|
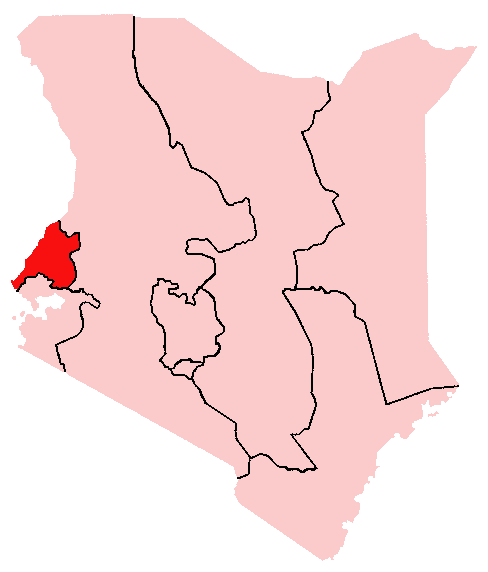
Maragoli
The Maragoli, or Logoli (''Ava-Logooli''), are now the second-largest ethnic group of the 6 million-strong Luhya nation in Kenya, numbering around 2.1 million, or 15% of the Luhya people according to the last Kenyan census. Their language is called Logoli, Lulogooli, Ululogooli, or Maragoli. The name Maragoli probably emerged later on after interaction of the people with missionaries of the Quaker Church. Maragoli also refers to the area that the descendants of a man called Mulogooli (also known as Maragoli) settled and occupied in the thirteenth century AD in the vast lands of vihiga county. Maragolis occupy the largest part of vihiga followed by Abanyore then Tiriki sub tribes.Maragoli clans include the va- masingira,Va-Gonda, Va-Mavi, Va-Sachi, Va-Saniaga, Va-Vulughi, Va-Ndega, Va-sari, Va-ng'ang'a, Va-Yonga,va-twa, va-gisemba... (The prefix ''Va-'' refers to the people or descendants, and is sometimes written as ''Ba-, Ava-,'' or ''Aba-''.) Maragolis have a unique cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luhya People
The Luhya (also known as ''Abaluyia'' or Luyia) comprise a number of Bantu ethnic groups native to western Kenya. They are divided into 20 culturally and linguistically related tribes. ''Luhya'' refers to both the 20 Luhya clans and their respective languages collectively called Luhya languages. There are 20 (and by other accounts, 21, when the Suba are included) clans that make up the Luhya. Each has a distinct dialect best on thelocality of the speakers.The different dialects shows maturity of the luhya language. The Luhya language can only be equated to the Baganda,Soga and Lugisu language in Uganda. The Luhya culture is similary to Great lakes region Bantu speakers that stretches all the way from their anceral land in DRC. The word ''Luhya'' or ''Luyia'' in some of the dialects means "the north", and ''Abaluhya (Abaluyia)'' thus means "people from the north". Other translations are "those of the same hearth." The seventeen sub-tribes are the Bukusu (''Aba-Bukusu''), Idak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logoli Language
Logooli (alternate names: Lugooli, Llugule, Llogole, Luragoli, Uluragooli, Maragooli, Maragoli, or Ragoli; native name: ''Lulogooli'') is a Bantu language with several hundred thousand speakers in Kenya and a few hundred speakers in Mara Region, Tanzania. It is spoken by the Maragoli, the second-largest Luhya tribe, but is not particularly close to other languages spoken by the Luhya. See also * Great Lakes Bantu languages The Great Lakes Bantu languages, also known as Lacustrine Bantu and Bantu zone J, are a group of Bantu languages of East Africa. They were recognized as a group by the ''Tervuren'' team, who posited them as an additional zone (zone J) to Guthrie' ... References Languages of Kenya Luhya language {{Narrow Bantu languages, J-M Great Lakes Bantu languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunyore
Bunyore is a locality in the Vihiga County in the western province of Kenya. It is largely inhabited by Luhya, who speak the OLunyole dialect of the Luhya language. In the local language, the place is known as Ebunyore and its people as the Abanyore (the descendants of Nyore). It is divided into eight locations namely Central Bunyore, West Bunyore, South Bunyore, South-West Bunyore, East Bunyore, North Bunyore, North East Bunyore, and Wekhomo. Prior to 1990, Bunyore was under Kakamega District, divided into East and West Bunyore locations. As population increased, the former West Bunyore was split into Central, West, South and South West locations while the former East Bunyore was split into North, North East, Wekhomo and East Bunyore locations in order to better serve the people. Bunyore is home to the national headquarters of the Church of God in Kenya, Bunyore Girls’ High School and Kima School of Theology all of which are located at Kima. A significant town in Bunyore is Lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misri Legend
The Misri legend is an origin myth common to a number of East African communities. In it, it is usually claimed that the community originated in a land called Misri located in the north. This land is in many accounts identified or associated with Egypt and sometimes an association with one of the lost tribes of Israel is implied and occasionally directly stated. Prevalence Dr Ochieng (1972) noted the legend among the Kisii people who claim that before they migrated to Mt Elgon, they lived in a country called 'Misri' that was located north of Mt Elgon. In the legend, the Kisii traveled south in the company of the Kuria, the Maragoli, Bukusu, and Meru. The Maragoli in turn claim that while they were at Misri, they lived with Arabs, the Kikuyu, Meru, Embu, Baganda, Basoga as well as the other Luhya subtribes. Dr Ochieng notes that the Misri legend had also been recorded among the other Luhya subtribes as well as the Haya, Alur, Kipsigis and the Marakwet. Origins The concept of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyasaye
Nyasaye (also Nyasae or Nasaye) is the Luo and Gusii word for God. The same or similar words are also used by speakers of Luhya languages, but they refer to the same entity. for the Luo people, Nyasaye means the creator of the beginning, The Luo also called Nyasaye with different names such as Obongo NyaKalaga, Obong'o means one of a kind, while NyaKaldaga means the all powerful everlasting one. Luos are strictly monotheistic. Some researchers have argued that the word ''Nyasaye'' doesn't mean exactly the same how comes thing for the Luo people as the word ''God'' does in English as a supreme high power, and even if the Luo people understand the concept, it doesn't necessarily carry the same connotations. The fact that English language is used to study religion in this case doesn't help to understand the way that these African populations apprehend the notion of God. However, some of the expressions in Luo languages which are used as prayers to speak about God/Nyasaye are direct tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Head
A village head, village headman or village chief is the community leader of a village or a small town. Usage Brunei In Brunei, village head is called or in the Malay language. It is an administrative post which leads the community of a village administrative division, the third and lowest subdivision of the country. Malaysia Generally in Malaysia, the village head is called , except for the proto Malay village where the position is called . Ketua Kampung was appointed and assisted by (Village Community Management Board). In Sarawak, the head of a traditional long house is called . Indonesia The village head in Indonesia is called . China In China, village head () is a local government or tribal post. The village headman is the person appointed to administer an area that is often a single village. Duties and functions The headman has several official duties in the village, and is sometimes seen as a mediator in disputes and a general “fixer” of village or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment by the groom, or his family, to the bride, or her family, dowry is the wealth transferred from the bride, or her family, to the groom, or his family. Similarly, dower is the property settled on the bride herself, by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control. Dowry is an ancient custom that is already mentioned in some of the earliest writings, and its existence may well predate records of it. Dowries continue to be expected and demanded as a condition to accept a marriage proposal in some parts of the world, mainly in parts of Asia, The custom of dowry is most common in cultures that are strongly patrilineal and that expect women to reside with or near their husband's family (patrilocality). Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witch
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have used malevolent magic against their own community, and often to have communed with evil beings. It was thought witchcraft could be thwarted by protective magic or counter-magic, which could be provided by cunning folk or folk healers. Suspected witches were also intimidated, banished, attacked or killed. Often they would be formally prosecuted and punished, if found guilty or simply believed to be guilty. European witch-hunts and witch trials in the early modern period led to tens of thousands of executions. In some regions, many of those accused of witchcraft were folk healers or midwives. European belief in witchcraft gradually dwindled during and after the Age of Enlightenment. Contemporary cultures that believe in magic and the superna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magician (paranormal)
Magic, sometimes spelled magick, is an ancient Praxis (process), praxis rooted in sacred rituals, spiritual Divination, divinations, and/or cultural Lineage (anthropology), lineage—with an intention to invoke, manipulate, or otherwise manifest supernatural forces, beings, or entities in the Nature, natural, incarnate world. It is a categorical yet often ambiguous term which has been used to refer to a wide variety of beliefs and practices, frequently considered separate from both religion and science. Although connotations have varied from positive to negative at times throughout history, magic continues to have an important religious and medicinal role in many cultures today. Within Western culture, magic has been linked to ideas of the Other (philosophy), Other, foreignness, and primitivism; indicating that it is "a powerful marker of cultural difference" and likewise, a non-modern phenomenon. During the late nineteenth and early twentieth century, Western intellectuals per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, society, culture, nation, religion, or social treatment within their residing area. The term ethnicity is often times used interchangeably with the term nation, particularly in cases of ethnic nationalism, and is separate from the related concept of races. Ethnicity may be construed as an inherited or as a societally imposed construct. Ethnic membership tends to be defined by a shared cultural heritage, ancestry, origin myth, history, homeland, language, or dialect, symbolic systems such as religion, mythology and ritual, cuisine, dressing style, art, or physical appearance. Ethnic groups may share a narrow or broad spectrum of genetic ancestry, depending on group identification, with many groups having mixed genetic ancestry. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God In Christianity
God in Christianity is believed to be the eternal, supreme being who created and preserves all things. Christians believe in a monotheistic conception of God, which is both transcendent (wholly independent of, and removed from, the material universe) and immanent (involved in the material universe). Christian teachings on the transcendence, immanence, and involvement of God in the world and his love for humanity exclude the belief that God is of the same substance as the created universe (rejection of pantheism) but accept that God's divine nature was hypostatically united to human nature in the person of Jesus Christ, in a unique event known as "the Incarnation". Early Christian views of God were expressed in the Pauline epistles and the early Christian creeds, which proclaimed one God and the divinity of Jesus. Although some early sects of Christianity, such as the Jewish-Christian Ebionites, protested against the apotheosis of Jesus, the concept of Jesus being one with G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's ability to experience the light within or see "that of God in every one". Some profess a priesthood of all believers inspired by the First Epistle of Peter. They include those with evangelical, holiness, liberal, and traditional Quaker understandings of Christianity. There are also Nontheist Quakers, whose spiritual practice does not rely on the existence of God. To differing extents, the Friends avoid creeds and hierarchical structures. In 2017, there were an estimated 377,557 adult Quakers, 49% of them in Africa. Some 89% of Quakers worldwide belong to ''evangelical'' and ''programmed'' branches that hold services with singing and a prepared Bible message coordinated by a pastor. Some 11% practice ''waiting worship'' or ''unprogramme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |