|
Makronisos
Makronisos ( el, Μακρόνησος, lit. ''Long Island''), or Makronisi, is an island in the Aegean sea, in Greece, notorious as the site of a political prison from the 1920s to the 1970s. It is located close to the coast of Attica, facing the port of Lavrio. The island has an elongated shape, north to south and east to west at its widest point, and its terrain is arid and rocky. It is the largest uninhabited Greek island. It is part of the Kea-Kythnos regional unit and in the municipality of Kea. History In ancient times the island was called Helen ( grc, Ἑλένη). It protected the ancient harbours of Thorikos and Sounion. It was also called Macris (Μάκρις), from its length. Strabo describes it as 60 stadia (9.4 km) in length; but its real length is seven geographical miles (12 km). It was uninhabited in antiquity, as it is at the present day; and it was probably only used then for the pasture of cattle. Both Strabo and Pausanias derive its name from Helen of Troy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kea Channel
The Kea Channel, is a passage of water in the Aegean Sea. lying between the islands of Kea and Makronisos, just off Cape Sounion, Attica on the mainland of Greece Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with .... The channel is the location of the wreck of , sunk on 21 November 1916. Bodies of water of Greece Landforms of Kea-Kythnos Landforms of the South Aegean Channels of Europe {{SouthAegean-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War ( el, ο Eμφύλιος [Πόλεμος], ''o Emfýlios'' [''Pólemos''], "the Civil War") took place from 1946 to 1949. It was mainly fought against the established Kingdom of Greece, which was supported by the United Kingdom and the United States and won in the end. The losing opposition held a self-proclaimed people's republic, the Provisional Democratic Government, Provisional Democratic Government of Greece, which was governed by the Communist Party of Greece (KKE) and its military branch, the Democratic Army of Greece (DSE). The rebels were supported by Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia and the Soviet Union. The war has its roots at the WW2 conflict, between the Communist Party of Greece, communist-dominated left-wing Greek Resistance, resistance organisation, the National Liberation Front (Greece), EAM-ELAS, and loosely-allied anticommunist resistance forces. It later escalated into a major civil war between the state and the communist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMHS Britannic
''Britannic'' () was the third and final vessel of the White Star Line's of steamships and the second White Star ship to bear the name ''Britannic''. She was the youngest sister of the and the and was intended to enter service as a transatlantic passenger liner. She was operated as a hospital ship from 1915 until her sinking near the Greek island of Kea, in the Aegean Sea, in November 1916. At the time she was the largest hospital ship in the world. ''Britannic'' was launched just before the start of the First World War. She was designed to be the safest of the three ships with design changes made during construction due to lessons learned from the sinking of the ''Titanic''. She was laid up at her builders, Harland and Wolff, in Belfast for many months before being requisitioned as a hospital ship. In 1915 and 1916 she served between the United Kingdom and the Dardanelles. On the morning of 21 November 1916 she was shaken by an explosion caused by a naval mine of the Im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikis Theodorakis
Michail "Mikis" Theodorakis ( el, Μιχαήλ "Μίκης" Θεοδωράκης ; 29 July 1925 – 2 September 2021) was a Greek composer and lyricist credited with over 1,000 works. He Film score, scored for the films ''Zorba the Greek (film), Zorba the Greek'' (1964), ''Z (1969 film), Z'' (1969), and ''Serpico'' (1973). He composed the "Mauthausen Trilogy", also known as "The Ballad of Mauthausen", which has been described as the "most beautiful musical work ever written about the The Holocaust, Holocaust" and possibly his best work. Up until his death, he was viewed as Greece's best-known living composer. He was awarded the Lenin Peace Prize. Politically, he was associated with the left because of his long-standing ties to the Communist Party of Greece (KKE). He was an MP for the KKE from 1981 to 1990. Despite this however, he ran as an independent candidate within the centre-right New Democracy (Greece), New Democracy party in 1989, in order for the country to emerge from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kea-Kythnos
Kea-Kythnos ( el, Περιφερειακή ενότητα Κέας-Κύθνου) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of South Aegean. The regional unit covers the islands of Kea, Kythnos, Makronisos and several smaller islands in the Aegean Sea. Administration As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the regional unit Kea-Kythnos was created out of part of the former Cyclades Prefecture. It is subdivided into 2 municipalities. These are (number as in the map in the infobox): *Kea (8) *Kythnos (10) Province The province of Kea ( el, Επαρχία Κέας) was one of the provinces A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ... of the Cyclades Prefecture. It had the same territory as the present regional unit Kea-Kythnos. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostolos Santas
Apostolos Santas ( el, Απόστολος Σάντας; 22 February 1922 – 30 April 2011), commonly known as Lakis, was a Greek veteran of the Resistance against the Axis Occupation of Greece during World War II, most notable for his participation, along with Manolis Glezos, in the taking down of the German flag from the Acropolis on 30 May 1941. Biography Apostolos Santas was born in 1922 in Patras, while his roots were from the Ionian island of Lefkada. His family moved to Athens in 1934. He completed his secondary education in Athens and was accepted to the law school of the University of Athens, completing his law studies after the liberation of the country from Nazi occupation in 1944. On the night of 30 May 1941, he and Manolis Glezos climbed on the Acropolis of Athens and tore down the Nazi flag, which had been there since 27 April, when the Nazi forces had entered and occupied Athens, leaving the flagpole empty. That was one of the first resistance acts in Greece. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavrio
Laurium or Lavrio ( ell, Λαύριο; grc, Λαύρειον (later ); before early 11th century BC: Θορικός ''Thorikos''; from Middle Ages until 1908: Εργαστήρια ''Ergastiria'') is a town in southeastern part of Attica, Greece. It is part of Athens metropolitan area and the seat of the municipality of Lavreotiki. Laurium was famous in Classical antiquity for its silver mines, which was one of the chief sources of revenue of the Athenian state. The metallic silver was mainly used for coinage. The Archaeological Museum of Lavrion shows much of the story of these mines. It is located about 60 km SE of Athens city center, SE of Keratea and N of Cape Sounio. Laurium is situated on a bay overlooking the island of Makronisos (ancient times: Helena) in the east. The port is in the middle and gridded streets cover the residential area of Lavrio. GR-89 runs through Lavrio and ends south in Sounio. History The modern town of Laurium is at the site of the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kea Island
Kea ( el, Κέα), also known as Tzia ( el, Τζια) and in antiquity Keos ( el, Κέως, la, Ceos), is a Greek island in the Cyclades archipelago in the Aegean Sea. Kea is part of the Kea-Kythnos regional unit. Geography It is the island of the Cyclades complex that is closest to Attica (about 1 hour by ferry from Lavrio) and is also from Cape Sounio as well as SE of Athens. Its climate is arid, and its terrain is hilly. Kea is long from north to south and wide from west to east. The area is with the highest point being above sea level. The municipality, which includes the island Makronisos, has an area of . Its capital, Ioulis, is inland at a high altitude (like most ancient Cycladic settlements, for fear of pirates) and is considered quite picturesque. Other major villages of Kea are the port of Korissia and the fishing village of Vourkari. After suffering depopulation for many decades, Kea has been recently rediscovered by Athenians as a convenient destination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris (mythology)
Paris ( grc, Πάρις), also known as Alexander (, ''Aléxandros''), the son of King Priam and Queen Hecuba of Troy, is a mythological nobleman that appears in a number of Greek legends. Of these appearances, probably the best known was the elopement with Helen, queen of Sparta, this being one of the immediate causes of the Trojan War. Later in the war, he fatally wounds Achilles in the heel with an arrow as foretold by Achilles's mother, Thetis. The name ''Paris'' is probably of Luwian origin, and comparable to '' Pari-zitis'', attested as a Hittite scribe's name. The name Paris is etymologically unrelated to the name of the French city of Paris, which derives its name from a Gaulish tribe called the Parisii. Description Paris was described by the chronicler Malalas in his account of the ''Chronography'' as " well-grown, sturdy, white, good nose, good eyes, black pupils, black hair, incipient beard, long-faced, heavy eyebrows, big mouth, charming, eloquent, agile, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
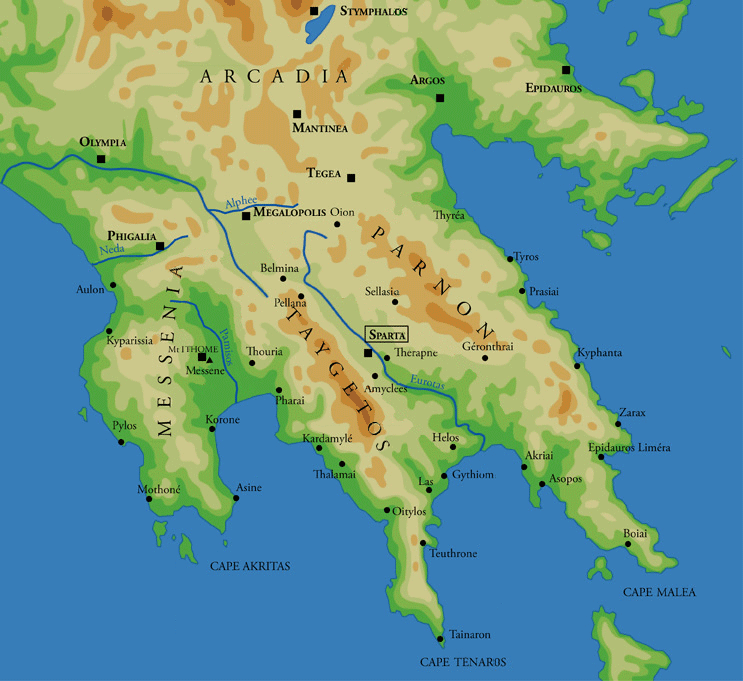
Gythium
Gytheio ( el, Γύθειο, ) or Gythio, also the ancient Gythium or Gytheion ( grc, Γύθειον), is a town on the eastern shore of the Mani Peninsula, and a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality East Mani, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 197.313 km2. It was the seaport of Sparta, some north. Gytheio is the site of ancient Cranae, a tiny island where according to legend Paris of Troy and Helen from Sparta spent their first night together before departing for Troy, thus igniting the Trojan War. Gytheio used to be an important port until it was destroyed in 4th century AD, possibly by an earthquake. Even thereafter its strategic location gave Gytheio a significant role in Maniot history. Today it is the largest and most important town in Mani. It is also the seat of the municipality of East Mani. Historical population Geography Gytheio is located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, Λακωνία, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word ''laconic''—to speak in a blunt, concise way—is derived from the name of this region, a reference to the ancient Spartans who were renowned for their verbal austerity and blunt, often pithy remarks. Geography Laconia is bordered by Messenia to the west and Arcadia to the north and is surrounded by the Myrtoan Sea to the east and by the Laconian Gulf and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. It encompasses Cape Malea and Cape Tainaron and a large part of the Mani Peninsula. The Mani Peninsula is in the west region of Laconia. The islands of Kythira and Antikythera lie to the south, but they administratively belong to the Attica regional unit of islands. The island, Elafonisos, situated between the Laconian mainland and Kythira, is part of Laconia. The Eurotas is the lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RMS Titanic
RMS ''Titanic'' was a British passenger liner, operated by the White Star Line, which sank in the North Atlantic Ocean on 15 April 1912 after striking an iceberg during her maiden voyage from Southampton, England, to New York City, United States. Of the estimated 2,224 passengers and crew aboard, more than 1,500 died, making it the deadliest sinking of a single ship up to that time. It remains the deadliest peacetime sinking of a superliner or cruise ship. The disaster drew public attention, provided foundational material for the disaster film genre, and has inspired many artistic works. RMS ''Titanic'' was the largest ship afloat at the time she entered service and the second of three s operated by the White Star Line. She was built by the Harland and Wolff shipyard in Belfast. Thomas Andrews, the chief naval architect of the shipyard, died in the disaster. ''Titanic'' was under the command of Captain Edward Smith, who went down with the ship. The ocean liner carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |