|
Makariv
Makariv (, ) is an urban-type settlement in Bucha Raion, in Kyiv Oblast (province) of Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Makariv settlement hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The population of the settlement is , down from 12,042 in 2001. History The initial documented history of Makarov is connected with the village of Voronin, which was one of the Yasinets estates of the Lithuanian feudal lords Ivashentsevichs ( Vasentsevichi). It was mentioned for the first time as part of the estates of the Yasinetsky family in 1506. Makar Vasentsevich, who began to live permanently in Voronin, changed his surname to Makarovich, and the name of the village to Makariv. In the late 16th century Makarovichi built an estate. During the Khmelnytsky Uprising (1648–1676), the Makariv estate was burned down, and the local population actively joined the Ukrainian national liberation movement. Later, Makariv people participated in uprisings led by Detsyk (1660s) and Semen Paliy (1694). A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makariv Settlement Hromada
Makariv (, ) is an urban-type settlement in Bucha Raion, in Kyiv Oblast (oblast, province) of Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Makariv settlement hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The population of the settlement is , down from 12,042 in 2001. History The initial documented history of Makarov is connected with the village of Voronin, which was one of the Yasinets estates of the Lithuanian feudal lords Ivashentsevichs (Vasentsevichi). It was mentioned for the first time as part of the estates of the Yasinetsky family in 1506. Makar Vasentsevich, who began to live permanently in Voronin, changed his surname to Makarovich, and the name of the village to Makariv. In the late 16th century Makarovichi built an estate. During the Khmelnytsky Uprising (1648–1676), the Makariv estate was burned down, and the local population actively joined the Ukrainian national liberation movement. Later, Makariv people participated in uprisings led by Detsyk (1660s) and Semen Paliy (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucha Raion
Bucha Raion ( uk, Бучанський район, translit=Buchanskyi raion) is a raion (district) of Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine. It was created in July 2020 as part of the reform of administrative divisions of Ukraine. Its administrative center is the town of Bucha. One abolished raion, Borodianka Raion, parts of abolished Kyiv-Sviatoshyn and Makariv Raions, as well as Irpin Municipality and the city of Bucha, which was previously incorporated as a city of oblast significance, were merged into Bucha Raion. The name of the raion is derived from the Dniester river. The population of the raion is Subdivisions At the time of establishment, the raion consisted of 12 hromadas: * Bilohorodka rural hromada with the administration in the selo of Bilohorodka, transferred from Kyiv-Sviatoshyn Raion;< * Borodianka settlement hromada with the administration in the < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
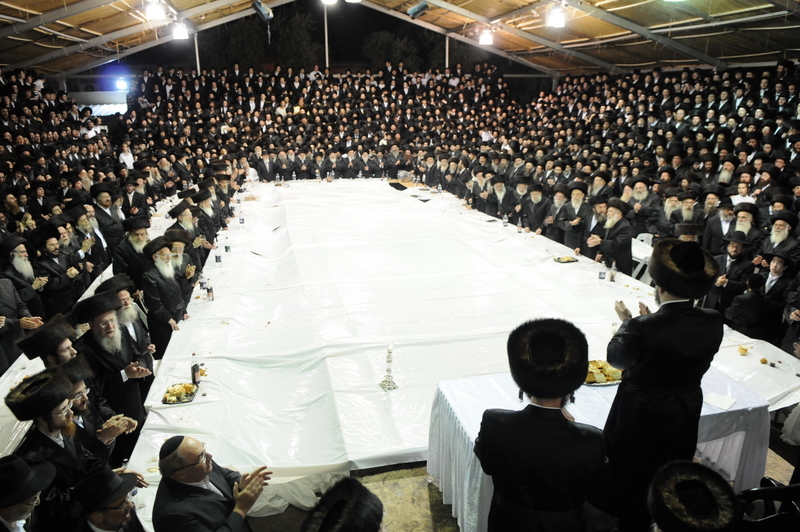
Makarov (Hasidic Dynasty)
Makarov is a Hasidic dynasty founded by the Rebbe Menachem Nochum Twerski of the Chernobyl dynasty. Makarov is the Yiddish name of Makariv, a town in present-day Ukraine. To this day, the Mekarev Shul is used in the old City of Safed for Shabbat Prayers by the Yeshiva Shalom Rav. Lineage * Rebbe Menachem Nochum Twerski of Makarov (1805–1851), son of the Rebbe Mordechai Twerski Mordechai Twersky (1770–1837), known as the ''Maggid'' of Chernobyl, was a Ukrainian rabbi. He was the son of Rabbi Menachem Nachum Twersky of Chornobyl and the second rebbe of the Chernobyl Hasidic dynasty. (The family surname originally co ... of Chernobyl ** Rebbe Yaakov Yitzchok of Makarov (died 1892), son of the Rebbe Nochum. *** Dov Ber Tversky (2002-now), son of Reb Yaakov Yitzchok Tversky. References * Encyclopedia of Jewish Life (2001), p. 786: "Makarov"Rebbe * Shtetl Finder (1980), p. 53: "Makarov" Słownik Geograficzny Królestwa Polskiego (1880-1902), VII, pp. 922-926: "Makarów"( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
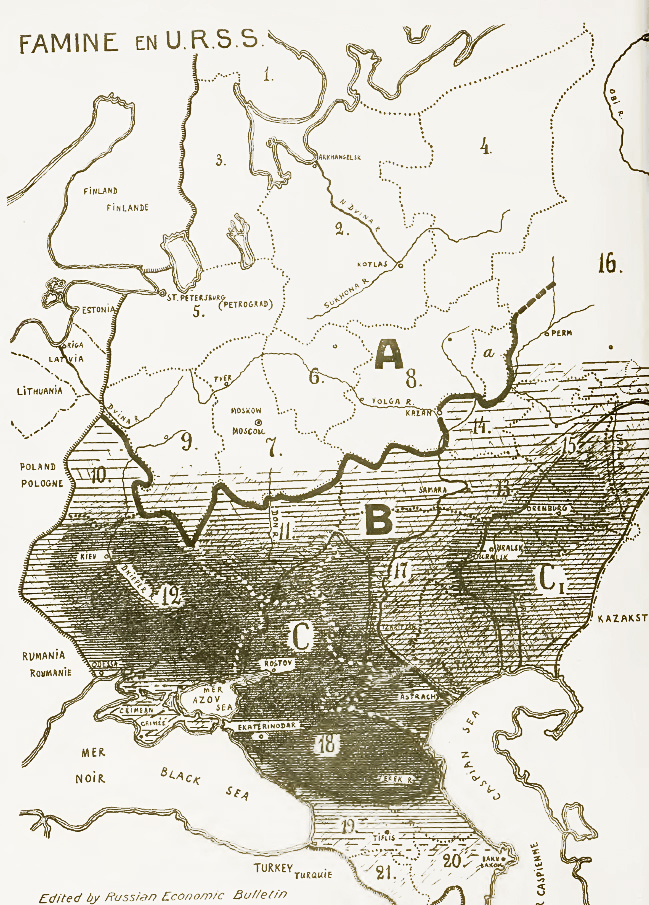
Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famine in Soviet Ukraine from 1932 to 1933 that killed millions of Ukrainians. The Holodomor was part of the wider Soviet famine of 1932–1933 which affected the major grain-producing areas of the Soviet Union. While scholars universally agree that the cause of the famine was man-made, whether the Holodomor constitutes a genocide remains in dispute. Some historians conclude that the famine was planned and exacerbated by Joseph Stalin in order to eliminate a Ukrainian independence movement. This conclusion is supported by Raphael Lemkin. Others suggest that the famine arose because of rapid Soviet industrialisation and collectivization of agriculture. Ukraine was one of the largest grain-producing states in the USSR and was subject to unre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalinist Terror
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Yezhov'), was Soviet General Secretary Joseph Stalin's campaign to solidify his power over the party and the state; the purges were also designed to remove the remaining influence of Leon Trotsky as well as other prominent political rivals within the party. It occurred from August 1936 to March 1938. Following the death of Vladimir Lenin in 1924 a power vacuum opened in the Communist Party. Various established figures in Lenin's government attempted to succeed him. Joseph Stalin, the party's General Secretary, outmaneuvered political opponents and ultimately gained control of the Communist Party by 1928. Initially, Stalin's leadership was widely accepted; his main political adversary Trotsky was forced into exile in 1929, and the doctrine of "socialism in one country" became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collectivization In The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
Collectivization in Ukraine, officially the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, was part of the policy of collectivization in the USSR and dekulakization that was pursued between 1928 and 1933 with the purpose to consolidate individual land and labour into collective farms called kolkhoz and to eliminate enemies of the working class. The idea of collective farms was seen by peasants as a revival of serfdom. In Ukraine this policy had a dramatic effect on the Ukrainian ethnic population and its culture as 86% of the population lived in rural settings. The forceful introduction of the policy of collectivization was one of the main causes of the Holodomor. In Ukraine collectivization had specific goals and outcomes. The Soviet policies related to collectivization have to be understood in the larger context of the social "revolution from above" that took place in the Soviet Union at the time.С. Кульчицький, Проблема колективізації сільсь� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English as the Bolshevists,. It signifies both Bolsheviks and adherents of Bolshevik policies. were a far-left, revolutionary Marxist faction founded by Vladimir Lenin that split with the Mensheviks from the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), a revolutionary socialist political party formed in 1898, at its Second Party Congress in 1903. After forming their own party in 1912, the Bolsheviks took power during the October Revolution in the Russian Republic in November 1917, overthrowing the Provisional Government of Alexander Kerensky, and became the only ruling party in the subsequent Soviet Russia and later the Soviet Union. They considered themselves the leaders of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia. Their beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Central Rada
The Central Council of Ukraine ( uk, Українська Центральна Рада, ) (also called the Tsentralna Rada or the Central Rada) was the All-Ukrainian council (soviet) that united deputies of soldiers, workers, and peasants deputies as well as few members of political, public, cultural and professional organizations of the Ukrainian People's Republic.Arkadii Zhukovsky. Central Rada'. Encyclopedia of Ukraine. After the All-Ukrainian National Congress (19–21 April 1917), the Council became the revolutionary parliament in the interbellum lasting until the Ukrainian-Soviet War. Unlike many other councils (soviets) in the Russian Republic, bolshevization of this soviet failed completely, causing members of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (Bolsheviks) in Ukraine, also known as Social-Democracy of Ukraine, to relocate to Kharkiv. Overview From its beginning the council directed the Ukrainian national movement and with its four Universals led the country from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish Language
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew (notably Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish is primarily written in the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, its worldwide peak was 11 million, with the number of speakers in the United States and Canada then totaling 150,000. Eighty-five percent of the approximately six million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hambu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasidic Judaism
Hasidism, sometimes spelled Chassidism, and also known as Hasidic Judaism (Ashkenazi Hebrew: חסידות ''Ḥăsīdus'', ; originally, "piety"), is a Judaism, Jewish religious group that arose as a spiritual revival movement in the territory of contemporary Western Ukraine during the 18th century, and spread rapidly throughout Eastern Europe. Today, most affiliates reside in Israel and the United States. Israel Ben Eliezer, the "Baal Shem Tov", is regarded as its founding father, and his disciples developed and disseminated it. Present-day Hasidism is a sub-group within Haredi Judaism and is noted for its religious conservatism and social seclusion. Its members adhere closely both to Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jewish practice – with the movement's own unique emphases – and the traditions of Eastern European Jews. Many of the latter, including various special styles of dress and the use of the Yiddish language, are nowadays associated almost exclusively with Hasidism. Hasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |