|
Main Turkmen Canal
The Main Turkmen Canal () was a large-scale irrigation project in the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic. The canal was intended to transport water from the Amu Darya river to Krasnovodsk (now Türkmenbaşy), a city in Turkmenistan on the coast of the Caspian Sea. The canal was going to use the course of the ancient dry Uzboy River bed. History The building of canals and channels for irrigation in Turkmenistan began in the 1930s. In 1929, the Bassaga-Kerkinskiy Canal was completed at a length of 100 km. The development of the outlet design for the Amu Darya River began in 1932. The design was to bring water from the Amu Darya across Turkmenistan to the coast of the Caspian Sea to irrigate the Karakum Desert. The project was supported by Hydrologist V. Tsinzerling, who estimated the volume of water taken from the river to be around , which, according to estimations, should not have injured the economy of Uzbekistan or the ecology of the Aral Sea. It was intended to fill Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamp Of USSR 1656
Stamp or Stamps or Stamping may refer to: Official documents and related impressions * Postage stamp, used to indicate prepayment of fees for public mail * Ration stamp, indicating the right to rationed goods * Revenue stamp, used on documents to indicate payment of tax * Rubber stamp, device used to apply inked markings to objects ** Passport stamp, a rubber stamp inked impression received in one's passport upon entering or exiting a country ** National Park Passport Stamps * Food stamps, tickets used in the United States that indicate the right to benefits in the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program Collectibles * Trading stamp, a small paper stamp given to customers by merchants in loyalty programs that predate the modern loyalty card * Eki stamp, a free collectible rubber ink stamp found at many train stations in Japan Places * Stamp Creek, a stream in Georgia * Stamps, Arkansas People * Stamp or Apiwat Ueathavornsuk (born 1982), Thai singer-songwriter * Stamp (surna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
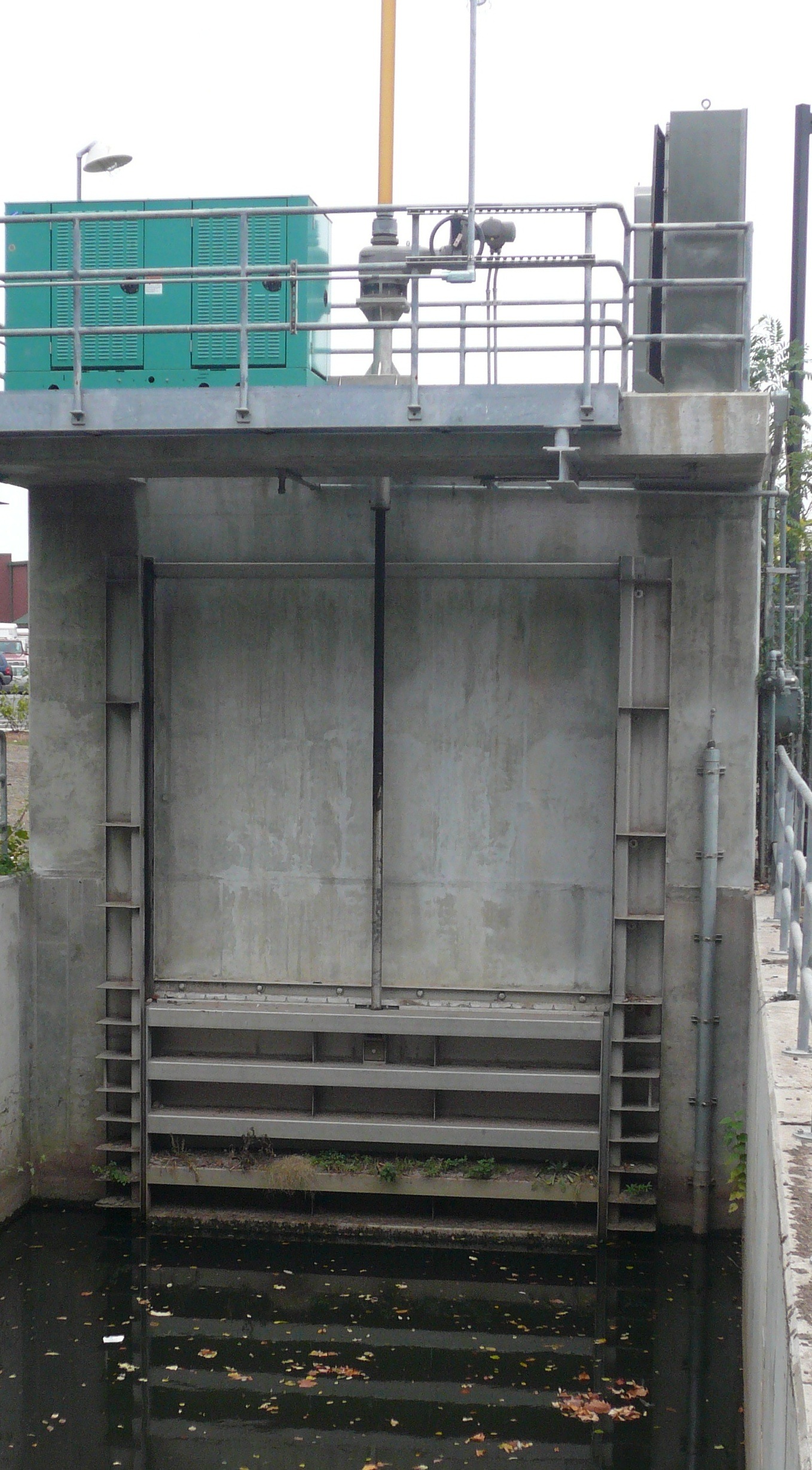
Sluices
Sluice ( ) is a word for a channel controlled at its head by a movable gate which is called a sluice gate. A sluice gate is traditionally a wood or metal barrier sliding in grooves that are set in the sides of the waterway and can be considered as a bottom opening in a wall. Sluice gates are one of the most common hydraulic structures in controlling flow rate and water level in open channels such as rivers and canals. They also could be used to measure the flow. A water channel containing a sluice gate forms a type of lock to manage the water flow and water level. It can also be an open channel which processes material, such as a River Sluice used in gold prospecting or fossicking. A mill race, leet, flume, penstock or lade is a sluice channeling water toward a water mill. The terms sluice, sluice gate, knife gate, and slide gate are used interchangeably in the water and wastewater control industry. They are also used in wastewater treatment plants and to recover minerals in minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Türkmenabat
Türkmenabat ( tk, Türkmenabat, Түркменабат), formerly and since medieval times Chardzhou, (russian: Чарджоу, ''Chardzhou''; tk, Çärjew, links=no, ) ( fa, چهارجوی 'čahârjuy', meaning 'four brooks') and in ancient times Āmul, is the second-largest city in Turkmenistan and the capital of Lebap Province. , it had a population of approximately 254,000 people (up from 161,000 in the 1989 census). From 1924 to 1927 it was briefly renamed Leninsk in honor of Vladimir Lenin. Etymology The former name of the city, Çärjew (also Chardzhou), is a Turkmen borrowing from the Persian ''čahârjuy'', which consists of two parts: ''čahâr'', meaning "four", and ''juy'', meaning "brook". This type of naming is also common in Iran, such as the village Se Juy (literally 'three brooks'). The current name of the city is simply a combining of '' Türkmen'' and the Persian suffix '' ābād (آباد)'', meaning "cultivated place" (village, city, region). Geography T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
Uzbekistan (, ) is the common English name for the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (Uzbek SSR; uz, Ўзбекистон Совет Социалистик Республикаси, Oʻzbekiston Sovet Sotsialistik Respublikasi, in Russian: Узбекская Советская Социалистическая Республика, Uzbekskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Respublika. It was also referred to as Uzbekistan SSR, Uzbek: Ўзбекистон ССР, O’zbekiston SSR; russian: Узбекская ССР, link=no, ''Uzbekskaya SSR'') and later, the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ўзбекистон Республикаси, Oʻzbekiston Respublikasi; Russian: Республика Узбекистан, Respublika Uzbekistan), that refers to the period of Uzbekistan from 1924 to 1991 as one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union. It was governed by the Uzbek branch of the Soviet Communist Party, the legal political party, from 1925 until 1990. From 1990 to 1991, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urgench
Urgench ( uz, Urganch//, ; russian: Ургенч, Urgench; fa, گرگانج, ''Gorgånch/Gorgānč/Gorgânc/Gurganj'') is a district-level city in western Uzbekistan. It is the capital of Xorazm Region. The estimated population of Urgench in 2021 was 145,000, an increase from 139,100 in 1999. It lies on the Amu Darya River and the Shavat canal. The city is situated west of Bukhara across the Kyzylkum Desert. The history of the city goes back to the second half of the 19th century. The city should not be confused with the similarly-named city of Konye-Urgench (also known as "Old Urgench" or "Gurgench") in Turkmenistan. The city of Old Urgench was left after the Amu Darya river changed its course in the 16th century, leaving the old town without water. New Urgench was founded by Russians in the second half of the 19th century at the site of a little trade station of the Khanate of Khiva. Modern Urgench is a Soviet-style city with cotton motifs adorning many objects, from street ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Ministers Of The Soviet Union
The Council of Ministers of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ( rus, Совет министров СССР, r=Sovet Ministrov SSSR, p=sɐˈvʲet mʲɪˈnʲistrəf ɛsɛsɛˈsɛr; sometimes abbreviated to ''Sovmin'' or referred to as the ''Soviet of Ministers''), was the ''de jure'' government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), comprising the main executive and administrative agency of the USSR from 1946 until 1991. During 1946 the Council of People's Commissars was reorganized as the Council of Ministers. Accordingly, the People's Commissariats were renamed as Ministries. The council issued declarations and instructions based on and in accordance with applicable laws, which had obligatory jurisdictional power in all republics of the Union. However, the most important decisions were made by joint declarations with the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Soviet Union (CPSU), which was ''de facto'' more powerful than the Council of Ministers. During 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow under atmospheric pressure, and can be thought of as artificial rivers. In most cases, a canal has a series of dams and locks that create reservoirs of low speed current flow. These reservoirs are referred to as ''slack water levels'', often just called ''levels''. A canal can be called a ''navigation canal'' when it parallels a natural river and shares part of the latter's discharges and drainage basin, and leverages its resources by building dams and locks to increase and lengthen its stretches of slack water levels while staying in its valley. A canal can cut across a drainage divide atop a ridge, generally requiring an external water source above the highest elevation. The best-known example of such a canal is the Panama Canal. Many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavator
Excavators are heavy construction equipment consisting of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The house sits atop an undercarriage with tracks or wheels. They are a natural progression from the steam shovels and often mistakenly called power shovels. All movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors. Due to the linear actuation of hydraulic cylinders, their mode of operation is fundamentally different from cable-operated excavators which use winches and steel ropes to accomplish the movements. Terminology Excavators are also called diggers, JCBs (a proprietary name, in an example of a generic trademark), mechanical shovels, or 360-degree excavators (sometimes abbreviated simply to "360"). Tracked excavators are sometimes called "trackhoes" by analogy to the backhoe. In the UK and Ireland, wheeled excavators are sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulldozer
A bulldozer or dozer (also called a crawler) is a large, motorized machine equipped with a metal blade to the front for pushing material: soil, sand, snow, rubble, or rock during construction work. It travels most commonly on continuous tracks, though specialized models riding on large off-road tires are also produced. Its most popular accessory is a ripper, a large hook-like device mounted singly or in multiples in the rear to loosen dense materials. Bulldozers are used heavily in large and small scale construction, road building, minings and quarrying, on farms, in heavy industry factories, and in military applications in both peace and wartime. The word "bulldozer" refers only to a motorized unit fitted with a blade designed for pushing. The word is sometimes used inaccurately for other heavy equipment such as a front-end loader designed for carrying rather than pushing material. Description Typically, bulldozers are large and powerful tracked heavy equipment. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dump Truck
A dump truck, known also as a dumping truck, dump trailer, dumper trailer, dump lorry or dumper lorry or a dumper for short, is used for transporting materials (such as dirt, gravel, or demolition waste) for construction as well as coal. A typical dump truck is equipped with an open-box bed, which is hinged at the rear and equipped with hydraulic rams to lift the front, allowing the material in the bed to be deposited ("dumped") on the ground behind the truck at the site of delivery. In the UK, Australia, South Africa and India the term applies to off-road construction plants only and the road vehicle is known as a tip lorry, tipper lorry (UK, India), tipper truck, tip truck, tip trailer or tipper trailer or simply a tipper (Australia, New Zealand, South Africa). History The dump truck is thought to have been first conceived in the farms of late 19th century western Europe. Thornycroft developed a steam dust-cart in 1896 with a tipper mechanism. The first motorized dump truck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of «Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry which is more than twice the size of Ukraine. It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average discharge (hydrology), discharge at delta – between and – and of drainage basin. It is widely regarded as the Rivers in Russia, national river of Russia. The hypothetical old Russian state, the Rus' Khaganate, arose along the Volga . Historically, the river served as an important meeting place of various Eurasian civilizations. The river flows in Russia through forests, Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilization, as well as fabric remnants dated back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |