|
Mariana Trough
The Mariana Trough is an active back-arc basin in the western Pacific Ocean . It is an integral part of the Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc system. Location and Bathymetry The Mariana Trough stretches 1300 km from north to south, about the distance from Los Angeles CA to Portland OR, Tokyo, Japan to Seoul, Korea, or London, England to Rome, Italy. The Mariana Trough has roughly the dimensions and areal extent of Japan or California. The Trough is crudely crescent-shaped, opening on the south; it is bounded to the east by the active Mariana arc, to the west by the remnant arc of the West Mariana Ridge , and to the south by the Challenger Deep, part of the Mariana Trench. It narrows northward until the Mariana arc and West Mariana Ridge meet at about 24°N. It is widest in the middle, at 18°N, where it is about 240 km wide, and narrows to about half this at its southern, open end. Depths in the basin are distributed asymmetrically, being greater adjacent to the West Mariana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
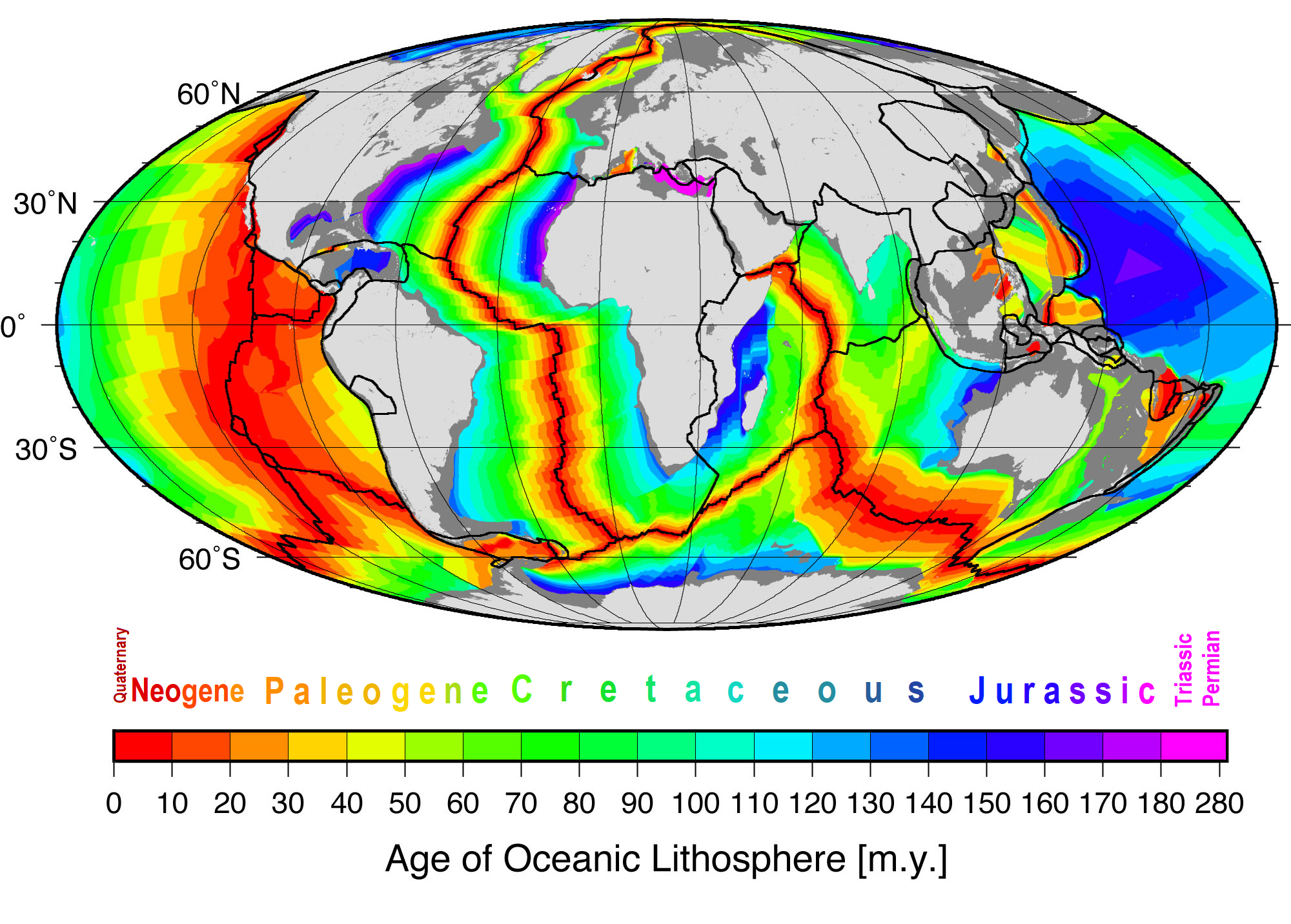
Seafloor Spreading
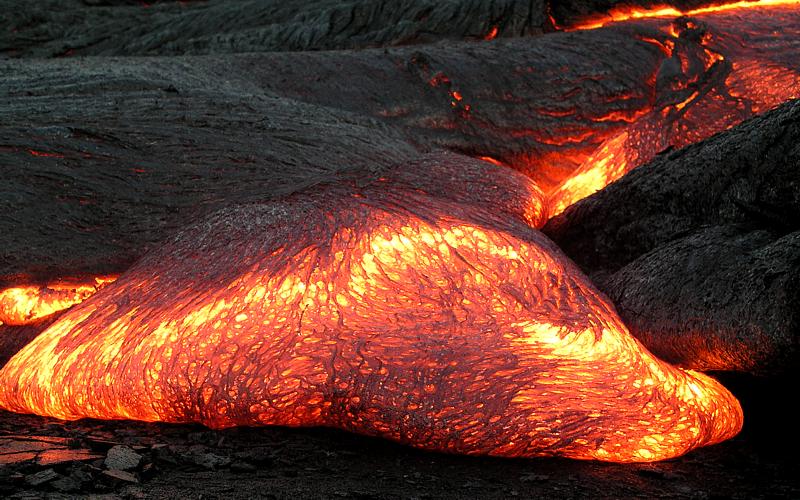
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. History of study Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener and Alexander du Toit of continental drift postulated that continents in motion "plowed" through the fixed and immovable seafloor. The idea that the seafloor itself moves and also carries the continents with it as it spreads from a central rift axis was proposed by Harold Hammond Hess from Princeton University and Robert Dietz of the U.S. Naval Electronics Laboratory in San Diego in the 1960s. The phenomenon is known today as plate tectonics. In locations where two plates move apart, at mid-ocean ridges, new seafloor is continually formed during seafloor spreading. Significance Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. When oceanic plates diverge, tensional stress causes fractures to occur in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonophysics (journal)
''Tectonophysics, The International Journal of Geotectonics and the Geology and Physics of the Interior of the Earth'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier. It was established in 1964 and covers the field of tectonophysics, including kinematics, structure, composition, and dynamics of the solid Earth at all scales. Organization The editors-in-chief are Philippe Agard (Pierre and Marie Curie University), Jean-Philippe Avouac (California Institute of Technology), Ramon Carbonell (Spanish National Research Council), Rob Govers (Utrecht University), Zheng Xiang Li (Curtin University), and Kelin Wang (Geological Survey of Canada). Abstracting and indexing This journal is abstracted and indexed in over fifty databases, including Current Contents, GeoRef, Inspec, Scopus and Web of Science. Notable articles According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Tectonophysics'' has a 2011 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iwo Jima
Iwo Jima (, also ), known in Japan as , is one of the Japanese Volcano Islands and lies south of the Bonin Islands. Together with other islands, they form the Ogasawara Archipelago. The highest point of Iwo Jima is Mount Suribachi at high. Although south of the metropolis of Tokyo on the mainland, this island of 21 km2 (8 square miles) is administered as part of the Ogasawara Subprefecture of Tokyo. Since July 1944, when all the civilians were forcibly evacuated, the island has had a military-only population. The island was the location of the Battle of Iwo Jima between February 1945 and March 1945. This engagement saw some of the fiercest fighting of the Pacific War, with each side suffering over 20,000 casualties in the battle. The island became globally recognized when Joe Rosenthal, of the Associated Press, published his photograph '' Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima'', taken on Mount Suribachi. The US military occupied Iwo Jima until 1968, when it was returned to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukutoku-oka-no-ba
is a submarine volcano that is part of the Volcano Islands in the Bonin Islands of Japan. It is located northeast of the island of South Iwo Jima. Geography The volcano is part of a larger elongated submarine volcano with two peaks and with a magma composition of trachyandesite. The volcano itself has erupted on multiple occasions with the last eruption before 2021 occurring during 2010. The first island to form when this volcano was discovered formed in 1904–5 and with a few more forming during the course of the 1900s. History The earliest recorded eruption of Fukutoku-Okanoba in 1904 formed an ephemeral island named Shin-Iwo-jima (''New Sulfur Island''). Other ephemeral islands have also formed, the most recent of which formed in 1986. In 2010, the Japanese coast guard spotted steam rising above the ocean and water discoloration of the surrounding area. In 2021, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) reported that a submarine eruption occurred at Fukutoku-Okanoba volcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoshonite
Shoshonite is a type of igneous rock. More specifically, it is a potassium-rich variety of basaltic trachyandesite, composed of olivine, augite and plagioclase phenocrysts in a groundmass with calcic plagioclase and sanidine and some dark-colored volcanic glass. Shoshonite gives its name to the shoshonite series and grades into absarokite with the loss of plagioclase phenocrysts and into banakite with an increase in sanidine. Shoshonite was named by Iddings in 1895 for the Shoshone River in Wyoming. Textural and mineralogical features of potash-rich rocks of the absarokite-shoshonite-banakite series strongly suggest that most of the large crystals and aggregates are not true phenocrysts as previously thought but are xenocrysts and microxenoliths, suggesting a hybrid origin involving assimilation of gabbro by high-temperature syenitic magma. Chemical characteristics Igneous rocks with shoshonitic chemical characteristics must be:Morrison, Gregg, 1980, ''Characteristics and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magmatic
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and gas bubbles. Magma is produced by melting of the mantle or the crust in various tectonic settings, which on Earth include subduction zones, continental rift zones, mid-ocean ridges and hotspots. Mantle and crustal melts migrate upwards through the crust where they are thought to be stored in magma chambers or trans-crustal crystal-rich mush zones. During magma's storage in the crust, its composition may be modified by fractional crystallization, contamination with crustal melts, magma mixing, and degassing. Following its ascent through the crust, magma may feed a volcano and be extruded as lava, or it may solidify underground to form an intrusion, such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles is essential to geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is associated with the stretching and thinning of the crust or the lithosphere. This type of tectonics is found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peridotite
Peridotite ( ) is a dense, coarse-grained igneous rock consisting mostly of the silicate minerals olivine and pyroxene. Peridotite is ultramafic, as the rock contains less than 45% silica. It is high in magnesium (Mg2+), reflecting the high proportions of magnesium-rich olivine, with appreciable iron. Peridotite is derived from Earth's mantle, either as solid blocks and fragments, or as crystals accumulated from magmas that formed in the mantle. The compositions of peridotites from these layered igneous complexes vary widely, reflecting the relative proportions of pyroxenes, chromite, plagioclase, and amphibole. Peridotite is the dominant rock of the upper part of Earth's mantle. The compositions of peridotite nodules found in certain basalts are of special interest along with diamond pipes (kimberlite), because they provide samples of Earth's mantle brought up from depths ranging from about 30 km to 200 km or more. Some of the nodules preserve isotope ratios of osm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and gas bubbles. Magma is produced by melting of the mantle or the crust in various tectonic settings, which on Earth include subduction zones, continental rift zones, mid-ocean ridges and hotspots. Mantle and crustal melts migrate upwards through the crust where they are thought to be stored in magma chambers or trans-crustal crystal-rich mush zones. During magma's storage in the crust, its composition may be modified by fractional crystallization, contamination with crustal melts, magma mixing, and degassing. Following its ascent through the crust, magma may feed a volcano and be extruded as lava, or it may solidify underground to form an intrusion, such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Half-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifting
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben with normal faulting and rift-flank uplifts mainly on one side. Where rifts remain above sea level they form a rift valley, which may be filled by water forming a rift lake. The axis of the rift area may contain volcanic rocks, and active volcanism is a part of many, but not all, active rift systems. Major rifts occur along the central axis of most mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust and lithosphere is created along a divergent boundary between two tectonic plates. ''Failed rifts'' are the result of continental rifting that failed to continue to the point of break-up. Typically the transition from rifting to spreading develops at a triple junction where three converging rifts meet over a hotspot. Two of these evolve to the poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |