|
Marble Point
Marble Point is a rocky promontory on the coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The United States operates a station at the point. The outpost is used as a helicopter refueling station supporting scientific research in the nearby continental interior, such as the McMurdo Dry Valleys. Dependent upon the weather conditions at the time, helicopters are able to fly in and out of the station 24 hours a day during the summer research season."Gas, food and lodging: Marble Point serves up warmth and good cheer" , ''The Antarctic Sun''. November 28, 1999. The station's remote location and adjoining frozen sea have largely discouraged tourism in the area. However, the Russian icebreaker conducts cruises in the |
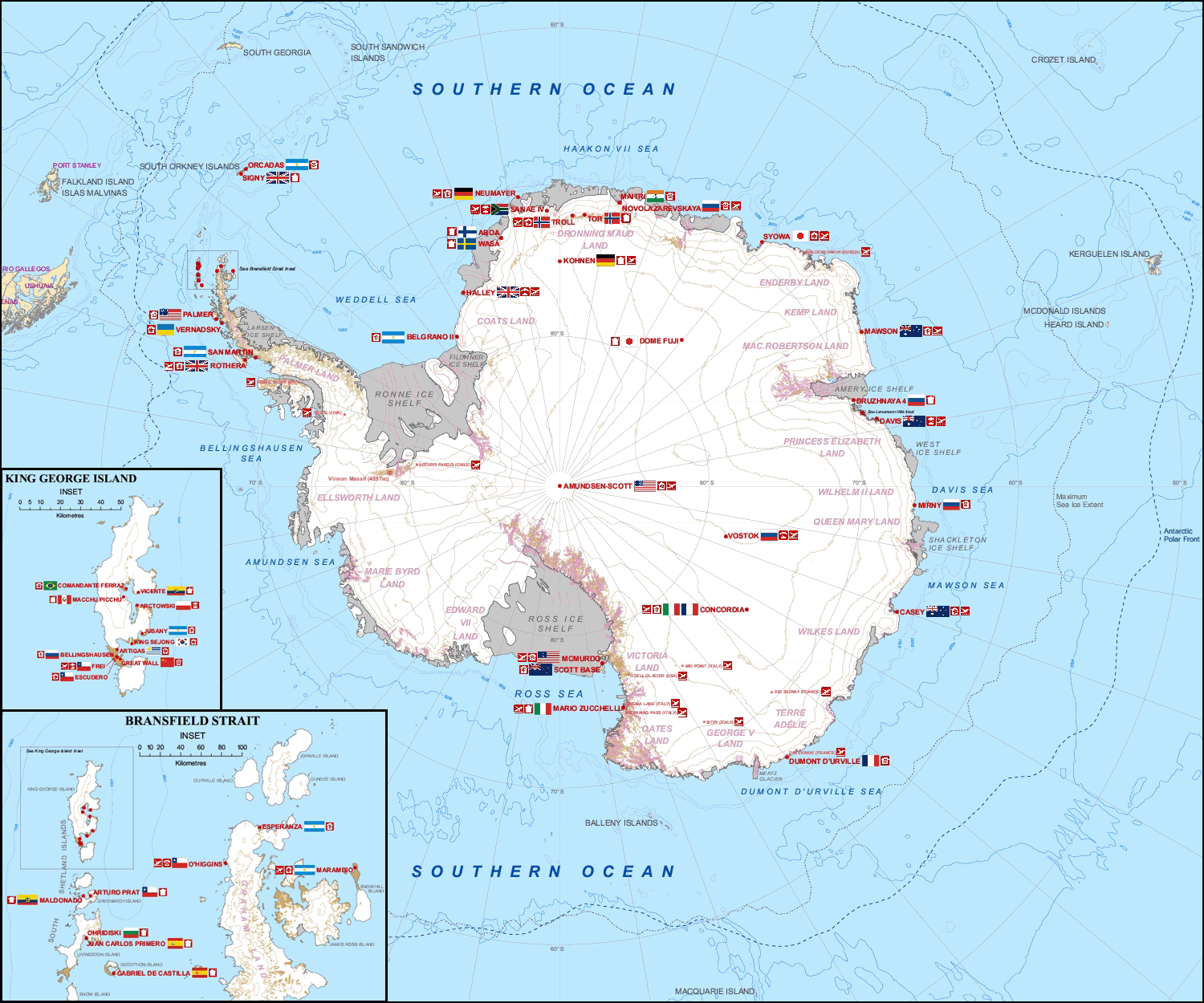
Research Stations In Antarctica
Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rock or on ice that is (for practical purposes) fixed in place. Many of the stations are staffed throughout the year. A total of 42 countries (as of October 2006), all signatories to the Antarctic Treaty, operate seasonal (summer) and year-round research stations on the continent. The population of people performing and supporting scientific research on the continent and nearby islands varies from approximately 4,000 during the summer season to 1,000 during winter (June). In addition to these permanent stations, approximately 30 field camps are established each summer to support specific projects. History First bases During the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration in the late 19th century, the first bases on the continent were established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Canada DHC-3 Otter
The de Havilland Canada DHC-3 Otter is a single-engined, high-wing, propeller-driven, short take-off and landing (STOL) aircraft developed by de Havilland Canada. It was conceived to be capable of performing the same roles as the earlier and highly successful Beaver, including as a bush plane, but is overall a larger aircraft. Design and development The rugged single-engined, high-wing, propeller-driven DHC-3 Otter was conceived in January 1951 by de Havilland Canada as a larger, more powerful version of its highly successful DHC2 Beaver STOL utility transport. Dubbed the "King Beaver" during design, it would be the veritable "one-ton truck" to the Beaver's "half-ton" role. The Otter received Canadian certification in November 1952 and entered production shortly thereafter. Using the same overall configuration as the Beaver, the new, much heavier design incorporated a longer fuselage, greater-span wing, and cruciform tail. Seating in the main cabin expanded from six to 10 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headlands Of Victoria Land
A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 80, 246. . Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff. Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is flanked by land on three sides, whereas a headland is flanked by water on three sides. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where bands of rock of alternating resistance run perpendicular to the coast. Bays form when weak (less resistant) rocks (such as sands and clays) are eroded, leaving bands of stronger (more resistant) rocks (such as chalk, limestone, and granite) forming a headland, or peninsula. Through the deposition of sediment within the bay and the erosion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams Field
Williams Field or Willy Field is a United States Antarctic Program airfield in Antarctica. Williams Field consists of two snow runways located on approximately 8 meters (25 ft) of compacted snow, lying on top of 8–10 ft of ice, floating over 550 meters (1,800 ft) of water. The airport, which is approximately seven miles from Ross Island, serves McMurdo Station and New Zealand's Scott Base. Until the 2009–10 summer season, Williams was the major airfield for on-continent aircraft operations in Antarctica. Williams Field is named in honor of Richard T. Williams, a United States Navy equipment operator who drowned when his D-8 tractor broke through the ice on January 6, 1956. Williams and other personnel were participants in the first Operation Deep Freeze, a U.S. military mission to build a permanent science research station at McMurdo Station in anticipation of the International Geophysical Year 1957–58. Operation The skiway was typically in operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Stream (Antarctica)
Wilson Piedmont Glacier () is a large piedmont glacier extending from Granite Harbour to Marble Point on the coast of Victoria Land. Scheuren Stream takes meltwater from the glacier into the Bay of Sails, while South Stream flows southeastward to Bernacchi Bay. Discovered by the ''Discovery'' expedition, 1901–04. The British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, named the feature for Dr. Edward A. Wilson, surgeon and artist with Scott's first expedition and chief of the scientific staff with the second. Wilson lost his life on the way back from the South Pole The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ... with Scott. See also * Ball Stream * King Pin Glaciers of Scott Coast {{ScottCoast-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Field Camps
Many Antarctic research stations support satellite field camps which are, in general, seasonal camps. The type of field camp can vary – some are permanent structures used during the annual Antarctic summer, whereas others are little more than tents used to support short term activities. Field camps are used for many things, from logistics (Sky Blu) to dedicated scientific research ( WAIS Divide Field Camp). List of field camps See also *Research stations in Antarctica * Demographics of Antarctica *List of Antarctic expeditions This list of Antarctic expeditions is a chronological list of expeditions involving Antarctica. Although the existence of a southern continent had been hypothesized as early as the writings of Ptolemy in the 1st century AD, the South Pole was ... * Transport in Antarctica References External links COMNAP Antarctic Facilities() COMNAP Antarctic Facilities Map() Antarctic Digital Database Map ViewerSCAR {{Polar exploration Fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Airports In Antarctica
__TOC__ List , 18/36Ice , - valign=top , Palmer SkiwayHeliport , , NZ12 , , Anvers Island , , 01/19Snow , - valign=top , Patriot Hills Blue-Ice Runway , , SCPZ , , Ellsworth Mountains , , 24MIce , - valign=top , Pegasus Field(serving McMurdo Station and Scott Base) , , NZPG , , Ross Island , , 15/33Ice08/26Ice (skiway) , - valign=top , Perseus RunwayTemporary Airfield , , , , , , 10/28Blue Ice , - valign=top , Petrel Skiway , , SA47 , , Dundee Island , , 08/26Ice , - valign=top , Phoenix Airfield(serving McMurdo Station and Scott Base) , , NZFX , , Ross Island , , 15/33Compacted Snow , - valign=top , Plateau Station Skiway , , AT20 , , Queen Maud Land , , 18/36Ice , - valign=top , Plog Island Skiway(serving Davis) , , , , Plog Island , , (variable)Ice , - valign=top , Princess Elisabeth Skiway , , QAP , AT99 , Utsteinen Nunatak , , Blue Ice , - valign=top , Progress Skiway , , , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, multi-mission service unique among the United States military branches for having a maritime law enforcement mission with jurisdiction in both domestic and international waters and a federal regulatory agency mission as part of its duties. It is the largest and most powerful coast guard in the world, rivaling the capabilities and size of most navies. The U.S. Coast Guard is a humanitarian and security service. It protects the United States' borders and economic and security interests abroad; and defends its sovereignty by safeguarding sea lines of communication and commerce across vast territorial waters spanning 95,000 miles of coastline and its Exclusive Economic Zone. With national and economic security depending upon open global t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum Helicopters International
Petroleum Helicopters International, Inc. (PHI), is an American commercial helicopter operator, founded in 1949, by Robert L. Suggs. The company is based in Lafayette, Louisiana and provides service for the oil and gas industry, aeromedical services, pilot training and aircraft maintenance. In October 2017, PHI acquired Helicopters (NZ) from HNZ Group. On March 15, 2019, the company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy. On June 5, 2019, court-supervised arbitration announced an agreement to force the retirement of CEO Al Gonsoulin and strip him of his shares. History PHI Inc. was founded by Robert L. Suggs and Maurice M. Bayon with a startup cost of $100,000, and three Bell 47 helicopters. They started by providing service to a seismographic group working in the wetlands of Louisiana. The company's service extended to offshore drilling platforms in the Gulf of Mexico, and grew their fleet with the addition of the Sikorsky S-55. and the Sikorsky S-58 helicopters. Over the nex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica New Zealand
Antarctica New Zealand is an Institute set up by the Government of New Zealand in 1996 to manage its interests in Antarctica and the Ross Sea. As well as providing logistics support to a large scientific programme, it also runs bases such as Scott Base. It has run other bases in the past, such as Vanda Station. New Zealand's involvement in Antarctica began in 1923, when activities were closely connected with the United Kingdom. Close cooperation with other nations has been an important part of New Zealand's involvement in Antarctica. Since 1959 Scott Base has been New Zealand's permanent base in Antarctica. From 1965 to 1988 the person responsible for much of Scott Base development as head of the Antarctic Division of the DSIR was Bob Thomson A 1994 review recognised Antarctica as strategically important to New Zealand as a Southern Hemisphere nation. This resulted in the establishment of the New Zealand Antarctic Institute, known as Antarctica New Zealand, on 1 July 1996. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell 212
The Bell 212 (also known as the ''Twin Two-Twelve'') is a two-blade, medium helicopter that first flew in 1968. Originally manufactured by Bell Helicopter in Fort Worth, Texas, United States, production was moved to Mirabel, Quebec, Canada in 1988, along with all Bell commercial helicopter production after that plant opened in 1986. The 212 was marketed to civilian operators and has up to a 15-seat capacity, with one pilot and fourteen passengers. In cargo-carrying configuration the 212 has an internal capacity of 220 ft3 (6.23 m3). An external load of up to 5,000 lb (2,268 kg) can be carried. Development Based on the stretched fuselage Bell 205, the Bell 212 was originally developed for the Canadian Forces as the ''CUH-1N'' and later redesignated as the '' CH-135''. The Canadian Forces took delivery of 50 starting in May 1971. At the same time the United States military services ordered 294 Bell 212s under the designation UH-1N. By 1971, the Bell 212 ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurocopter AS350 Écureuil
The Eurocopter AS350 Écureuil (or Squirrel), now Airbus Helicopters H125, is a single-engine light utility helicopter originally designed and manufactured in France by Aérospatiale and Eurocopter (now Airbus Helicopters). In North America, the AS350 is marketed as the AStar. The AS355 Ecureuil 2 is a twin-engine variant, marketed in North America as the TwinStar. The Eurocopter EC130 is a derivative of the AS350 airframe and is considered by the manufacturer to be part of the Écureuil single-engine family. Development In the early 1970s, Aérospatiale initiated a development programme to produce a replacement for the aging Aérospatiale Alouette II. While the Aérospatiale Gazelle, which had been developed in the 1960s and 1970s, had been met with numerous orders by military customers, commercial sales of the type had been less than anticipated, thus the need for a civil-oriented development was identified. The development of the new rotorcraft, which was headed by Chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |