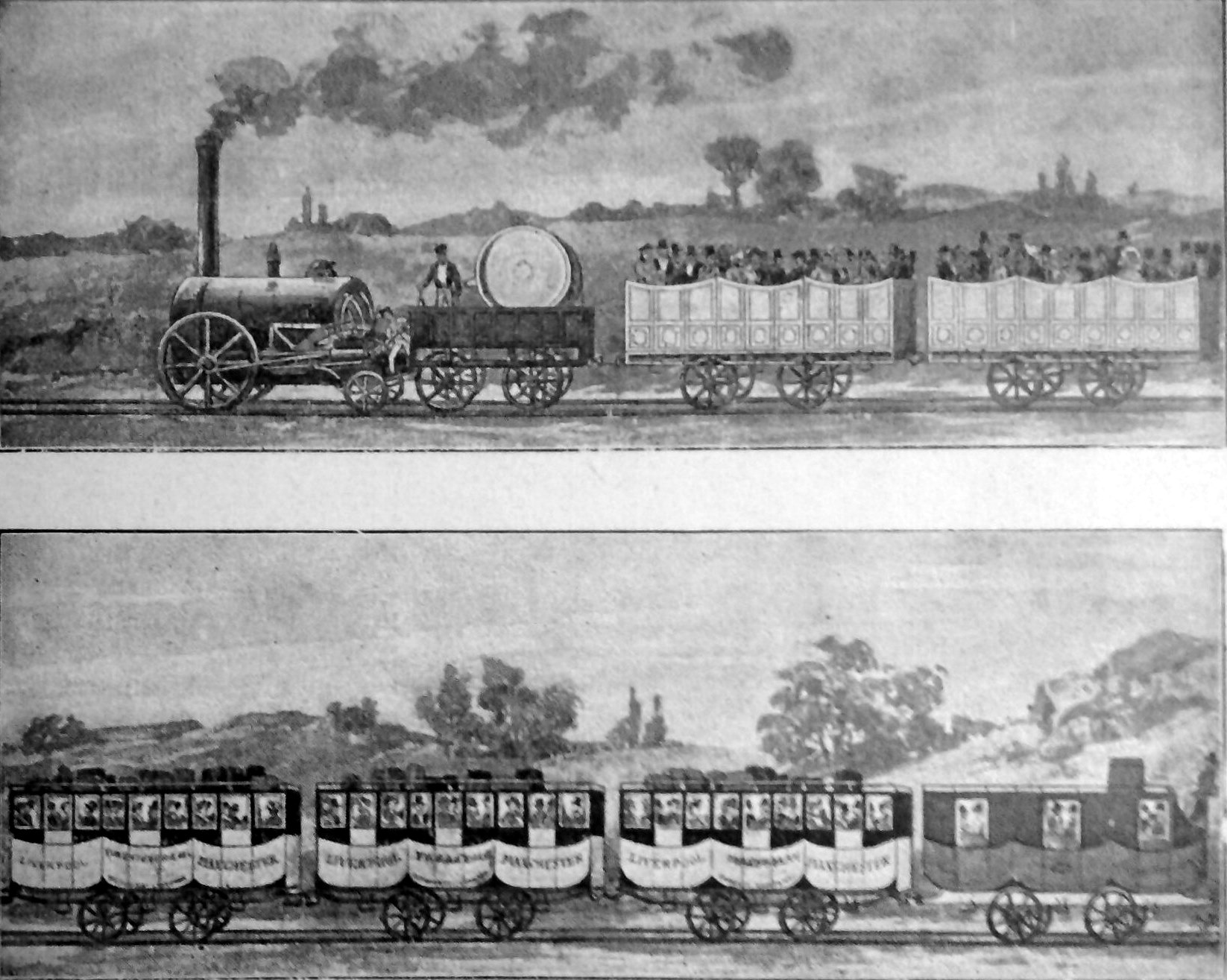|
Manchester Collieries
Manchester Collieries was a coal mining company with headquarters in Walkden formed from a group of independent companies operating on the Manchester Coalfield in 1929. The Mining Industry Act of 1926 attempted to stem the post-war decline in coal mining and encourage independent companies to merge in order to modernise and better survive the economic conditions of the day. Robert Burrows of the Atherton company Fletcher Burrows proposed a merger of several independent companies operating to the west of Manchester. The merger was agreed and took place in March 1929. Constituent companies The constituent companies of Manchester Collieries in 1929 were Fletcher, Burrows and Company who owned the Howe Bridge, Gibfield and Chanters Collieries in Atherton, Andrew Knowles and Sons, the Clifton and Kersley Coal Company, John Speakman and Sons owners of Bedford Colliery in Leigh, Bridgewater Collieries who operated pits in Little Hulton, Walkden and Mosley Common and the Astley and Tylde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
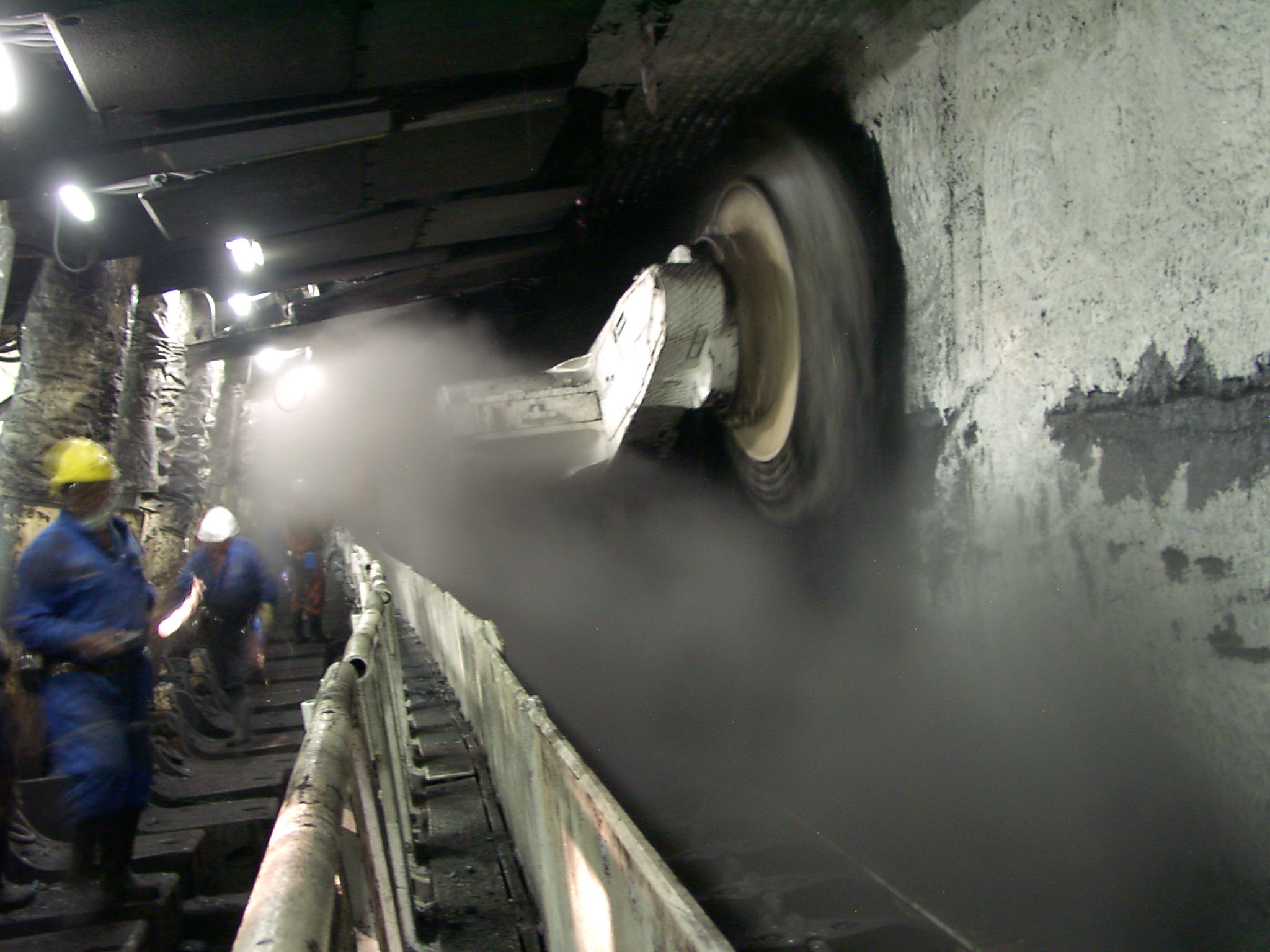
Coal Mining
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United Kingdom and South Africa, a coal mine and its structures are a colliery, a coal mine is called a 'pit', and the above-ground structures are a 'pit head'. In Australia, "colliery" generally refers to an underground coal mine. Coal mining has had many developments in recent years, from the early days of men tunneling, digging and manually extracting the coal on carts to large open-cut and longwall mines. Mining at this scale requires the use of draglines, trucks, conveyors, hydraulic jacks and shearers. The coal mining industry has a long history of significant negative environmental impacts on local ecosystems, health impacts on local communities and workers, and contributes heavily to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astley, Greater Manchester
Astley is a village in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan, Greater Manchester, England. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Lancashire, it is crossed by the Bridgewater Canal and the A580 East Lancashire Road. Continuous with Tyldesley, it is equidistant from Wigan and Manchester, both away. Astley Mosley Common ward had a population of 11,270 at the 2011 Census. Astley's name is Old English, indicating Anglo-Saxon settlement. It means either "east (of) Leigh", or ''ēastlēah'' the "eastern wood or clearing". Throughout the Middle Ages, Astley constituted a township within the parish of Leigh and hundred of West Derby. Astley appears in written form as ''Asteleghe'' in 1210, when its lord of the manor granted land to the religious order of Premonstratensian canons at Cockersand Abbey. Medieval and Early Modern Astley is distinguished by the dignitaries who occupied Damhouse, the local manor house around which a settlement expanded. The Bridgewater Canal reached As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool And Manchester Railway
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) was the first inter-city railway in the world. It opened on 15 September 1830 between the Lancashire towns of Liverpool and Manchester in England. It was also the first railway to rely exclusively on locomotives driven by steam power, with no horse-drawn traffic permitted at any time; the first to be entirely double track throughout its length; the first to have a true signalling system; the first to be fully timetabled; and the first to carry mail. Trains were hauled by company steam locomotives between the two towns, though private wagons and carriages were allowed. Cable haulage of freight trains was down the steeply-graded Wapping Tunnel to Liverpool Docks from Edge Hill junction. The railway was primarily built to provide faster transport of raw materials, finished goods and passengers between the Port of Liverpool and the cotton mills and factories of Manchester and surrounding towns. Designed and built by George Stephen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyldesley Loopline
The Tyldesley Loopline was part of the London and North Western Railway's Manchester and Wigan Railway line from Eccles to the junction west of Tyldesley station and its continuance south west via Bedford Leigh to Kenyon Junction on the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. The line opened on 1 September 1864 with stations at Worsley, Ellenbrook, Tyldesley, Leigh and Pennington before joining the Liverpool and Manchester Railway at Kenyon Junction. Construction The London and North Western Railway Bill received Royal Assent in July 1861 and the first sod was cut at Worsley by the Earl of Ellesmere in the September. During construction, a Roman road was uncovered at Worsley. The railway was just over 16 miles long with 88 bridges, a sandstone cutting at Parr Brow, Tyldesley and a 22-arch viaduct which took the railway through Leigh and over the Bridgewater Canal. The work was expected to have been completed by May 1863 but lasted until the summer of 1864. Development Stations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walkden Yard
Walkden is a town in the City of Salford in Greater Manchester, England, northwest of Salford, and of Manchester. Historically in the township of Worsley in Lancashire, Walkden was a centre for coal mining and textile manufacture. In 2014, the electoral wards of Walkden North, Walkden South and Little Hulton had a combined population of 35,616. History The name Walkden or ''Walkeden'' derives from the Old English ''denu'', a valley, belonging to a man possibly called Wealca ( fuller), an Old English personal name. It has been in existence since at least the 13th century. The name was recorded in documents dating to 1246. In the local dialect and accent, it is pronounced Wogden. A Roman road crossed the area roughly on the line of the present A6 road through Walkden and Little Hulton. In 1313, in a dispute involving land, a jury decided that Walkden was too small to be considered a hamlet or a town but was "only a place in Farnworth". In the 15th century Walkden appears t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pit Ponies
A pit pony, otherwise known as a mining horse, was a horse, pony or mule commonly used underground in mines from the mid-18th until the mid-20th century. The term "pony" was sometimes broadly applied to any equine working underground.English Pit PoniesThe Colliery Engineer Vol. VIII, No. 1 (August 1887); pages 6-7. History The first known recorded use of ponies underground in Great Britain was in the Durham coalfield in 1750. Following the drowning deaths of 26 children when the Huskar Colliery in Silkstone flooded on 4 July 1838, "A report was published in ''The Times'', and the wider British public learned for the first time that women and children worked in the mines. There was a public outcry, led by politician and reformer Anthony Ashley Cooper, later Lord Shaftesbury," who then introduced the Mines and Collieries Act 1842 to Parliament which barred women, girls and boys under 10 (later amended to 13) from working underground, leading to the widespread use of horses and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hewer
A hewer (german: Hauer or ''Häuer'') is a miner who loosens rock and minerals in a mine. In medieval mining in Europe a ''Hauer'' was the name given to a miner who had passed his test (''Hauerprüfung'') as a hewer. Training In Europe in former times, before he could become a hewer, the miner had to learn to be a "sorter boy" (''Scheidejunge''), identifying ores and separating the ore from the gangue. After that he would continue his training in the pit itself. Here, he had to learn further skills, initially as a putter (''Hundtstößer'' literally "truck pusher"), transporting material around the mine in wagons. Only afterwards could he learn the skills, as an apprentice hewer (''Lehrhäuer''), that he would later need as a hewer. This form of training, the acquisition of knowledge by experience, was practised in mining until the First World War. From the 1920s, the training of hewers was legally regulated as a result of union demands. Because, in the meantime, many skills re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradford, Greater Manchester
Bradford is a district of east Manchester, England, two miles north east of the city centre. The population at the 2011 census was 15,784. Historically in Lancashire, after the closure of its heavy industries Bradford was for many years an economically deprived area but has undergone regeneration with the building of the City of Manchester Stadium which hosted the 2002 Commonwealth Games and is now home to Manchester City F.C. Bradford is neighboured by Beswick to the south and the two areas are sometimes referred to as Bradford-with-Beswick. The River Medlock and the Ashton Canal run through Bradford. History The name of the area is ancient and in 1196 the village was recorded as Bradeford, meaning the broad ford. Up to the Industrial Revolution, it was rural with woodland, pastures and brooks. Wolves and eagles once inhabited the woodlands and honey production was part of the local economy. Coal mining From Tudor times (1485–1603), sufficient coal was mined to supply mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradford Colliery
Bradford Colliery was a coal mine in Bradford, Manchester, England. Although part of the Manchester Coalfield, the seams of the Bradford Coalfield correspond more closely to those of the Oldham Coalfield. The Bradford Coalfield is crossed by a number of fault lines, principally the Bradford Fault, which was reactivated by mining activity in the mid-1960s. Coal had been mined at Bradford since at least the early 17th century, when the area around the pits was largely rural; it became increasingly built-up and industrialised as nearby Manchester expanded during the 19th century. Coal was transported from the colliery by canal and railway, but most was consumed locally by the adjacent Bradford Ironworks. In the mid-20th century a 469-yard (420 m) tunnel was dug to supply coal directly to the Stuart Street Power Station. Damage to buildings in the area around the colliery caused by subsidence led to it becoming uneconomic despite its sitting on large reserves of high-quality coal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson Pit
Nelson Pit was a coal mine operating on the Manchester Coalfield from the 1830s or 1840s in Shakerley, Tyldesley, Greater Manchester, then in the historic county of Lancashire, England. Originally named Shakerley Colliery, the pit was sunk on land leased from Ellis Fletcher and worked by Nathan Eckersley in 1851. In 1861 the colliery passed to William Ramsden who owned Messhing Trees Colliery half a mile to the south. A shaft was sunk to 840 feet and the pit produced house coal from the Trencherbone mine. The colliery was renamed after 1880. The shaft was deepened to the Arley mine at 1486 feet. Nelson Pit closed in 1938. Shakerley Colliery and Messhing Trees were owned by William Ramsden's Shakerley Collieries. The colliery was isolated from the main roads and railway and access to it was via a toll road, Shakerley Lane, connecting it to the Bolton to Leigh turnpike which continued to charge tolls until 1948. After the opening of the Tyldesley Loopline in 1864, Willi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington Pit
Wellington Colliery was a coal mine operating on the Manchester Coalfield before 1869 in Tyldesley, Greater Manchester, then in the historic county of Lancashire, England. Originally named Messhing Trees, the colliery was sunk by William Ramsden and, with Nelson Pit, formed Ramsden's Shakerley Collieries. The colliery worked the Trencherbone mine at 360 yards and was ventilated by furnace in 1895. Coal to make gas and household coal was produced in 1896 from the Arley, Hell hole, Trencherbone and Yard mines. Shakerley Collieries' combined workforce for the two pits was 422 underground and 87 surface workers. The colliery lasted until 1935 when the company was taken over by Manchester Collieries and closed the same year. See also * List of Collieries in Astley and Tyldesley *Glossary of coal mining terminology This is a partial glossary of coal mining terminology commonly used in the coalfields of the United Kingdom. Some words were in use throughout the coalfields, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakerley Collieries
Ramsden's Shakerley Collieries was a coal mining company operating the Nelson and Wellington Pits from the mid 19th century in Shakerley, Tyldesley in the historic county of Lancashire, England. History Coal had been dug in Shakerley since the 15th century when a dispute over "seacole" was recorded in 1429. Coal was used in the smithies of the nailers who plied their trade in Shakerley. There was a colliery between Higher Oak and Common Fold in Shakerley in 1798. John Hope of Chaddock Hall left it to his son, John, and his son-in-law, Thomas Smith. In 1836 Jacob Fletcher of Peel Hall Little Hulton bought the Shakerley estates and acquired "514 acres of land, and the valuable mines of coal and stone lying under the same; the estates abounded with thriving young timber; the mines of coal were inexhaustible, of excellent quality, and being in a manufacturing district found a ready sale". Shakerley Colliery, which was later renamed the Nelson Pit was sunk in the 1830s or 1840s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |