|
Marcatili's Method
Marcatili’s method is an approximate analytical method that describes how light propagates through rectangular dielectric optical waveguides . It was published by Enrique Marcatili in 1969. Optical dielectric waveguides guide electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum (light). This type of waveguide consists of dielectric materials (e.g., glass, silicon, indium phosphide, etc). The core of the waveguide has a higher index of refraction than its surrounding and the light is guided due to total internal reflection. In a ray description, the light zig-zags between the walls. The geometry of the waveguide dictates the light to propagate with specific velocities and specific distributions of the electric and magnetic fields, known as modes. For rectangular waveguides, these modes cannot be computed analytically. This can be done either using a numerical mode solver, or using an approximate method such as Marcatili’s method. Propagation velocity of the light in the waveguide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Propagation
Wave propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel. Single wave propagation can be calculated by 2nd order wave equation ( standing wavefield) or 1st order one-way wave equation. With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves. For electromagnetic waves, propagation may occur in a vacuum as well as in the material medium. Other wave types cannot propagate through a vacuum and need a transmission medium to exist. Reflection of plane waves in a half-space The propagation and reflection of plane waves—e.g. Pressure waves (P-wave) or Shear waves (SH or SV-waves) are phenomena that were first characterized within the field of classical seismology, and are now considered fundamental concepts in modern seismic tomography. The analytical solution to this problem exists and is well known. The frequency domain solution can be obtained by first finding the Helmholtz deco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
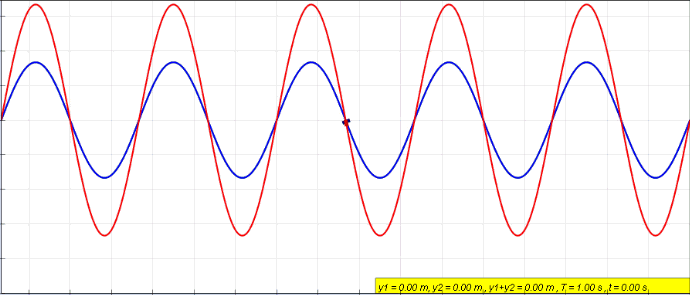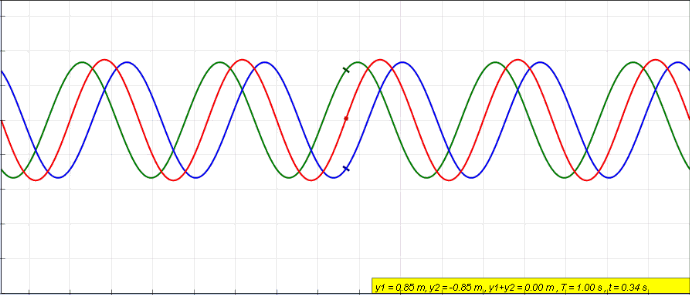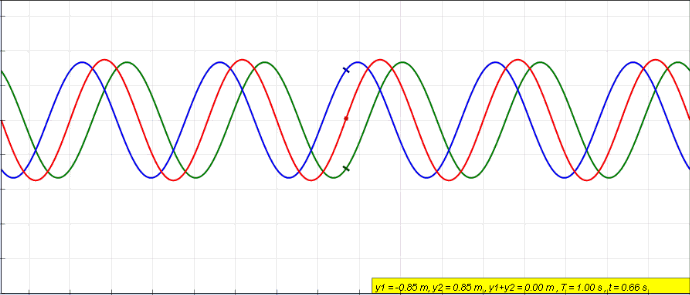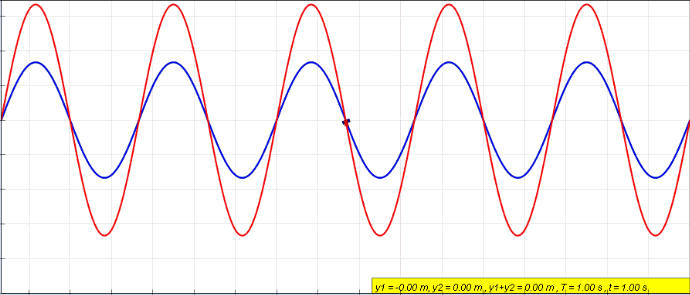
Explanation Of The Standing Waves In Marcatili Method (silicon-on-insulator Waveguide)
An explanation is a set of statements usually constructed to describe a set of facts which clarifies the causes, context, and consequences of those facts. It may establish rules or laws, and may clarify the existing rules or laws in relation to any objects or phenomena examined. Explanation, in philosophy, is a set of statements that makes intelligible the existence or occurrence of an object, event, or state of affairs. Among its most common forms are: * Causal explanation * Deductive-nomological explanation, which involves subsuming the explanandum under a generalization from which it may be derived in a deductive argument (e.g., “All gases expand when heated; this gas was heated; therefore, this gas expanded”) * Statistical explanation, which involves subsuming the explanandum under a generalization that gives it inductive support (e.g., “Most people who use tobacco contract cancer; this person used tobacco; therefore, this person contracted cancer”). Explanations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized software development model that encourages open collaboration. A main principle of open-source software development is peer production, with products such as source code, blueprints, and documentation freely available to the public. The open-source movement in software began as a response to the limitations of proprietary code. The model is used for projects such as in open-source appropriate technology, and open-source drug discovery. Open source promotes universal access via an open-source or free license to a product's design or blueprint, and universal redistribution of that design or blueprint. Before the phrase ''open source'' became widely adopted, developers and producers have used a variety of other terms. ''Open source'' gained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell’s Equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar etc. They describe how electric field, electric and magnetic fields are generated by electric charge, charges, electric current, currents, and changes of the fields.''Electric'' and ''magnetic'' fields, according to the theory of relativity, are the components of a single electromagnetic field. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon. The modern f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavenumber
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber (also wave number or repetency) is the ''spatial frequency'' of a wave, measured in cycles per unit distance (ordinary wavenumber) or radians per unit distance (angular wavenumber). It is analogous to temporal frequency, which is defined as the number of wave cycles per unit time (''ordinary frequency'') or radians per unit time (''angular frequency''). In multidimensional systems, the wavenumber is the magnitude of the ''wave vector''. The space of wave vectors is called ''reciprocal space''. Wave numbers and wave vectors play an essential role in optics and the physics of wave scattering, such as X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction, electron diffraction, and elementary particle physics. For quantum mechanical waves, the wavenumber multiplied by the reduced Planck's constant is the ''canonical momentum''. Wavenumber can be used to specify quantities other than spatial frequency. For example, in optical spectroscopy, it is often used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Velocity
The phase velocity of a wave is the rate at which the wave propagates in any medium. This is the velocity at which the phase of any one frequency component of the wave travels. For such a component, any given phase of the wave (for example, the crest) will appear to travel at the phase velocity. The phase velocity is given in terms of the wavelength (lambda) and time period as :v_\mathrm = \frac. Equivalently, in terms of the wave's angular frequency , which specifies angular change per unit of time, and wavenumber (or angular wave number) , which represent the angular change per unit of space, :v_\mathrm = \frac. To gain some basic intuition for this equation, we consider a propagating (cosine) wave . We want to see how fast a particular phase of the wave travels. For example, we can choose , the phase of the first crest. This implies , and so . Formally, we let the phase and see immediately that and . So, it immediately follows that : \frac = -\frac \frac = \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Vector
In physics, a wave vector (or wavevector) is a vector used in describing a wave, with a typical unit being cycle per metre. It has a magnitude and direction. Its magnitude is the wavenumber of the wave (inversely proportional to the wavelength), and its direction is perpendicular to the wavefront. In isotropic media, this is also the direction of wave propagation. A closely related vector is the angular wave vector (or angular wavevector), with a typical unit being radian per metre. The wave vector and angular wave vector are related by a fixed constant of proportionality, 2π radians per cycle. It is common in several fields of physics to refer to the angular wave vector simply as the ''wave vector'', in contrast to, for example, crystallography. It is also common to use the symbol ''k'' for whichever is in use. In the context of special relativity, ''wave vector'' can refer to a four-vector, in which the (angular) wave vector and (angular) frequency are combined. Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first noticed by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of the wave, or it can arise in a stationary medium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Optics
In physics, physical optics, or wave optics, is the branch of optics that studies interference, diffraction, polarization, and other phenomena for which the ray approximation of geometric optics is not valid. This usage tends not to include effects such as quantum noise in optical communication, which is studied in the sub-branch of coherence theory. Principle ''Physical optics'' is also the name of an approximation commonly used in optics, electrical engineering and applied physics. In this context, it is an intermediate method between geometric optics, which ignores wave effects, and full wave electromagnetism, which is a precise theory. The word "physical" means that it is more physical than geometric or ray optics and not that it is an exact physical theory. This approximation consists of using ray optics to estimate the field on a surface and then integrating that field over the surface to calculate the transmitted or scattered field. This resembles the Born approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveguide (optics)
An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum. Common types of optical waveguides include optical fiber waveguides, transparent dielectric waveguides made of plastic and glass, liquid light guides, and liquid waveguides. Optical waveguides are used as components in integrated optical circuits or as the transmission medium in local and long-haul optical communication systems. Optical waveguides can be classified according to their geometry (planar, strip, or fiber waveguides), mode structure (single-mode optical fiber, single-mode, multi-mode optical fiber, multi-mode), refractive index distribution (step or gradient index), and material (glass, polymer, semiconductor). Total internal reflection The basic principles behind optical waveguides can be described using the concepts of geometrical optics, geometrical or ray optics, as illustrated in the diagram. Light passing into a medium with higher refractive index bends towa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in an electrical conductor, because they have no loosely bound, or free, electrons that may drift through the material, but instead they shift, only slightly, from their average equilibrium positions, causing dielectric polarisation. Because of dielectric polarisation, positive charges are displaced in the direction of the field and negative charges shift in the direction opposite to the field (for example, if the field is moving parallel to the positive ''x'' axis, the negative charges will shift in the negative ''x'' direction). This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polaris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.gif)