|
Marlex
Marlex is a trademarked name for crystalline polypropylene and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). These plastics were invented by J. Paul Hogan and Robert Banks, two research chemists at the Phillips Petroleum Company. Interest in the material in the 1950s arose from its high melting point and tensile strength, making it more desirable than the more common form of polyethylene. For example, the medical community in 1958 was eager to use Marlex 50 crystalline polyethylene which softens at . Objects made of Marlex could be sterilized in high-temperature autoclaves without affecting their form. Marlex was used by Wham-O for their Hula Hoops in the 1950s, which helped create a market for this form of plastic. It is now used surgically as a reinforcing mesh in inguinal hernia repair Inguinal hernia surgery is an operation to repair a weakness in the abdominal wall that abnormally allows abdominal contents to slip into a narrow tube called the inguinal canal in the groin region. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wham-O
Wham-O Inc. is an American toy company based in Carson, California, United States. It is known for creating and marketing many popular toys for nearly 70 years, including the Hula hoop, Frisbee, Slip 'N Slide, Super Ball, Trac-Ball, Silly String, Hacky sack, Wham-O Bird Ornithopter and Boogie Board, many of which have become genericized trademarks. Corporate history Richard Knerr (1925–2008) and Arthur "Spud" Melin (1924–2002), two University of Southern California graduates who were friends since their teens, were unhappy with their jobs and decided to start their own business. In 1948 they formed the WHAM-O Manufacturing Company in the Knerr family garage in South Pasadena. Their first product was the Wham-O Slingshot, made of ash wood, which Knerr and Melin promoted by holding demonstrations of their own slingshot skills. The name "Wham-O" was inspired by the sound of the slingshot's shot hitting the target. The powerful slingshot was adopted by clubs for competitive ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Banks (chemist)
Robert L. Banks (November 24, 1921 – January 3, 1989) was an American chemist. He was born and grew up in Piedmont, Missouri. He attended the University of Missouri - Rolla, and initiated into Alpha Phi Omega in 1940. He joined the Phillips Petroleum company in 1946 and worked there until he retired in 1985. He died in Missouri on January 3, 1989. Technical contributions He was a fellow research chemist of J. Paul Hogan. They began working together in 1946, and in 1951 invented "crystalline polypropylene" and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). These plastics were initially known by the name Marlex. The polymerization of ethylene was made possible by their discovery of the so-called Phillips catalyst. Recognition In 1987, Banks and Hogan won the Perkin Medal, and in 2001 they were inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame. Both were given a '' Heroes of Chemistry'' award by the American Chemical Society in 1989. Dr. Banks was inducted into the Plastics Hall of Fame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hula Hoop
A hula hoop is a toy hoop that is twirled around the waist, limbs or neck. It can also be wheeled along the ground like a wheel, with careful execution. They have been used by children and adults since at least 500 BC. The modern hula hoop was inspired by Australian bamboo hoops. Common lore posits the creators of the plastic hoop popularised in the US witnessed Australian children playing with bamboo hoops while driving past in an automobile. The new plastic version was popularized in 1958 by the Wham-O toy company and became a fad. Hula hoops for children generally measure approximately in diameter, while those for adults measure around . Traditional materials for hoops include willow, rattan (a flexible and strong vine), grapevines and stiff grasses. Commercial hoops are usually made of plastic tubing. Origins Native American Hoop Dance is a form of storytelling dance incorporating hoops as props. These props are used to create both static and dynamic shapes, which repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene. Polypropylene belongs to the group of polyolefins and is partially crystalline and non-polar. Its properties are similar to polyethylene, but it is slightly harder and more heat-resistant. It is a white, mechanically rugged material and has a high chemical resistance. Bio-PP is the bio-based counterpart of polypropylene (PP). Polypropylene is the second-most widely produced commodity plastic (after polyethylene). In 2019, the global market for polypropylene was worth $126.03 billion. Revenues are expected to exceed US$145 billion by 2019. The sales of this material are forecast to grow at a rate of 5.8% per year until 2021. History Phillips Petroleum chemists J. Paul Hogan and Robert Banks first demonstrated the polymerization of propylene in 1951. The stereoselective polymerization t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-density Polyethylene
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or "polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density ratio, HDPE is used in the production of plastic bottles, corrosion-resistant piping, geomembranes and plastic lumber. HDPE is commonly recycled, and has the number "2" as its resin identification code. In 2007, the global HDPE market reached a volume of more than 30 million tons. Properties HDPE is known for its high strength-to-density ratio. The density of HDPE ranges from 930 to 970 kg/m3. The standard method to test plastic density is ISO 1183 part 2 (gradient columns), alternatively ISO 1183 part 1MVS2PRO density analyzer. Although the density of HDPE is only marginally higher than that of low-density polyethylene, HDPE has little branching, giving it stronger intermolecular forces and tensile strength (38 MPa versus 21 MPa) than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives. 9.2 billion tonnes of plastic are estimated to have been made between 1950 and 2017. More than half this plastic has been produced since 2004. In 2020, 400 million tonnes of plastic were produced. If global trends on plastic demand continue, it is estimated that by 2050 annual global plastic production will reach over 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phillips Petroleum Company
Phillips Petroleum Company was an American oil company incorporated in 1917 that expanded into petroleum refining, marketing and transportation, natural gas gathering and the chemicals sectors. It was Phillips Petroleum that first found oil in the North Sea on December 23, 1969, at a position that was later named Ekofisk. On August 30, 2002, Conoco Inc. merged with Phillips Petroleum to form ConocoPhillips, becoming the third largest integrated energy company and second-largest refining company in the United States. The company moved its headquarters to Houston.Christopher J. Castaneda,"Phillips Petroleum Company." ''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''.Accessed 04 February 2013. In 2012, ConocoPhillips split into two separate companies. The legacy company kept its name, and spun off the midstream and downstream portions of its business. The new company, which owns the refinery, chemical and pipeline assets formerly held in ConocoPhillips, is named Phillips 66, the bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
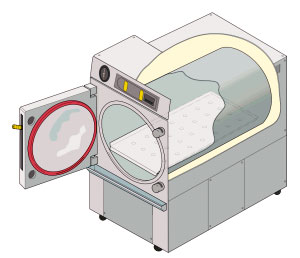
Autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for around 30-60 minutes at a pressure of 15 psi (103 kPa or 1.02 atm) depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization autoclav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inguinal Hernia Repair
Inguinal hernia surgery is an operation to repair a weakness in the abdominal wall that abnormally allows abdominal contents to slip into a narrow tube called the inguinal canal in the groin region. There are two different clusters of hernia: groin and ventral (abdominal) wall. Groin hernia includes femoral, obturator, and inguinal. Inguinal hernia is the most common type of hernia and consist of about 75% of all hernia surgery cases in the US. Inguinal hernia, which results from lower abdominal wall weakness or defect, is more common among men with about 90% of total cases. In the inguinal hernia, fatty tissue or a part of the small intestine gets inserted into the inguinal canal. Other structures that are uncommon but may get stuck in inguinal hernia can be the appendix, caecum, and transverse colon. Hernias can be asymptomatic, incarcerated, or strangled. Incarcerated hernia leads to impairment of intestinal flow, and strangled hernia obstructs blood flow in addition to intest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |