|
Male Lactation
Production of milk (lactation) from a male mammal's mammary glands is well-documented in the Dayak fruit bat and the Bismarck masked flying fox. The term "male lactation" is not used in human medicine. It has been used in popular literature, such as Louise Erdrich's ''The Antelope Wife'', to describe the phenomenon of male galactorrhea, which is a human condition unrelated to childbirth or nursing. Newborn babies of both sexes can occasionally produce milk. This is called neonatal milk (also as "witch's milk") and not considered male lactation. History Male lactation was of some interest to Alexander von Humboldt, who reports in ''Voyage aux régions équinoxiales du Nouveau Continent'' about a citizen of the Venezuelan village of Arenas (close to Cumana) who allegedly nurtured his son for three months when his wife was ill, as well as Charles Darwin, who commented on it in ''The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex'' (1871): Darwin later considered the nearly pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
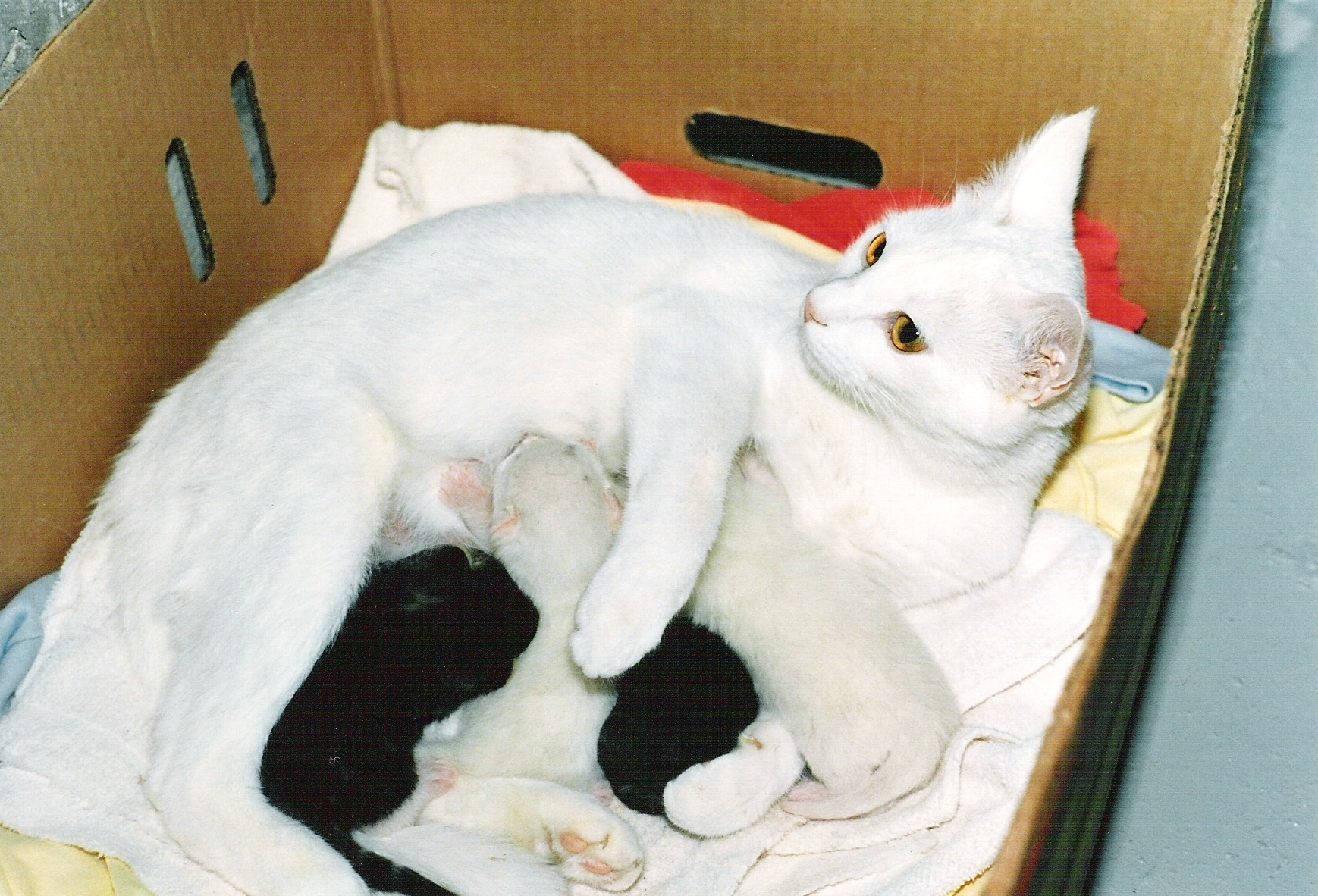
Lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all animals (including humans) is called ''nursing'', and in humans it is also called ''breastfeeding''. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk. In most species, lactation is a sign that the female has been pregnant at some point in her life, although it can happen without pregnancy. Nearly every species of mammal has nipples; except for monotremes, egg-laying mammals, which instead release milk through ducts in the abdomen. In only one species of mammal, the Dayak fruit bat from Southeast Asia, is milk production a normal male function. ''Galactopoiesis'' is the maintenance of milk production. This stage requires prolactin. Oxytocin is critical for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descent Of Man/Chapter VI
Descent may refer to: As a noun Genealogy and inheritance * Common descent, concept in evolutionary biology * Kinship, one of the major concepts of cultural anthropology **Pedigree chart or family tree **Ancestry **Lineal descendant **Heritage **Royal descent - lineal descent from a monarch *Phylogenetics **Tree diagram (other) *Inheritance (law and property) Mathematics * Infinite descent, a method going back to Fermat to solve Diophantine equations * Descent (mathematics), an idea extending the notion of "gluing" in topology * Hadamard's method of descent, a technique for solving partial differential equations * Gradient descent, a first-order optimization algorithm going back to Newton * Descents in permutations, a classical permutation statistic in combinatorics Other uses *Descent (aeronautics), the decrease of an aircraft in altitude during flight *Descent (font), the distance that a typeface descends below the baseline in typography *Katabasis As a proper name F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male Egg
Male egg can refer to either: #An egg that artificially contains genetic material from a male. #An egg from a haplodiploid species such as an ant or bee that is unfertilized and will hatch a male #A fertilized egg that a male organism is developing in This article focuses on the first definition. Male eggs are the result of a process in which the eggs of a female would be emptied of their genetic contents (a technique similar to that used in the cloning process), and those contents would be replaced with male DNA. Such eggs could then be fertilized by sperm. The procedure was conceived by Calum MacKellar, a Scottish bioethicist. With this technique, two males could be the biological parents of a child. However, such a procedure would additionally require an artificial womb or a female gestational carrier. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milking The Bull
Milking the bull is a proverb which uses the metaphor of milking a bull to indicate that an activity would be fruitless or futile. In the 16th century, the German painter Hans Leonhard Schäufelein, Hans Schäufelein illustrated the proverb on the eight of suit (cards)#Correspondence table, bells in a deck of playing cards. Samuel Johnson, Dr Johnson used the proverb to criticise the work of David Hume and other philosophical skepticism, skeptical philosophers. See also *Tilting at windmills *Male lactation *Frozen_bovine_semen#How_semen_is_collected, Collection of semen from bulls References {{reflist Metaphors Proverbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGBT Reproduction
LGBT reproduction refers to lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people having biological children by means of assisted reproductive technology. It is distinct from LGBT parenting, which is a broader cultural phenomenon including LGBT adoption. In recent decades, developmental biologists have been researching and developing techniques to facilitate same-sex reproduction. The obvious approaches, subject to a growing amount of activity, are female sperm and male eggs. In 2004, by altering the function of a few genes involved with imprinting, other Japanese scientists combined two mouse eggs to produce daughter mice and in 2018 Chinese scientists created 29 female mice from two female mice mothers but were unable to produce viable offspring from two father mice. One of the possibilities is obtaining sperm and eggs from skin stem cells. Gay men Some gay couples decide to have a surrogate pregnancy. A surrogate is a woman carrying an egg fertilized by sperm of one of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intersex
Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies". Sex assignment at birth usually aligns with a child's anatomical sex and phenotype. The number of births with ambiguous genitals is in the range of 1:2000–1:4500 (0.022%–0.05%). Other conditions involve atypical chromosomes, gonads, or hormones. Some persons may be assigned and raised as a girl or boy but then identify with another gender later in life, while most continue to identify with their assigned sex. The number of births where the baby is intersex has been reported differently depending on who reports and which definition of intersex is used. Anne Fausto-Sterling and her co-authors suggest that the prevalence of "nondimorphic sexual development" might be as high as 1.7%. A study publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactagogue
A galactagogue, or galactogogue (from el, γάλα �αλακτ- milk, + ἀγωγός, leading), also known as a lactation inducer or milk booster, is a substance that promotes lactation in humans and other animals. It may be synthetic, plant-derived, or endogenous. They may be used to induce lactation and to treat low milk supply. Pharmaceutical Synthetic galactagogues such as domperidone and metoclopramide interact with the dopamine system in such a way to increase the production of prolactin; specifically, by blocking the D2 receptor. There is some evidence to suggest that mothers who are unable to meet their infants' breastfeeding needs may benefit from galactogogues. Galactagogues may be considered when non-pharmacologic interventions are found to be insufficient. For example, domperidone may be an option for mothers of preterm babies who at over 14 days from delivery and after full lactation support still have difficulty expressing breast milk in sufficient quantity fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgender Women
A trans woman or a transgender woman is a woman who was assigned male at birth. Trans women have a female gender identity, may experience gender dysphoria, and may transition; this process commonly includes hormone replacement therapy and sometimes sex reassignment surgery, which can bring relief and resolve feelings of gender dysphoria. Like cisgender women, trans women may have any sexual orientation. The term ''transgender woman'' is not always interchangeable with ''transsexual woman'', although the terms are often used interchangeably. ''Transgender'' is an umbrella term that includes different types of gender variant people (including transsexual people). Trans women face significant discrimination in many areas of life, including in employment and access to housing, and face physical and sexual violence and hate crimes, including from partners; in the United States, discrimination is particularly severe towards trans women who are members of a racial minority, who oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
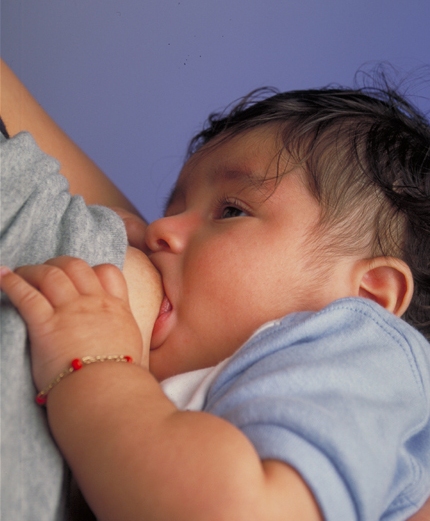
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfeeding has a numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyacopterus Spadiceus
The dayak fruit bat or dyak fruit bat (''Dyacopterus spadiceus'') is a relatively rare frugivorous megabat species found only on the Sunda Shelf of southeast Asia, specifically the Malay Peninsula south of the Isthmus of Kra, and the islands of Borneo and Sumatra. There are three species in the genus ''Dyacopterus'': ''D. spadiceus'', ''D. brooksi'' and ''D. rickarti''. All are found in the forests of Malaysia, Thailand, and the Philippines. Few specimens of any of the three species exist, due not only to their rarity, but also because they rarely enter the subcanopy of the forest where they can be caught in scientists' nets. Distribution ''D. spadiceus'' is considered a very rare fruit bat species in Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo and none in Thailand. The species were netted in four sites at Poring, Kubah, Kota Samarahan and Pontianak, all on Borneo. The specimens, MTA96268 and MTA96269, that were held at Tanjungpura University, are the first record for this distinctive speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Tumor
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pituitary Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version NIH National Cancer Institute Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial and the estimated prevalence rate in the general population is approximately 17%. Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be |
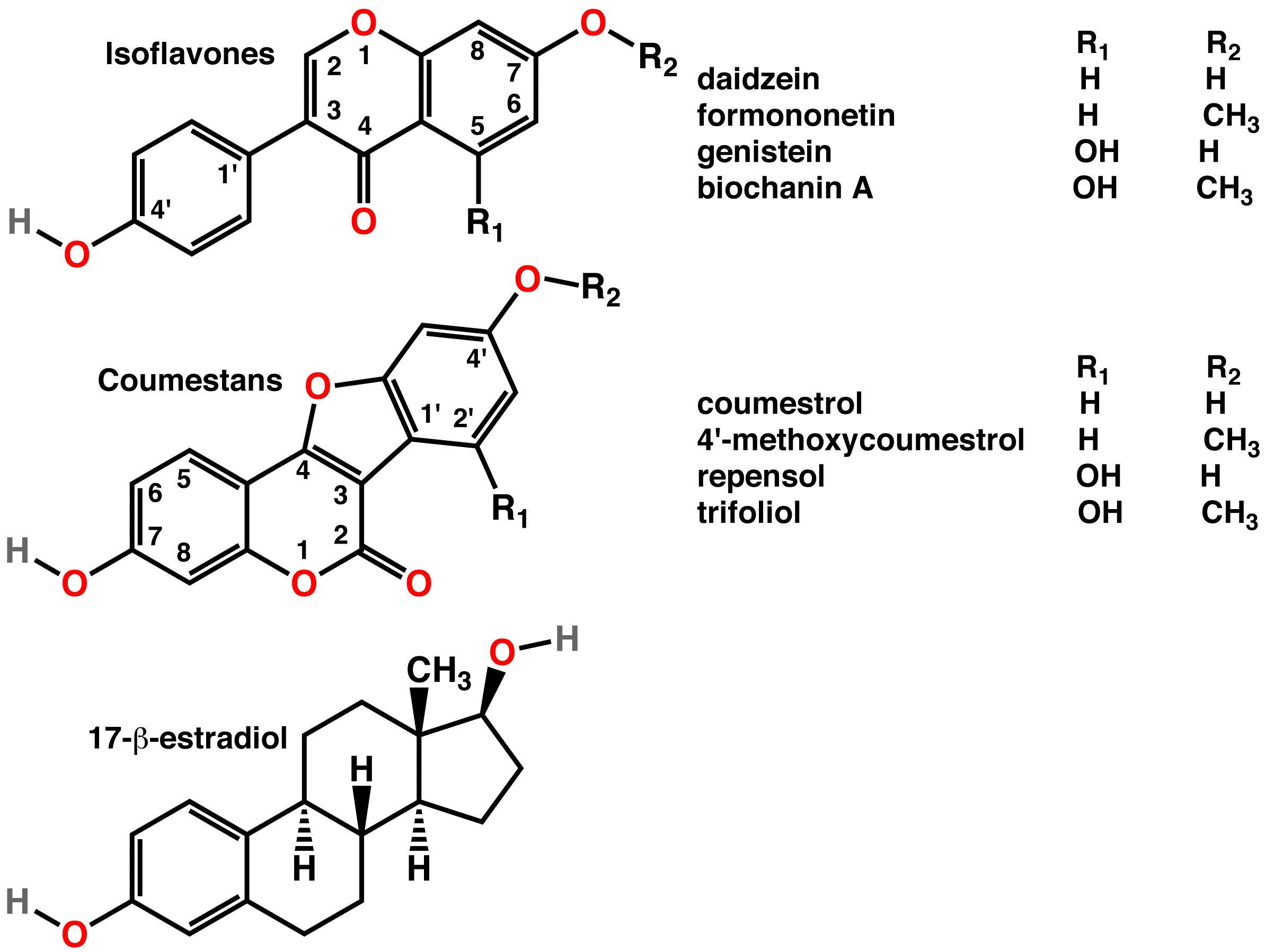
Phytoestrogens
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen (see estrogen) not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity with estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soy protein, beans, oats, barley, rice, coffee, apples, carrots (see Food Sources section below for bigger list). Its name comes from the Greek ''phyto'' ("plant") and ''estrogen'', the hormone which gives fertility to female mammals. The word "estrus" - Greek οίστρος - means "sexual desire", and "gene" - Greek γόνο - is "to generate". It has been hypoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |