islands in this archipelago. These are mainly formed by igneous rocks and are covered with tundra vegetation. Except for two polar stations, one which was permanent in Russky Island between 1935 and 1999 and a temporary one in Tyrtov Island (Tyrtova) (1940-1975), there is no permanent human presence in any island of the archipelago. Geography The Nordenskiöld Archipelago stretches for almost from west to east and about from north to south in the Kara Sea, off the Siberian shores, where there are large coastal islands around Taymyr Island. The average elevation of the islands is relatively low. The highest point of the archipelago (107 m) is located in Chabak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shpanberg Island
Shpanberg Island (russian: остров Шпанберга, ''ostrov Shpanberga''), sometimes Spanberg Island, is an island of the Nordenskiöld Archipelago in the Kara Sea, off the coast of Siberia. Administratively this island belongs to the Krasnoyarsk Krai Federal subject of Russia and is part of the Great Arctic State Nature Reserve, the largest nature reserve of Russia. Geography Shpanberg Island is located in the central area of the archipelago on the southern side of the Lenin Strait. The island is long and has a maximum width of . Cape Razvodnoy (мыс Разводной) is the headland at its SE end and Cape Ustalosti (мыс Усталости) at its NE end. It is part of the Pakhtusov Islands (острова Пахтусова) subgroup of the Nordenskiöld Archipelago. The closest islands are Petersen Island to the southeast, Dobrynia Nikitich Island to the SW and Pakhtusov Island to the west.Google Earth The climate in the archipelago is severe and the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
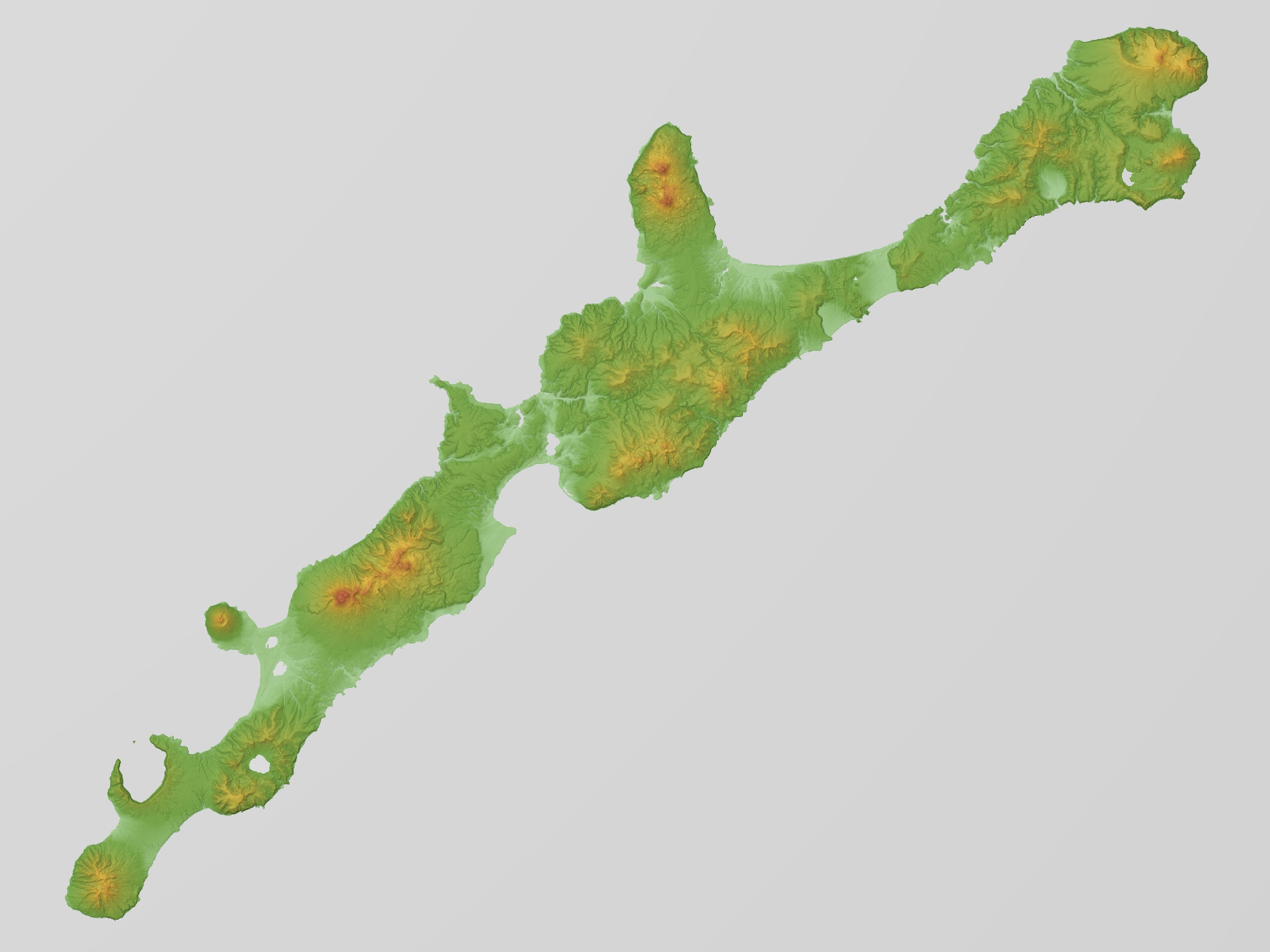
Shpanberg Island (Kuril Islands)
; ja, 色丹島 , location = Pacific Ocean , coordinates = , archipelago = Kuril Islands , total_islands = 1 , major_islands = , area_km2 = 225 , length = , width = , coastline = , highest_mount = Mount Tomari , elevation_m = 412 , country_claim = , country_claim_divisions_title_1 = Prefecture , country_claim_divisions_1 = Hokkaido , country_claim_divisions_title_2 = Subprefecture , country_claim_divisions_2 = Nemuro , country = , country_admin_divisions_title_1 = Federal subject , country_admin_divisions_1 = Sakhalin Oblast , country_admin_divisions_title_2 = District , country_admin_divisions_2 = Yuzhno-Kurilsky , population = 2,100 , population_as_of = , density = , ethnic_groups = , additional_info = Shikotan (Russian: Шик� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iturup
, other_names = russian: Итуру́п; ja, 択捉島 , location = Sea of Okhotsk , coordinates = , archipelago = Kuril Islands , total_islands = , major_islands = , area_km2 = 3139 , length_km = 200 , width_km = 27 , coastline = , highest_mount = Stokap , elevation_m = 1634 , country_claim = , country_claim_divisions_title_1 = Prefecture , country_claim_divisions_1 = Hokkaido , country_claim_divisions_title_2 = Subprefecture , country_claim_divisions_2 = Nemuro , country = , country_admin_divisions_title_1 = Federal subject , country_admin_divisions_1 = Sakhalin Oblast , country_admin_divisions_title_2 = District , country_admin_divisions_2 = Kurilsky , population = 7,500 , population_as_of = 2003 , density = , ethnic_groups = , additional_info = Iturup (russian: Остров Итуру́п, Ostrov Iturúp; ain, エツ゚ヲロㇷ゚� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urup
Urup ( ja, 得撫島, Uruppu-to; russian: Уру́п, Urúp, ain, ウルㇷ゚, Urup) is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Kuril Islands chain in the south of the Sea of Okhotsk, northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language word for salmon trout. It was formerly known as Company's Land. Geography and climate Urup has a roughly rectangular shape, measuring along its long axis and approximately along its narrow axis. It is the fourth largest of the Kuril Islands, with an area of . The highest point is Gora Ivao at . The strait between Urup and Iturup is known as the Vries Strait, after Dutch explorer Maarten Gerritsz Vries, the first recorded European to explore the area. The strait between Urup and Simushir is known as Bussol Strait, after the French word for "compass", which was the name of one of La Pérouse's vessels. This French mariner explored the area of the Kuril Islands in 1787. Urup consists of four major groups of active or dormant stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |