|
Marcellus (comes Excubitorum)
Marcellus ( el, Μάρκελλος) was an East Roman (Byzantine) judicial official, one of the closest aides of the Byzantine emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565) and commander of the imperial bodyguard of the '' excubitores'' in circa 541–552. Biography Nothing is known of his early life and career, but he was evidently an experienced judge, for on April 8, 539 Emperor Justinian appointed him as one of the four senior judges (). It is possible that he was one of the '' comites consistoriani'', since he is referred to as ''comes'' in 540. In the Novel concerning his appointment, he is recorded by Emperor Justinian as being a close associate and "famous for his concern for justice", while the historian Procopius of Caesarea describes him as very austere, incorruptible, and a forbidding personality, with a profound concern for justice and truth.. By early 541, Marcellus had been appointed to the very influential post of ''comes excubitorum'', head of the imperial and palace guard. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
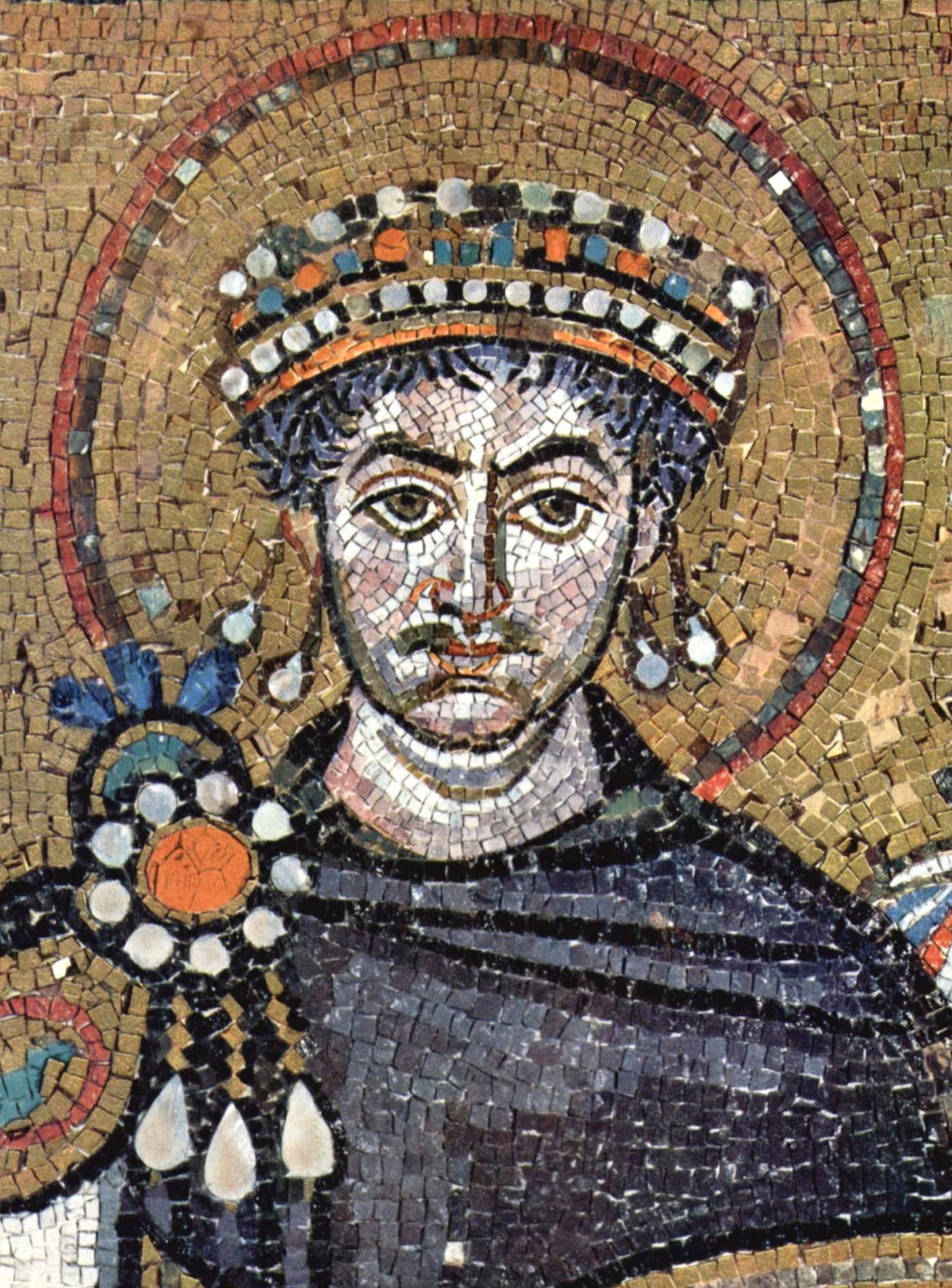
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praepositus Sacri Cubiculi
The ''praepositus sacri cubiculi'' (Latin: "provost of the sacred bedchamber", in gr, πραιπόσιτος τοῦ εὐσεβεστάτου κοιτῶνος, praipositos tou eusebestatou koitōnos) was one of the senior palace offices in the Late Roman Empire. Its holder was usually a eunuch, and acted as the grand chamberlain of the palace, wielding considerable authority and influence. In the 7th or 8th century, the title was also given to an order of rank for eunuch palace servants. The title and office continued in use in the simplified form of ''praipositos'' (πραιπόσιτος) in the Byzantine Empire until the late 11th century. History and evolution The first securely identifiable holder of the office was Eusebius under Emperor Constantius II (), but the position may have been introduced already under Constantine the Great (), in replacement of the older ''a cubiculo''. He controlled the corps of the '' cubicularii'' (κουβικουλάριοι, ), also eunuchs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consistorium
The ''sacrum consistorium'' or ''sacrum auditorium'' (from la, consistere, "discuss a topic"; gr, θεῖον συνέδριον, theion synedrion, "sacred assembly") was the highest political council of the Roman Empire from the time of Constantine the Great on. It replaced the '' consilium principis'' that had existed during the Principate. The council's powers and membership varied, being ultimately dependent on the emperor. The ''magister officiorum'', the ''quaestor sacri palatii'', the ''comes sacrarum largitionum'', the ''comes rerum privatarum'' and a few other high court officials were ''ex officio'' members, but the emperor was free to appoint additional members. These were specially appointed ''comites consistoriani'', who in the 6th century held the rank of ''vir spectabilis The title ''vir illustris'' ('illustrious man') is used as a formal indication of standing in late antiquity to describe the highest ranks within the senates of Ancient Rome, Rome and Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = Ethnicity , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = Sicilian , demographics1_info1 = 98% , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-82 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €89.2 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justin (consul 540)
Flavius Mar. Petrus Theodorus Valentinus Rusticius Boraides Germanus Iustinus, simply and commonly known as Justin ( la, Iustinus, el, ; ), was an East Roman (Byzantine) aristocrat and general. A member of the Justinian Dynasty and nephew of Emperor Justinian I (), he was appointed as one of the last Roman consuls in 540, before going on to assume senior military commands in the Balkans and in Lazica. He fought against the Slavs, the Sassanid Persians and supervised the Byzantine Empire's first contacts with the Avars. At the time of Justinian's death, he was seen as a probable successor, but was beaten to the throne by his cousin, Justin II (), who exiled him to Egypt, where he was murdered. Biography Early life and campaigns Justin was born around 525, the eldest son of Germanus and his wife Passara. Germanus was a cousin of the Byzantine emperor Justinian I () and thus a member of the wider Justinian dynasty and cousin to Justinian's successor, Emperor Justin II ().. In 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanus (cousin Of Justinian I)
Germanus ( el, Γερμανός; died 550) was an East Roman (Byzantine) general, one of the leading commanders of Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565). Germanus was Emperor Justinian's cousin, and a member of the ruling dynasty. He held commands in Thrace, North Africa, and the East against Persia, and was slated to command the final Byzantine expedition against the Ostrogoths. Having married into the Gothic Amal royal line through his second wife Matasuntha and a distinguished service record, at the time of his sudden death, he was considered the probable heir to Emperor Justinian. Biography Origins and early career Germanus was born before 505, the nephew of Emperor Justin I (r. 518–527) and thus cousin of Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565), and not his nephew, as is often erroneously stated... According to a statement in Jordanes's ''Getica'', Germanus was a descendant of the noble Roman clan of the Anicii. The exact nature of his connection, however, if indeed it is anything ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praejecta
Praejecta or Praiecta was a niece to Byzantine emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565) by blood and of his empress Theodora by marriage. Biography Praejecta was a daughter of Vigilantia and Dulcidio (or Dulcissimus), respectively the sister and brother-in-law of Emperor Justinian. She was also a sister of the later Byzantine emperor Justin II (r. 565–578) and the '' patricius'' Marcellus. She was initially married to the '' patricius'' Areobindus, a senator of noble birth. In 545, as the situation in Africa had gotten out of control following the death of Solomon and his replacement by his incompetent nephew Sergius, Areobindus, although having no prior military experience, was dispatched there with a small force. Areobindus was placed as joint commander with Sergius, but the two generals did not agree, with predictably disastrous results for the Byzantine imperial effort: the imperial forces were severely defeated at Thacia, although they managed to kill the rebel Stotzas. Follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between them and their in-laws. It is considered a cultural universal, but the definition of marriage varies between cultures and religions, and over time. Typically, it is an institution in which interpersonal relationships, usually sexual, are acknowledged or sanctioned. In some cultures, marriage is recommended or considered to be compulsory before pursuing any sexual activity. A marriage ceremony is called a wedding. Individuals may marry for several reasons, including legal, social, libidinal, emotional, financial, spiritual, and religious purposes. Whom they marry may be influenced by gender, socially determined rules of incest, prescriptive marriage rules, parental choice, and individual desire. In some areas of the world, arrang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artabanes (general)
Artabanes ( el, , Armenian: ''Artawan'', from Parthian ''Artawân'', '' fl.'' 538–554) was an East Roman (Byzantine) general of Armenian origin who served under Justinian I (r. 527–565). Initially a rebel against Byzantine authority, he fled to the Sassanid Persians but soon returned to Byzantine allegiance. He served in Africa, where he won great fame by killing the rebel general Guntharic and restoring the province to imperial allegiance. He became engaged to Justinian's niece Praejecta, but did not marry her due to the opposition of the Empress Theodora. Recalled to Constantinople, he became involved in a failed conspiracy against Justinian in 548/549, but wasn't punished severely after its revelation. He was soon pardoned and sent to Italy to fight in the Gothic War, where he participated in the decisive Byzantine victory at Casilinum. Early life Artabanes was a descendant of the royal Armenian Arsacid line, a branch of which at the time was recognized as autonomous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magister Militum Praesentalis
(Latin for "master of soldiers", plural ) was a top-level military command used in the later Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, the emperor remaining the supreme commander) of the empire. In Greek sources, the term is translated either as ''strategos'' or as ''stratelates''. Establishment and development of the command The title of ''magister militum'' was created in the 4th century, when the emperor Constantine the Great deprived the praetorian prefects of their military functions. Initially two posts were created, one as head of the infantry, as the ''magister peditum'' ("master of foot"), and one for the more prestigious cavalry, the ''magister equitum'' ("master of horse"). The latter title had existed since republican times, as the second-in-command to a Roman ''dictator''. Under Constantine's successors, the title was also established at a territorial l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora of around five million people of full or partial Armenian ancestry living outside modern Armenia. The largest Armenian populations today exist in Russia, the United States, France, Georgia, Iran, Germany, Ukraine, Lebanon, Brazil, and Syria. With the exceptions of Iran and the former Soviet states, the present-day Armenian diaspora was formed mainly as a result of the Armenian genocide. Richard G. Hovannisian, ''The Armenian people from ancient to modern times: the fifteenth century to the twentieth century'', Volume 2, p. 421, Palgrave Macmillan, 1997. Armenian is an Indo-European language. It has two mutually intelligible spoken and written forms: Eastern Armenian, today spoken mainly in Armenia, Artsakh, Iran, and the former Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyzicus
Cyzicus (; grc, Κύζικος ''Kúzikos''; ota, آیدینجق, ''Aydıncıḳ'') was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peninsula (the classical Arctonnesus), a tombolo which is said to have originally been an island in the Sea of Marmara only to be connected to the mainland in historic times either by artificial means or an earthquake. The site of Cyzicus, located on the Erdek and Bandırma roads, is protected by Turkey's Ministry of Culture. History Ancient The city was said to have been founded by Pelasgians from Thessaly, according to tradition at the coming of the Argonauts; later it received many colonies from Miletus, allegedly in 756 BC, but its importance began near the end of the Peloponnesian War when the conflict centered on the sea routes connecting Greece to the Black Sea. At this time, the cities of Athens and Miletus diminished in impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |