|
Mancera Island
Mancera Island ( es, Isla Mancera) is a minor island at the mouth of Valdivia River in Corral Bay. Prior to being named after the Marquis of Mancera the island was known as ''Güiguacabin'' (from ''ühueñn'', "whistle", or ''ühua'', "maize", and ''cahuin'', "party") to the indigenous Mapuches. In his 1544 expedition Juan Bautista Pastene, made the island known for the Spanish and named it ''Imperial''. Later the island became known to the Spanish as ''Constantino'' after its owner Constantino Pérez, then it was known for a time as ''Santa Ines''. The name finally settled as Mancera after the Spanish viceroy of Peru Pedro de Toledo, 1st Marquis of Mancera, who ordered the fortification of the island. The fort in Mancera Island begun to be built in 1646 receiving the names ''Castillo de San Pedro de Alcántara de Mancera'' or simply ''Castillo de Mancera''. The fort was a vital point in the Valdivian Fort System, allowing with the aid of the forts in Corral and Niebla to cross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niebla, Chile
Niebla (Spanish for ''fog'') is a coastal Chilean town close to the city of Valdivia, Valdivia Province, Los Ríos Region. Niebla is located on the northern edge, at the mouth of the Valdivia River, across from Corral. Niebla's beach and folk market are popular tourist destinations during the summer, together with the ruins of a Spanish colonial fort and its museum. In 2017 Niebla had a population of 2,989 inhabitants up from 2,202 in 2002. References See also * Valdivian Fort System * List of towns in Chile This article contains a list of towns in Chile. A town is defined by Chile's National Statistics Institute (INE) as an urban entity possessing between 2,001 and 5,000 inhabitants—or between 1,001 and 2,000 inhabitants if 50% or more of its popu ... Populated places in Valdivia Province Beaches of Chile Populated coastal places in Chile Landforms of Los Ríos Region Coasts of Los Ríos Region {{LosRíos-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro De Toledo, 1st Marquis Of Mancera
Pedro Álvarez de Toledo y Leiva, 1st Marquis of Mancera (c. 1585–1654), was a Spanish nobility, Spanish nobleman, general, colonial administrator, and diplomat. He served as Captain General of Galicia (Spain), Galicia and Viceroy of Peru from December 18, 1639 to September 20, 1648. Early life Pedro de Toledo was the son of Don Luis de Toledo, 4th Lord of Mancera, and of his second wife Isabel de Leiva. He served with the Spanish armies in Italy, rising to the rank of lieutenant general in the royal galleys of Sicily. King Philip IV of Spain raised his title from Lord to Marquis of Mancera de Arriba, Mancera in 1623. Thereafter he served eight years as governor and Captain General of Galicia (Spain), Galicia. Viceroy of Peru Pedro de Toledo was named the 15th Viceroy of Peru in 1639, at the age of 54. He traveled to the Viceroyalty of Peru with his son Antonio Sebastián de Toledo, 2nd Marquis of Mancera, Antonio Sebastián de Toledo, who later became the Viceroy of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islands Of Los Ríos Region
An island or isle is a piece of subcontinental land completely surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges Delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental islands and oceanic islands. There are also artificial islands (man-made islands). There are about 900,000 official islands in the world. This number consists of all the officially-reported islands of each country. The total number of islands in the world is unknown. There may be hundreds of thousands of tiny islands that are unknown and uncounted. The number of sea islands in the world is estimated to be more than 200,000. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Valdivia
The Capture of Valdivia ( es, Toma de Valdivia) was a battle in the Chilean War of Independence between Royalist forces commanded by Colonel Manuel Montoya and Fausto del Hoyo and the Patriot forces under the command of Thomas Cochrane and Jorge Beauchef, held on 3 and 4 February 1820. The battle was fought over the control of the city Valdivia and its strategic and heavily fortified harbour. In the battle Patriots gained control of the southwestern part of the Valdivian Fort System after an audacious assault aided by deception and the darkness of the night. The following day the demoralised Spanish evacuated the remaining forts, looted local Patriot property in Valdivia and withdrew to Osorno and Chiloé. Thereafter, Patriot mobs looted the property of local Royalists until the Patriot army arrived to the city restoring order. The capture of Valdivia was a major victory to the Patriots as it deprived the Spanish Empire an important naval base from where to harass or quell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convent
A convent is a community of monks, nuns, religious brothers or, sisters or priests. Alternatively, ''convent'' means the building used by the community. The word is particularly used in the Catholic Church, Lutheran churches, and the Anglican Communion. Etymology and usage The term ''convent'' derives via Old French from Latin ''conventus'', perfect participle of the verb ''convenio'', meaning "to convene, to come together". It was first used in this sense when the eremitical life began to be combined with the cenobitical. The original reference was to the gathering of mendicants who spent much of their time travelling. Technically, a monastery is a secluded community of monastics, whereas a friary or convent is a community of mendicants (which, by contrast, might be located in a city), and a canonry is a community of canons regular. The terms abbey and priory can be applied to both monasteries and canonries; an abbey is headed by an abbot, and a priory is a lesser dependent ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Quadruple Alliance
The War of the Quadruple Alliance (1718–1720) was caused by Spanish attempts to recover territories in Italy (geographical region), Italy ceded in the 1713 Peace of Utrecht. Largely focused on Sicily, it included minor engagements in North America and Northern Europe as well as the Spanish-backed Jacobite rising of 1719 in Scotland. In August–October 1717, Spanish conquest of Sardinia, Spain recaptured Sardinia from Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Austria with little opposition, which it then followed by a landing in Sicily in July 1718. On 2 August 1718, a Quadruple Alliance was formed by Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain, Kingdom of France, France, Habsburg monarchy, Austria, and the Dutch Republic. The war ended with the 1720 Treaty of The Hague (1720), Treaty of The Hague, which restored the position prior to 1717, but with Duchy of Savoy, Savoy and Austria exchanging Sardinia and Sicily. Background Post-1714, Spain recovered remarkably quickly from the War of the Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valdivia
Valdivia (; Mapuche: Ainil) is a city and commune in southern Chile, administered by the Municipality of Valdivia. The city is named after its founder Pedro de Valdivia and is located at the confluence of the Calle-Calle, Valdivia, and Cau-Cau Rivers, approximately east of the coastal towns of Corral and Niebla. Since October 2007, Valdivia has been the capital of Los Ríos Region and is also the capital of Valdivia Province. The national census of 2017 recorded the commune of Valdivia as having 166,080 inhabitants (''Valdivianos''), of whom 150,048 were living in the city. The main economic activities of Valdivia include tourism, wood pulp manufacturing, forestry, metallurgy, and beer production. The city is also the home of the Austral University of Chile, founded in 1954 and the Centro de Estudios Científicos. The city of Valdivia and the Chiloé Archipelago were once the two southernmost outliers of the Spanish Empire. From 1645 to 1740 the city depended directly on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossfire
A crossfire (also known as interlocking fire) is a military term for the siting of weapons (often automatic weapons such as assault rifles or sub-machine guns) so that their arcs of fire overlap. This tactic came to prominence in World War I. Siting weapons this way is an example of the application of the defensive principle of ''mutual support''. The advantage of siting weapons that mutually support one another is that it is difficult for an attacker to find a covered approach to any one defensive position. Use of armour, air support, indirect fire support, and stealth are tactics that may be used to assault a defensive position. However, when combined with land mines, snipers, barbed wire, and air cover, crossfire became a difficult tactic to counter in the early 20th century. Trench warfare The tactic of using overlapping arcs of fire came to prominence during World War I where it was a feature of trench warfare. Machine guns were placed in groups, called machine-gun nests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corral, Chile
Corral is a town, commune and sea port in Valdivia Province, Los Ríos Region, Chile. It is located south of Corral Bay. Corral is best known for the forts of Corral Bay, a system of defensive batteries and forts made to protect Valdivia during colonial times. Corral was the headquarters of the system. Economic activities in Corral revolve around forestry, aquaculture, fishing, port services and both heritage and eco tourism. The town is connected to Valdivia by a gravel road, to Caleta Chaihuín by an asphalted road and to Niebla on the other side of the bay by a ferry service. History The settlement of Corral grew out from the headquarters of the forts of Corral Bay that were built in 1645 to protect the city of Valdivia. By that time Spanish ships sailed through Valdivia River all the way to Valdivia but Corral soon took over the role of receiving major ships. Until 1749 the fort of Corral had no more than four cannons.Guarda 1953, p. 153. Renewed interest in the defense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
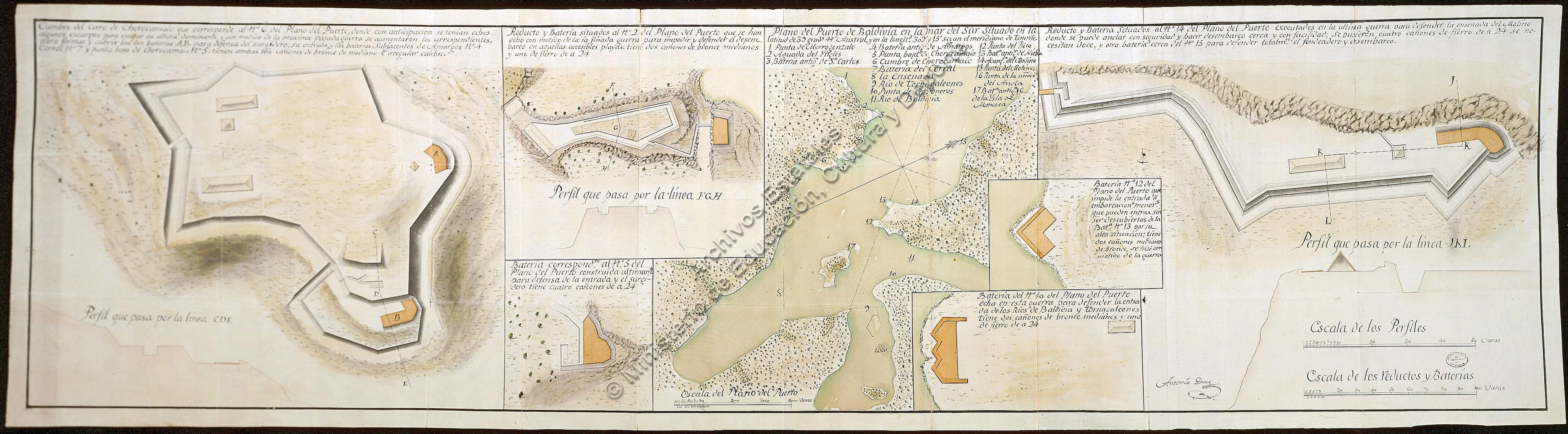
Valdivian Fort System
The Fort System of Valdivia ( es, Sistema de fuertes de Valdivia) is a series of Spanish colonial fortifications at Corral Bay, Valdivia and Cruces River established to protect the city of Valdivia, in southern Chile. During the period of Spanish rule (1645–1820), it was one of the biggest systems of fortification in the Americas. It was also a major supply source for Spanish ships that crossed the Strait of Magellan. Building of the fort system began in 1645 and was overhauled after the Seven Years' War (1756–1763) by the military engineers Juan Garland and Manuel Olaguer Feliú. Having been a first-rate fort system in Spanish America, in the 18th century it was overshadowed by the forts of Cartagena de Indias, Havana and Puerto Rico.Guarda 1970, p. 30. The Valdivian Fort System was however still the main coastal fortification on Spanish America's Pacific coast. During its existence the fort system has seen hostilities twice; first in 1670 when it dealt with a susp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anales De La Universidad De Chile
''Anales de la Universidad de Chile'' is a biannual peer-reviewed academic journal containing research and critical reflections on arts, humanities, and science. It was established in 1843 and is published by the University of Chile. The editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ... is Jennifer Abate Cruces (University of Chile). External links * Latin American studies journals Publications established in 1843 University of Chile academic journals Spanish-language journals 1943 establishments in Chile Biannual journals {{humanities-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Peru
The viceroys of Peru ruled the Viceroyalty of Peru from 1544 to 1824 in the name of the monarch of Spain. The territories under ''de jure'' rule by the viceroys included in the 16th and 17th century almost all of South America except eastern Brazil. Governors of New Castile (1532–1544) Viceroys of Peru (1544–1824) See also *Viceroyalty of Peru *History of Peru * List of presidents of Peru References {{DEFAULTSORT:Viceroys Of Peru, List Of Viceroyalty of Peru * *Peru Colonial Peru Viceroy Peru, viceroys Viceroys 16th-century Peruvian people 17th-century Peruvian people 18th-century Peruvian people 19th-century Peruvian people Viceroy of Peru Viceroy of Peru Viceroy of Peru Viceroy of Peru Viceroy of Peru Viceroy of Peru The viceroys of Peru ruled the Viceroyalty of Peru from 1544 to 1824 in the name of the monarch of Spain. The territories under ''de jure'' rule by the viceroys included in the 16th and 17th century almost all of South America except e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)