|
Mandibular Nerve
In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only afferent fibers, the mandibular nerve contains both afferent and efferent fibers. These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication. Structure The large sensory root emerges from the lateral part of the trigeminal ganglion and exits the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale. Portio minor, the small motor root of the trigeminal nerve, passes under the trigeminal ganglion and through the foramen ovale to unite with the sensory root just outside the skull. The mandibular nerve immediately passes between tensor veli palatini, which is medial, and lateral pterygoid, which is lateral, and gives off a meningeal branch (n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibular Division
In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth Cranial nerves, cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (Ophthalmic nerve, ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only Afferent nerve fiber, afferent fibers, the mandibular nerve contains both afferent and Efferent nerve fiber, efferent fibers. These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication. Structure The large sensory root emerges from the lateral part of the trigeminal ganglion and exits the cranial cavity through the Foramen ovale (skull), foramen ovale. Portio minor, the small motor root of the trigeminal nerve, passes under the trigeminal ganglion and through the Foramen ovale (skull), foramen ovale to unite with the sensory root just outside the skull. The mandibular nerve immediately passes betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
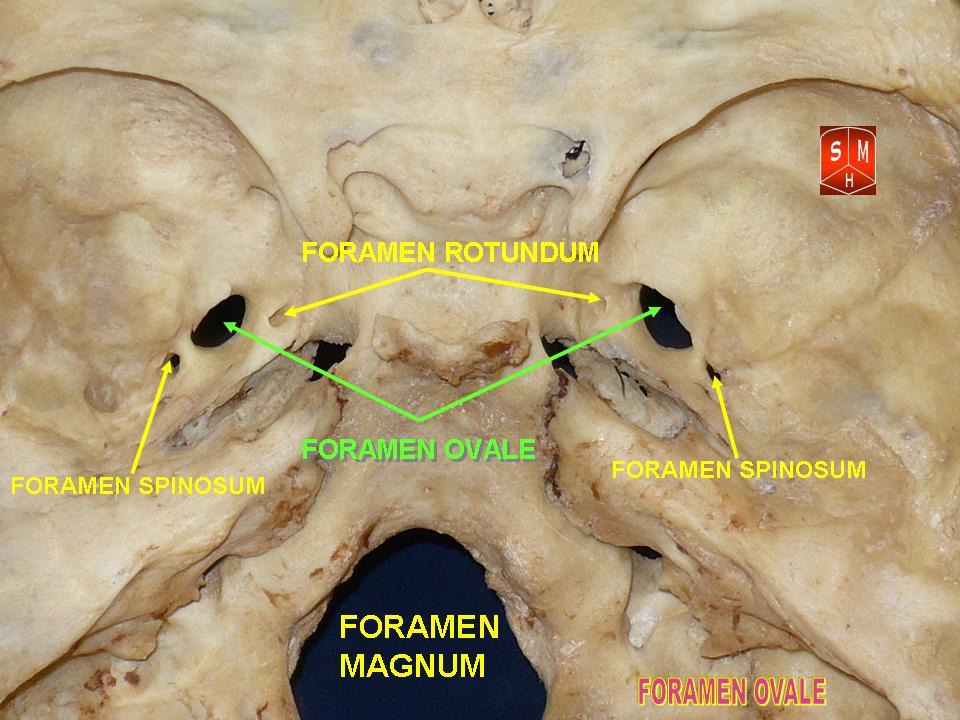
Foramen Ovale (skull)
The foramen ovale (Latin: oval window) is a hole in the posterior part of the sphenoid bone, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum. It is one of the larger of the several holes (the foramina) in the skull. It transmits the mandibular nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve. Structure The foramen ovale is an opening in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. The foramen ovale is one of two cranial foramina in the greater wing, the other being the foramen spinosum. The foramen ovale is posterolateral to the foramen rotundum and anteromedial to the foramen spinosum. Posterior and medial to the foramen is the opening for the carotid canal. Variation Similar to other foramina, the foramen ovale differs in shape and size throughout the natural life. The earliest perfect ring-shaped formation of the foramen ovale was observed in the 7th fetal month and the latest in 3 years after birth, in a study using over 350 skulls.In a study conducted on 100 skulls, the foramen ovale was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Tympani
The tensor tympani is a muscle within the middle ear, located in the bony canal above the bony part of the auditory tube, and connects to the malleus bone. Its role is to dampen loud sounds, such as those produced from chewing, shouting, or thunder. Because its reaction time is not fast enough, the muscle cannot protect against hearing damage caused by sudden loud sounds, like explosions or gunshots. Structure The tensor tympani is a muscle that is present in the middle ear. It arises from the cartilaginous part of the auditory tube, and the adjacent great wing of the sphenoid. It then passes through its own canal, and ends in the tympanic cavity as a slim tendon that connects to the handle of the malleus. The tendon makes a sharp bend around the ''processus cochleariformis'', part of the wall of its cavity, before it joins with the malleus. The tensor tympani receives blood from the middle meningeal artery via the superior tympanic branch. It is one of two muscles in the tympani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Pterygoid Muscle
The medial pterygoid muscle (or internal pterygoid muscle), is a thick, quadrilateral muscle of the face. It is supplied by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V). It is important in mastication (chewing). Structure The medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads. The bulk of the muscle arises as a deep head from just above the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate. The smaller, superficial head originates from the maxillary tuberosity and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. Its fibers pass downward, lateral, and posterior, and are inserted, by a strong tendinous lamina, into the lower and back part of the medial surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible, as high as the mandibular foramen. The insertion joins the masseter muscle to form a common tendinous sling which allows the medial pterygoid and masseter to be powerful elevators of the jaw. Nerve supply The medial pterygoid muscle is supplied by the medial pterygoid nerve, a branch of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Belly Of Digastric
The digastric muscle (also digastricus) (named ''digastric'' as it has two 'bellies') is a small muscle located under the jaw. The term "digastric muscle" refers to this specific muscle. However, other muscles that have two separate muscle bellies include the suspensory muscle of duodenum, omohyoid, occipitofrontalis. It lies below the body of the mandible, and extends, in a curved form, from the mastoid notch to the mandibular symphysis. It belongs to the suprahyoid muscles group. A broad aponeurotic layer is given off from the tendon of the digastric muscle on either side, to be attached to the body and greater cornu of the hyoid bone; this is termed the suprahyoid aponeurosis. Structure The digastricus (digastric muscle) consists of two muscular bellies united by an intermediate rounded tendon. The two bellies of the digastric muscle have different embryological origins, and are supplied by different cranial nerves. Each person has a right and left digastric muscle. In mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mylohyoid Muscle
The mylohyoid muscle or diaphragma oris is a paired muscle of the neck. It runs from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the mouth. It is named after its two attachments near the molar teeth. It forms the floor of the submental triangle. It elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue, important during swallowing and speaking. Structure The mylohyoid muscle is flat and triangular, and is situated immediately superior to the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. It is a pharyngeal muscle (derived from the first pharyngeal arch) and classified as one of the suprahyoid muscles. Together, the paired mylohyoid muscles form a muscular floor for the oral cavity of the mouth. The two mylohyoid muscles arise from the mandible at the mylohyoid line, which extends from the mandibular symphysis in front to the last molar tooth behind. The posterior fibers pass inferomedially and insert at anterior surface of the hyoid bone. The medial fibres of the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Alveolar Nerve
The inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) (also the inferior dental nerve) is a branch of the mandibular nerve, which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve. The inferior alveolar nerves supply sensation to the lower teeth. Structure The inferior alveolar nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve. After branching from the mandibular nerve, the inferior alveolar nerve travels behind the lateral pterygoid muscle. It gives off a branch, the mylohyoid nerve, and then enters the mandibular foramen. While in the mandibular canal within the mandible, it supplies the lower teeth (molars and second premolar) with sensory branches that form into the inferior dental plexus and give off small gingival and dental nerves to the teeth. Anteriorly, the nerve gives off the mental nerve at about the level of the mandibular 2nd premolars, which exits the mandible via the mental foramen and supplies sensory branches to the chin and lower lip. The inferior alveolar nerve continues anteriorl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Nerve
The lingual nerve carries sensory innervation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It contains fibres from both the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3 ) and from the facial nerve (CN VII). The fibres from the trigeminal nerve are for touch, pain and temperature (general sensation), and the ones from the facial nerve are for taste (special sensation). Structure The lingual nerve lies at first beneath the lateral pterygoid muscle, medial to and in front of the inferior alveolar nerve, and is occasionally joined to this nerve by a branch which may cross the internal maxillary artery. The chorda tympani (a branch of the facial nerve, CN VII) joins it at an acute angle here, carrying taste fibers from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and parasympathetic fibers to the submandibular ganglion. The nerve then passes between the medial pterygoid muscle and the ramus of the mandible, and crosses obliquely to the side of the tongue beneath the constrictor pharyngis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auriculotemporal
The auriculotemporal nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to various regions on the side of the head. Structure Origin The auriculotemporal nerve arises from the mandibular nerve (CN V3). The mandibular nerve is a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), and the mandibular nerve exits the skull through the foramen ovale.Gray's Anatomy for Students, 2nd edition (2010), Drake Vogel and Mitchell, Elseview These roots encircle the middle meningeal artery (a branch of the mandibular part of the maxillary artery, which is in turn a terminal branch of the external carotid artery). The roots encompass the middle meningeal artery then converge to form a single nerve. Course The auriculotemporal nerve passes between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament. It gives off parotid branches and then turns superiorly, posterior to its head and moving anteriorly, giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccal Nerve
The buccal nerve (long buccal nerve) is a nerve in the face. It is a branch of the mandibular nerve (which is itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve) and transmits sensory information from skin over the buccal membrane (in general, the cheek) and from the second and third molar teeth. Not to be confused with the buccal branch of the facial nerve which transmits motor information to the buccinator muscle. Structure The buccal nerve courses between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle, underneath the tendon of the temporalis muscle. It then runs under the masseter muscle, anterior to the ramus of the mandible. It connects with the buccal branches of the facial nerve on the surface of the buccinator muscle. It gives off many significant branches. Relations The facial nerve (CN VII) also has buccal branches, which carry motor innervation to the buccinator muscle, a muscle of facial expression. This follows from the trigeminal (V3) supplying all muscles of mastication and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve To Medial Pterygoid
The medial pterygoid nerve (or internal pterygoid nerve) is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3). It supplies the medial pterygoid muscle, the tensor veli palatini muscle, and the tensor tympani muscle. Structure The medial pterygoid nerve is a slender branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It is the first branch of the mandibular nerve. It enters the deep surface of the medial pterygoid muscle. It passes through the otic ganglion without synapsing, so is neurologically distinct. However, it provides physical support. The medial pterygoid nerve receives some motor fibres from the otic ganglion. Function The medial pterygoid nerve supplies the medial pterygoid muscle. It also supplies tensor veli palatini muscle, through the nerve to tensor veli palatini, one of its branches. Of the five paired skeletal muscles to the soft palate, tensor veli palati muscle is the only muscle not innervated by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningeal Branch Of The Mandibular Nerve
The meningeal (recurrent) branch of the mandibular nerve (nervus spinosus) is a branch of the mandibular nerve that supplies the dura mater. Course The meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve enters the skull through the foramen spinosum along with the middle meningeal artery. It divides into two branches, anterior and posterior, which accompany the main divisions of the artery and supply the dura mater: * The ''posterior'' branch also supplies the mucous lining of the mastoid cells. * The ''anterior'' communicates with the meningeal branch of the maxillary nerve In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve (V) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (CN V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxilla, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate a .... References External links Overview at tufts.edu* Mandibular nerve Meninges {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |