|
Marsimik La
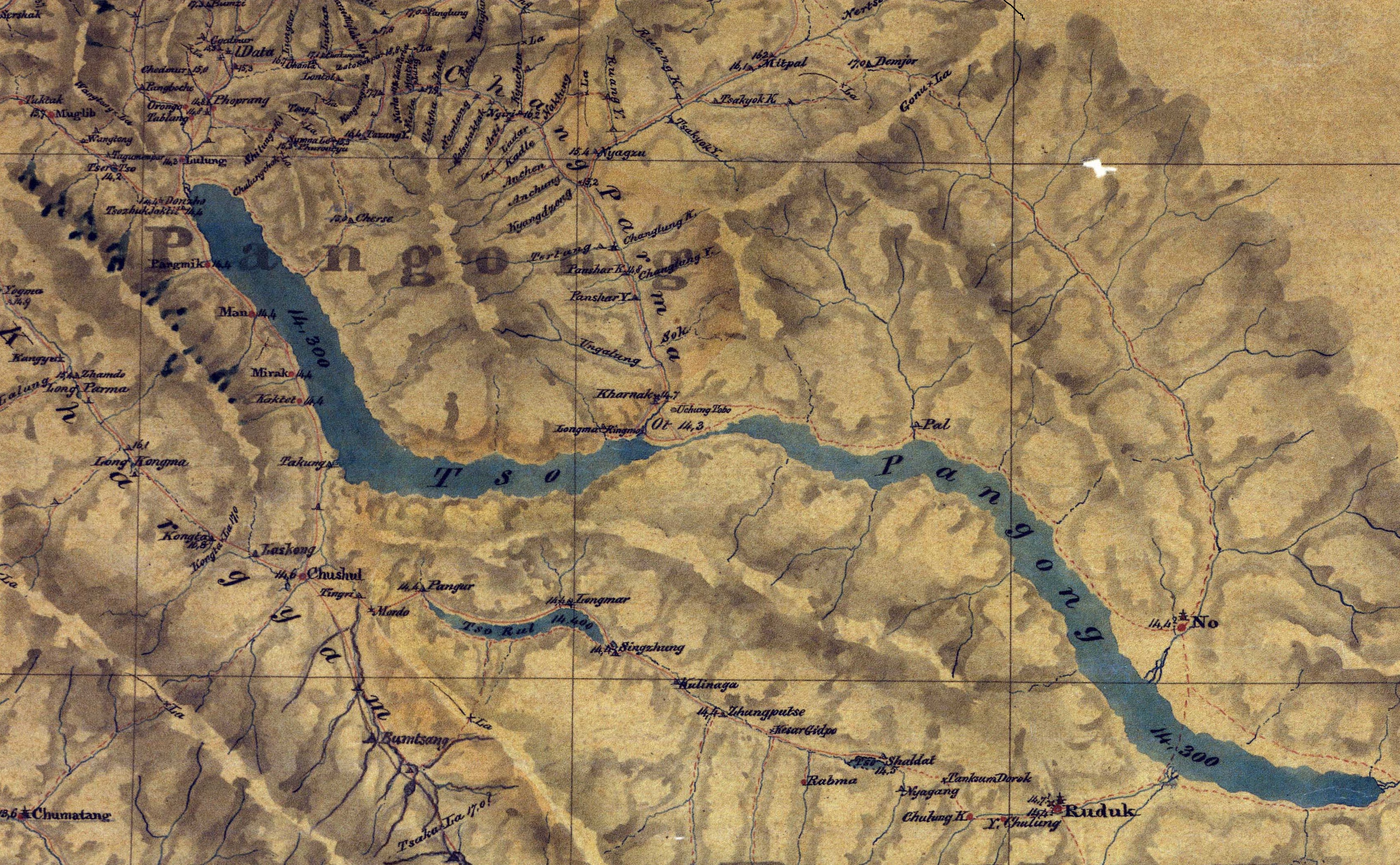
Marsimik La or Marsemik La, also called Lankar La, elevation is a high mountain pass in the Chang Chenmo Range in the Indian union territory of Ladakh, east of Leh as the crow flies. Ladakh's route to the Chang Chenmo Valley traverses the pass. Geography Marsimik La is located about northeast of Lukung at the tip of Pangong Lake, and southwest of Pamzal in the Chang Chenmo Valley. The ridge line of Marsimik La divides the basin of the Pangong Lake from the Chang Chenmo River. About 4 km to the east of Marsimik La is another ridge line with the pass Kiu La (also called ''Kangseng La''). Via this pass lies the Ladakhi route to the valley of Chang Parma (also called Changlung Lungpa), leading to the Khurnak Plain in the middle of the Pangong Lake. The description of Marsimik La in the ''Gazetteer of Kashmir and Ladak'' (1890) states: Sino-Indian border The pass is on the shortest route from Lukung to Kongka Pass area some away, where the China-India Line of Actual C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir, state of India, located in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent in the vicinity of the Karakoram and westernmost Himalayan mountain ranges. From 1947 to 2019, Ladakh was part of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir, which has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since the partition of the subcontinent in 1947." Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir: Territory in northwestern India, subject to a dispute between India and Pakistan. It has borders with Pakistan and China." Ladakh is bordered by the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east, the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh to the south, both the Indian-administered union territory of Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir and the Pakistan-administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamzal
__NOTOC__ Hot Springs (traditional name: Kyam) is a campsite and the location of an Indian border outpost in the Chang Chenmo River valley in Ladakh near the disputed border with China. It is so named because there is a hot spring at this location. The Line of Actual Control near Kongka Pass is only to the east. Name Historically, the name for the hot spring was ''Kyam'' (''Kiam'', ''Kayam''). The Chinese still refer to it by this name. Geography Geologist Frederic Drew states that the Chang Chenmo river flows on a barren gravel bed, with occasional alluvial patches where vegetation is found. Hot Springs is one such location. In the vicinity are also other such patches, named Pamzal, Tsogtsalu (or ''Tsolu'') and Gogra. They were historical halting places for travellers and trading caravans, with a supply of water, fuel and fodder. Nomadic Ladakhi graziers also used them for grazing cattle. A large tributary called Kugrang joins the Chang Chenmo River near Hot Spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Points Of Earth
This article lists extreme locations on Earth that hold geographical records or are otherwise known for their geophysical or meteorological superlatives. All of these locations are Earth-wide extremes; extremes of individual continents or countries are not listed. Latitude and longitude Northernmost * The northernmost point on Earth is the Geographic North Pole, in the Arctic Ocean. ** The northernmost point of land is the northern tip of Kaffeklubben Island, north of Greenland (), which lies slightly north of Cape Morris Jesup, Greenland (). Various shifting gravel bars lie farther north, the most famous being Oodaaq. There have been other islands more northern such as 83-42 and ATOW1996 but they have not been confirmed as permanent. Southernmost * The southernmost point on Earth and the southernmost point on land is the Geographic South Pole, which is on the continent of Antarctica. ** The southernmost continental point of land outside Antarctica is in South America at Cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Border Roads Organisation
The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) is a road construction executive force in India that provides support to and is now a part of the Indian Armed Forces. BRO develops and maintains road networks in India's border areas and friendly neighboring countries. This includes infrastructure operations in 19 states and three union territories (including Andaman and Nicobar Islands) and neighboring countries such as Afghanistan, Bhutan, Myanmar, Tajikistan and Sri Lanka. By 2022, BRO had constructed over of roads, over 450 permanent bridges with a total length of over length and 19 airfields in strategic locations. BRO is also tasked with maintaining this infrastructure including operations such as snow clearance.Annual Report 2014–2015. Border Roads Organisation. (Chapter 7)'. Ministry of Road Transport and Highways. Government of IndiaArchivedon 12 February 2021.Annual Report 2015–2016'. Ministry of Defence. Government of India. Accessed on 13 June 2021. Officers from the Border R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Of Actual Control
The Line of Actual Control (LAC), in the context of the Sino-Indian border dispute, is a notional demarcation lineAnanth KrishnanLine of Actual Control , India-China: the line of actual contest, 13 June 2020: "In contrast, the alignment of the LAC has never been agreed upon, and it is has neither been delineated nor demarcated. There is no official map in the public domain that depicts the LAC. It can best be thought of as an idea, reflecting the territories that are, at present, under the control of each side, pending a resolution of the boundary dispute." that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory. The concept was introduced by Chinese premier Zhou Enlai in a 1959 letter to Jawaharlal Nehru as the "line up to which each side exercises actual control", but rejected by Nehru as being incoherent. Subsequently the term came to refer to the line formed after the 1962 Sino-Indian War. The LAC is different from the borders claimed by each c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kongka Pass
The Kongka Pass or Kongka La () is a low mountain pass on the Line of Actual Control between India and China in eastern Ladakh. It lies on a spur of the Karakoram range that intrudes into the Chang Chenmo Valley adjacent to the disputed Aksai Chin region. China claimed the location as its border in a 1956 map, and attacked an Indian patrol party in 1959 killing ten policemen and apprehending ten others. Known as the Kongka Pass incident, the event was a milestone in the escalation of the border dispute between the two countries. Name In the Ladakhi language, Kongka () means a "low pass or ridge, high point or rise of a plateau". In the first reference we have of this pass, it was called "Salmu Kongka" and explained as a "small pass". : Describing the route from Leh to Keriya: "Leaving hangchenmo valleyshortly after the Shahidulla road turns off to the left, it ascends to the plateau by a small pass (the Salmu Kongka); descending again into the valley and crossing the Changch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khurnak Plain
The Khurnak Fort () is a ruined fort on the northern shore of the Pangong Lake that spans eastern Ladakh in India and Rutog County in the Tibet region of China. The area of the Khurnak Fort is disputed by India and China, and has been under Chinese administration since 1958. Though the ruined fort itself is not of much significance, it serves as a landmark denoting the middle of the Pangong Lake. The fort lies at the western edge of a large plain formed as the alluvial fan of a stream known as Chumesang, which falls into the Pangong lake from the north. The plain itself is called ''Ote Plain'' locally, but now generally called the Khurnak Plain. Geography The Khurnak Fort stands on a large plain called ''Ot'' or ''Ote'' at the centre of the Pangong Lake on its northern bank. In recent times, the plain has come to be called the "Khurnak Plain", after the fort. The plain divides the Pangong Lake into two halves: to the west is the ''Pangong Tso'' proper and to the east are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang Parma
The Khurnak Fort () is a ruined fort on the northern shore of the Pangong Lake that spans eastern Ladakh in India and Rutog County in the Tibet region of China. The area of the Khurnak Fort is disputed by India and China, and has been under Chinese administration since 1958. Though the ruined fort itself is not of much significance, it serves as a landmark denoting the middle of the Pangong Lake. The fort lies at the western edge of a large plain formed as the alluvial fan of a stream known as Chumesang, which falls into the Pangong lake from the north. The plain itself is called ''Ote Plain'' locally, but now generally called the Khurnak Plain. Geography The Khurnak Fort stands on a large plain called ''Ot'' or ''Ote'' at the centre of the Pangong Lake on its northern bank. In recent times, the plain has come to be called the "Khurnak Plain", after the fort. The plain divides the Pangong Lake into two halves: to the west is the ''Pangong Tso'' proper and to the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangong Tso
Pangong Tso or Pangong Lake (; ; hi, text=पैंगोंग झील) is an endorheic lake spanning eastern Ladakh and West Tibet situated at an elevation of . It is long and divided into five sublakes, called ''Pangong Tso'', ''Tso Nyak'', ''Rum Tso'' (twin lakes) and ''Nyak Tso''. Approximately 50% of the length of the overall lake lies within Tibet in China, 40% in Ladakh, India and the remaining 10% is disputed and is a de-facto buffer zone between India and China. The lake is wide at its broadest point. All together it covers almost 700 km2. During winter the lake freezes completely, despite being saline water. It has a land-locked basin separated from the Indus River basin by a small elevated ridge, but is believed to have been part of the latter in prehistoric times. Names Historically, the lake is viewed as being made up five sublakes, which are connected through narrow water channels. The name ''Pangong Tso'' only applied to the westernmost lake that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lukung
Lukung is a village located on the banks of Pangong Tso, near Line of Actual Control in the Leh District, Ladakh. Location Lukung is located 142 km east of Leh Leh () ( lbj, ) is the joint capital and largest city of Ladakh, a union territory of India. Leh, located in the Leh district, was also the historical capital of the Kingdom of Ladakh, the seat of which was in the Leh Palace, the former res ... and is known as Gateway to Pangong Tso. It's elevation is . Gallery File:Tangtse river at Muglib.jpg, Lukung valley area (May 2016) File:Tangtse_near_Lukung,_Ladakh.JPG, Welcomen to Lukung, the milestone (September 2013) File:The Pangong Tso and Lukung (on the right) (10067277855).jpg, The Pangong Tso and Lukung on the right (September 2013) References Villages in Durbuk tehsil {{Ladakh-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




%2C_in_New_Delhi_on_December_01%2C_2020.jpg)