|
Margaret Of Valois
Margaret of Valois (french: Marguerite, 14 May 1553 – 27 March 1615), popularly known as La Reine Margot, was a French princess of the Valois dynasty who became Queen of Navarre by marriage to Henry III of Navarre and then also Queen of France at her husband's 1589 accession to the latter throne as Henry IV. Margaret was the daughter of King Henry II of France and Catherine de' Medici and the sister of Kings Francis II, Charles IX and Henry III. Her union with the King of Navarre, which had been intended to contribute to the reconciliation of Roman Catholics and the Huguenots in France, was tarnished six days after the marriage ceremony by the St Bartholomew's Day massacre and the resumption of the French Wars of Religion. In the conflict between Henry III of France and the Malcontents, she took the side of Francis, Duke of Anjou, her younger brother, which caused Henry to have a deep aversion towards her. As Queen of Navarre, Margaret also played a pacifying role in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Consort Of France
This is a list of the women who were queens or empresses as wives of French monarchs from the 843 Treaty of Verdun, which gave rise to West Francia, until 1870, when the Third Republic was declared. Living wives of reigning monarchs technically became queen consorts, including Margaret of Burgundy and Blanche of Burgundy who were kept in prison during their whole queenships. Carolingian dynasty Capetian dynasty Direct Capetians House of Valois House of Lancaster Some sources refer to Margaret of Anjou as Queen of France,Mary Ann Hookham: "The life and times of Margaret of Anjou, queen of England and France ", 1872 but her right to enjoy that title is disputed. She was briefly recognized only in English-controlled territories of France. (See also: Dual monarchy of England and France) Capetian dynasty House of Valois House of Valois-Orléans House of Valois-Angoulême House of Bourbon Françoise d'Aubigné, Marquise de Maintenon, who secretly m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incest
Incest ( ) is human sexual activity between family members or close relatives. This typically includes sexual activity between people in consanguinity (blood relations), and sometimes those related by affinity ( marriage or stepfamily), adoption, or lineage. It is strictly forbidden and considered immoral in most societies, and can lead to an increased risk of genetic disorders in children. The incest taboo is one of the most widespread of all cultural taboos, both in present and in past societies. Most modern societies have laws regarding incest or social restrictions on closely consanguineous marriages. In societies where it is illegal, consensual adult incest is seen by some as a victimless crime. Some cultures extend the incest taboo to relatives with no consanguinity such as milk-siblings, step-siblings, and adoptive siblings, albeit sometimes with less intensity. Third-degree relatives (such as half-aunt, half-nephew, first cousin) on average have 12.5% common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymphomania
Hypersexuality is extremely frequent or suddenly increased libido. It is controversial whether it should be included as a clinical diagnosis used by mental healthcare professionals. Nymphomania and satyriasis were terms previously used for the condition in women and men, respectively. Hypersexuality may be a primary condition, or the symptom of another medical disease or condition; for example, Klüver–Bucy syndrome or bipolar disorder. Hypersexuality may also present as a side effect of medication such as drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease. Clinicians have yet to reach a consensus over how best to describe hypersexuality as a primary condition, or to determine the appropriateness of describing such behaviors and impulses as a separate pathology. Hypersexual behaviors are viewed variously by clinicians and therapists as a type of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or "OCD-spectrum disorder", an addiction, or a disorder of impulsivity. A number of authors do not acknowle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandre Dumas Père
Alexandre Dumas (, ; ; born Dumas Davy de la Pailleterie (), 24 July 1802 – 5 December 1870), also known as Alexandre Dumas père (where '' '' is French for 'father', to distinguish him from his son Alexandre Dumas fils), was a French writer. His works have been translated into many languages and he is one of the most widely read French authors. Many of his historical novels of adventure were originally published as serials, including ''The Count of Monte Cristo'', ''The Three Musketeers'', ''Twenty Years After'' and '' The Vicomte of Bragelonne: Ten Years Later''. His novels have been adapted since the early twentieth century into nearly 200 films. Prolific in several genres, Dumas began his career by writing plays, which were successfully produced from the first. He also wrote numerous magazine articles and travel books; his published works totalled 100,000 pages. In the 1840s, Dumas founded the Théâtre Historique in Paris. His father, General Thomas-Alexandre Dumas Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court (royal)
A royal court, often called simply a court when the royal context is clear, is an extended royal household in a monarchy, including all those who regularly attend on a monarch, or another central figure. Hence, the word "court" may also be applied to the coterie of a senior member of the nobility. Royal courts may have their seat in a designated place, several specific places, or be a mobile, itinerant court. In the largest courts, the royal households, many thousands of individuals comprised the court. These courtiers included the monarch or noble's camarilla and retinue, household, nobility, clergy, those with court appointments, bodyguards, and may also include emissaries from other kingdoms or visitors to the court. Foreign princes and foreign nobility in exile may also seek refuge at a court. Near Eastern and Far Eastern courts often included the harem and concubines as well as eunuchs who fulfilled a variety of functions. At times, the harem was walled off and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platonic Academy (Florence)
The Accademia Platonica di Firenze or Platonic Academy of Florence was an informal discussion group which formed around Marsilio Ficino in the Florentine Renaissance of the fifteenth century. History In about 1462 Cosimo de' Medici established the young Marsilio Ficino at Montevecchio, a villa close to his own Villa di Careggi in the Florentine countryside. There Ficino, who was an ardent Neo-Platonist, was to study ancient Greek and work on translating the works of Plato into Latin. Ficino became the central figure of an informal group of people interested in his work, who both corresponded and met for intellectual discussions at Montevecchio, at Careggi, or perhaps in Florence itself. It was never a formal body – it had no statutes and kept no records of membership – and there is no contemporary evidence that it was ever known as a "Platonic academy". Arnaldo della Torre identified about a hundred people as participants in the group, among them Alessandro Braccesi, Demet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sainte-Beuve
Charles Augustin Sainte-Beuve (; 23 December 1804 – 13 October 1869) was a French literary critic. Early life He was born in Boulogne, educated there, and studied medicine at the Collège Charlemagne in Paris (1824–27). In 1828, he served in the St Louis Hospital. Beginning in 1824, he contributed literary articles, the ''Premier lundis'' of his collected ''Works'', to the newspaper ''Globe'', and in 1827 he came, by a review of Victor Hugo's ''Odes et Ballades'', into close association with Hugo and the Cénacle, the literary circle that strove to define the ideas of the rising Romanticism and struggle against classical formalism. Sainte-Beuve became friendly with Hugo after publishing a favourable review of the author's work but later had an affair with Hugo's wife, Adèle Foucher, which resulted in their estrangement. Curiously, when Sainte-Beuve was made a member of the French Academy in 1845, the ceremonial duty of giving the reception speech fell upon Hugo. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
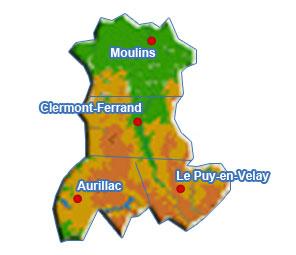
Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; oc, label= Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes.. The administrative region of Auvergne is larger than the historical province of Auvergne, one of the seven counties of Occitania, and includes provinces and areas that historically were not part of Auvergne. The Auvergne region is composed of the following old provinces: * Auvergne: departments of Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal, northwest of Haute-Loire, and extreme south of Allier. The province of Auvergne is entirely contained inside the Auvergne region * Bourbonnais: department of Allier. A small part of Bourbonnais lies outside Auvergne, in the neighbouring Centre-Val de Loire region (south of the department of Cher). * Velay: centre and southeast of department of Haute-Loire. Velay is entirely contained inside the Auver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic League (France)
The Catholic League of France (french: Ligue catholique), sometimes referred to by contemporary (and modern) Catholics as the Holy League (), was a major participant in the French Wars of Religion. The League, founded and led by Henry I, Duke of Guise, intended the eradication of Protestantism from Catholic France, as well as the replacement of King Henry III. Pope Sixtus V, Philip II of Spain, and the Jesuits were all supporters of this Catholic party. Origins Local confraternities were initially established by French Catholics to counter the Edict of Beaulieu in 1576. King Henry III placed himself at the head of these associations as a political counter to the ultra-Catholic League of Peronne. Following the repudiation of that edict by the Estates General, most of the local leagues were disbanded. Following the illness and death of Francis, duke of Anjou, heir to the French throne, on 10 June 1584, Catholic nobles gathered at Nancy. In December 1584, the League drew u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis, Duke Of Anjou
''Monsieur'' Francis, Duke of Anjou and Alençon (french: Hercule François; 18 March 1555 – 10 June 1584) was the youngest son of King Henry II of France and Catherine de' Medici. Early years He was scarred by smallpox at age eight, and his pitted face and slightly deformed spine did not suit his birth name of ''Hercule''. He changed his name to Francis in honour of his late brother Francis II of France when he was confirmed. The royal children were raised under the supervision of the governor and governess of the royal children, Claude d'Urfé and Françoise d'Humières, under the orders of Diane de Poitiers. In 1574, following the death of his brother Charles IX of France and the accession of his other brother Henry III of France, he became heir to the throne. In 1576 he was made Duke of Anjou, Touraine, and Berry. Alençon and the Huguenots During the night of 13 September 1575, Alençon fled from the French court after being alienated from his brother King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcontents (France)
{{Other uses, Malcontents (other){{!Malcontents The Malcontents were a faction of gentlemen in the Fifth French War of Religion (1574–1576). It opposed the policy of Henry of Valois, duc d'Anjou, who had become king under the name Henry III on 30 May 1574, and allied itself to the Huguenots The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bez .... The leader was the King's brother Francis, Duke of Alençon (made Duke of Anjou in 1576). The main goal of the Malcontents was to oppose the absolutist ambitions of the King. They were unhappy (''malcontent'') with the way the King treated the old French nobility. The Malcontent movement has been compared to the Fronde, 70 years later. Members The Malcontents had both Catholic and Huguenot members. The leaders were: * The D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)