|
Mangum Mound Site
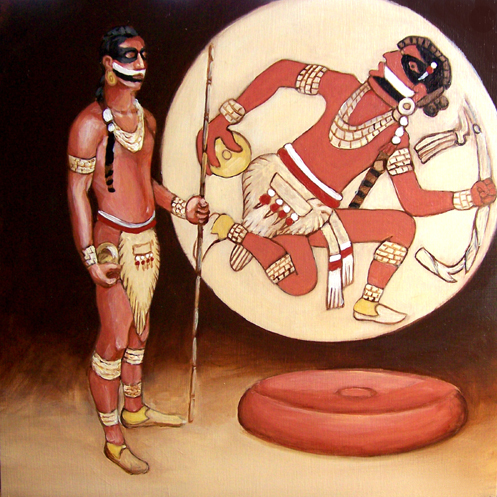
Mangum Mound Site ( 22 CB 584) is an archaeological site of the Plaquemine culture in Claiborne County, Mississippi. It is located at milepost 45.7 on the Natchez Trace Parkway. Two very rare Mississippian culture repoussé copper plates have been discovered during excavations of the site. The site was used as a burial mound during the Foster Phase of the culture (1350 to 1500 CE) and is believed to have been abandoned before the 1540 expedition of Hernando de Soto. Description The burial mound was first investigated in 1936 by its owner Spurgeon C. Mangum, a farmer. Mangum found human remains, various pottery fragments belonging to the Plaquemine culture, chunkey stones, and three fragments of a repoussé copper plate with an avian design similar to other plates found throughout the American Midwest and Southeast. These portray the '' Birdman'' motif important to the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (SECC). The site underwent a series of test excavations in April 1951 as part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Gibson, Mississippi
Port Gibson is a city in Claiborne County, Mississippi, United States. The population was 1,567 at the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. Port Gibson is the county seat of Claiborne County, which is bordered on the west by the Mississippi River. It is the site of the Claiborne County Courthouse. The first European settlers in Port Gibson were French colonists in 1729; it was part of their ''La Louisiane''. After the United States acquired the territory from France in 1803 in the Louisiana Purchase, the town was chartered that same year. To develop cotton plantations in the American South, plantations in the area after Indian Removal of the 1830s, planters who moved to the state brought with them or imported thousands of enslaved African Americans from the Upper South, disrupting many families. Well before the Civil War, the majority of the county's population were enslaved blacks. Several notable people are natives of Port Gibson. The town saw action during the American Civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Culture Pottery
Mississippian culture pottery is the ceramic tradition of the Mississippian culture (800 to 1600 CE) found as artifacts in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. It is often characterized by the adoption and use of riverine (or more rarely marine) shell- tempering agents in the clay paste. Shell tempering is one of the hallmarks of Mississippian cultural practices. Analysis of local differences in materials, techniques, forms, and designs is a primary means for archaeologists to learn about the lifeways, religious practices, trade, and interaction among Mississippian peoples. The value of this pottery on the illegal antiquities market has led to extensive looting of sites. Materials and techniques Mississippian culture pottery was made from locally available clay sources, which often gives archaeologists clues as to where a specific example originated. The clay was tempered with an additive to keep it from shrinking and cracking in the drying and firing pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mounds In Mississippi
A mound is an artificial heap or pile, especially of earth, rocks, or sand. Mound and Mounds may also refer to: Places * Mound, Louisiana, United States * Mound, Minnesota, United States * Mound, Texas, United States * Mound, West Virginia * Mound Creek, a stream in Minnesota * Mounds, Illinois, United States * Mounds, Oklahoma, United States * The Mound, a street in Edinburgh, Scotland, linking the Old Town and the New Town * The Mound railway station, a former station in northern Scotland Arts, entertainment, and media * Mound, a fictional entity in the work of artist Trenton Doyle Hancock * ''The Mound'' (novella), a 1940 work by H. P. Lovecraft Other uses * Mound, monumental earthwork mound built by prehistoric Mound builder (people) A number of pre-Columbian cultures are collectively termed "Mound Builders". The term does not refer to a specific people or archaeological culture, but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks erected for an extended period of more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaquemine Mississippian Culture
The Plaquemine culture was an archaeological culture (circa 1200 to 1700 CE) centered on the Lower Mississippi River valley. It had a deep history in the area stretching back through the earlier Coles Creek (700-1200 CE) and Troyville cultures (400-700 CE) to the Marksville culture (100 BCE to 400 CE). The Natchez and related Taensa peoples were their historic period descendants. The type site for the culture is the Medora site in Louisiana; while other examples include the Anna, Emerald, Holly Bluff, and Winterville sites in Mississippi. History Definition The Plaquemine culture was a Mississippian culture variant centered on the Mississippi River valley, stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to just south of its junction with the Arkansas River, encompassing the Yazoo River basin and Natchez Bluffs in western Mississippi, and the lower Ouachita and Red River valleys in southeastern Arkansas, and eastern Louisiana. They were primarily agriculturists who grew maize, pumpkins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Archaeological Periods (North America)
North American archaeological periods divides the history of pre-Columbian North America into a number of named successive eras or periods, from the earliest-known human habitation through to the early Colonial period which followed the European colonization of the Americas. Stage classification One of the most enduring classifications of archaeological periods and cultures was established in Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips (archaeologist), Philip Phillips' 1958 book ''Method and Theory in American Archaeology.'' They divided the archaeological record in the Americas into 5 phases, only three of which applied to North America. The use of these divisions has diminished in most of North America due to the development of local classifications with more elaborate breakdowns of times. :1. The Paleo-Indians, Paleo-Indians stage and/or Lithic stage :2. The Archaic stage :3. Formative stage or Post-archaic stage - At this point the North American classifications system differs from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemia, kidney dysfunction, and infections may occur. Complications may include amyloidosis. The cause of multiple myeloma is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, radiation exposure, family history, and certain chemicals. There is an increased risk of multiple myeloma in certain occupations. This is due to the occupational exposure to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents having a role in causation of multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma may develop from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance that progresses to smoldering myeloma. The abnormal plasma cells produce abnormal antibodies, which can cause kidney problems and overly thick blood. The plasma cells can also form a mass in the bone marrow or soft tissue. When one tumor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational properties with various title designations. The U.S. Congress created the agency on August 25, 1916, through the National Park Service Organic Act. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., within the main headquarters of the Department of the Interior. The NPS employs approximately 20,000 people in 423 individual units covering over 85 million acres in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and US territories. As of 2019, they had more than 279,000 volunteers. The agency is charged with a dual role of preserving the ecological and historical integrity of the places entrusted to its management while also making them available and accessible for public use and enjoyment. History Yellowstone National Park was created as the first national par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Nebraska Press
The University of Nebraska Press, also known as UNP, was founded in 1941 and is an academic publisher of scholarly and general-interest books. The press is under the auspices of the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, the main campus of the University of Nebraska system. UNP publishes primarily non-fiction books and academic journals, in both print and electronic editions. The press has particularly strong publishing programs in Native American studies, Western American history, sports, world and national affairs, and military history. The press has also been active in reprinting classic books from various genres, including science fiction and fantasy. Since its inception, UNP has published more than 4,000 books and 30 journals, adding another 150 new titles each year, making it the 12th largest university press in the United States. Since 2010, two of UNP's books have received the Bancroft Prize, the highest honor bestowed on history books in the U.S. History UNP began in Novem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natchez Trace
The Natchez Trace, also known as the Old Natchez Trace, is a historic forest trail within the United States which extends roughly from Nashville, Tennessee, to Natchez, Mississippi, linking the Cumberland, Tennessee, and Mississippi rivers. The trail was created and used by Native Americans for centuries, and was later used by early European and American explorers, traders, and emigrants in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. European Americans founded inns, also known as "stands", along the Trace to serve food and lodging to travelers. As travel shifted to steamboats on the Mississippi and other rivers, most of these stands closed. Today, the path is commemorated by the Natchez Trace Parkway, which follows the approximate path of the Trace, as well as the related Natchez Trace Trail. Parts of the original trail are still accessible, and some segments are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Origins Largely following a geologic ridge line, prehist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Antiquity
The professional journal ''American Antiquity'' is published by Cambridge University Press for the Society for American Archaeology, an organization of professional archaeologists of the Americas. The journal is considered to be the flagship journal of American archaeology. ''American Antiquity'' is a quarterly, peer-reviewed journal published in January, April, July and October. Each copy of the journal has about 200 pages, with articles covering topics such as archaeological method, archaeological science, pre-Columbian societies or civilizations, ongoing work at archaeological sites, and interim reports of excavations. The journal also includes book reviews, editorials, and comments and responses on previous articles. ''American Antiquity'' has been in publication since 1935. Since the publication of the first issue of the related journal ''Latin American Antiquity ''Latin American Antiquity'' is a professional journal published by the Society for American Archaeology, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
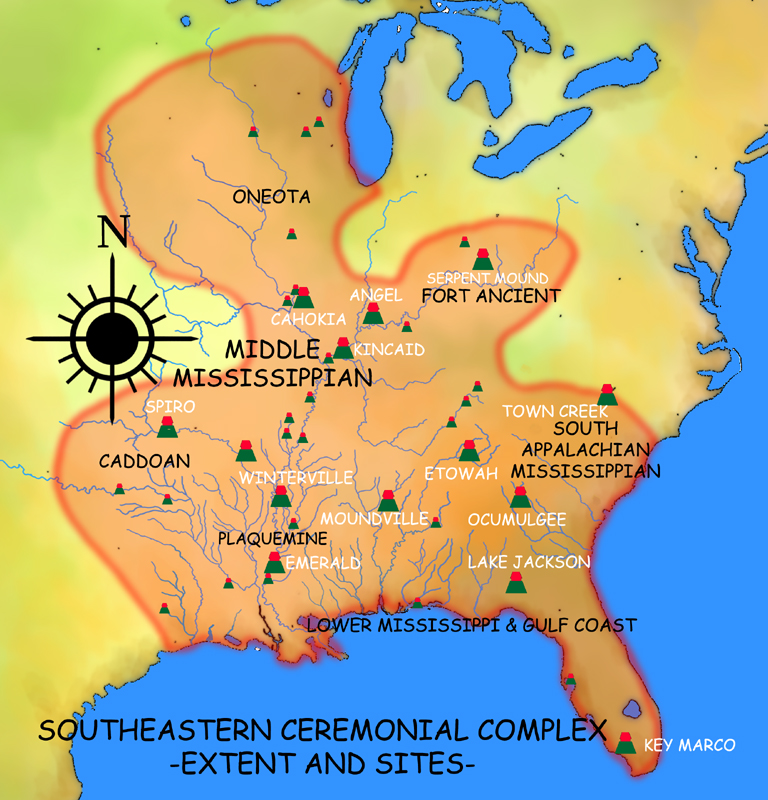
Southeastern Ceremonial Complex
The Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly the Southern Cult), aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture. It coincided with their adoption of maize agriculture and chiefdom-level complex social organization from 1200 to 1650 CE. Due to some similarities between S.E.C.C. and contemporary Mesoamerican cultures (i.e., artwork with similar aesthetics or motifs; maize-based agriculture; and the development of sophisticated cities with large pyramidal structures), scholars from the late 1800s to mid-1900s suspected there was a connection between the two locations. But, later research indicates the two cultures have no direct links and that their civilizations developed independently. Obsolete names for this ceremonial complex, found in some anthropological sources, include Buzzard Cult and Southern Death Cult. Theories and names The complex operated as an exchange network. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chunkey
Chunkey (also known as chunky, chenco, tchung-kee or the hoop and stick game ) is a game of Native American origin. It was played by rolling disc-shaped stones across the ground and throwing spears at them in an attempt to land the spear as close to the stopped stone as possible. It originated around 600 CE in the Cahokia region of what is now the United States (near modern St. Louis, Missouri). Chunkey was played in huge arenas as large as 47 acres (19 ha) that housed great audiences designed to bring people of the region together (i.e. Cahokians, farmers, immigrants, and even visitors). It continued to be played after the fall of the Mississippian culture around 1500 CE. Variations were played throughout North America. Early ethnographer James Adair translated the name to mean "running hard labor". Gambling was frequently connected with the game, with some players wagering everything they owned on the outcome of the game. Losers were even known to commit suicide. Graphic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |