|
Magnesium In Biology
Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems. Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA. Over 300 enzymes require the presence of magnesium ions for their catalytic action, including ''all'' enzymes utilizing or synthesizing ATP, or those that use other nucleotides to synthesize DNA and RNA. In plants, magnesium is necessary for synthesis of chlorophyll and photosynthesis. Function A balance of magnesium is vital to the well-being of all organisms. Magnesium is a relatively abundant ion in Earth's crust and mantle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat whereas the latter is defined as the emotional response to a real threat. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, somatic complaints, and rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight or flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of future threat including dread. People facing anxiety may withdraw fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dietary Supplements
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill (pharmacy), pill, capsule (pharmacy), capsule, tablet (pharmacy), tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order to increase the quantity of their consumption. The class of nutrient compounds includes vitamins, Dietary mineral, minerals, Dietary fiber, fiber, fatty acids, and amino acids. Dietary supplements can also contain substances that have not been confirmed as being essential to life, but are marketed as having a beneficial biological effect, such as plant pigments or polyphenols. Animals can also be a source of supplement ingredients, such as collagen from chickens or fish for example. These are also sold individually and in combination, and may be combined with nutrient ingredients. The European Commission has also established harmonized rules to help insure that food supplements are safe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustained-release
Modified-release dosage is a mechanism that (in contrast to immediate-release dose (biochemistry), dosage) delivers a drug with a delay after its route of administration, administration (delayed-release dosage) or for a prolonged period of time (extended-release [ER, XR, XL] dosage) or to a specific target in the body (targeted-release dosage).Pharmaceutics: Drug Delivery and Targeting p. 7-13 Sustained-release dosage forms are dosage forms designed to liberation (pharmacology), release (liberate) a drug at a predetermined rate in order to maintain a constant drug concentration for a specific period of time with minimum side effects. This can be achieved through a variety of formulations, including liposomes and drug-polymer conjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side-effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequences of the use of a drug. Developing drugs is a complicated process, because no two people are exactly the same, so even drugs that have virtually no side effects, might be difficult for some people. Also, it is difficult to make a drug that targets one part of the body but that does not affect other parts, the fact that increases the risk of side effects in the untargeted parts. Occasionally, drugs are prescribed or procedures performed specifically for their side effects; in that case, said side effect ceases to be a side effect and is now an intended effect. For instance, X-rays were historically (and are currently) used as an imaging technique; the discovery of their oncolytic capability led to their employ in radiotherapy (ablation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
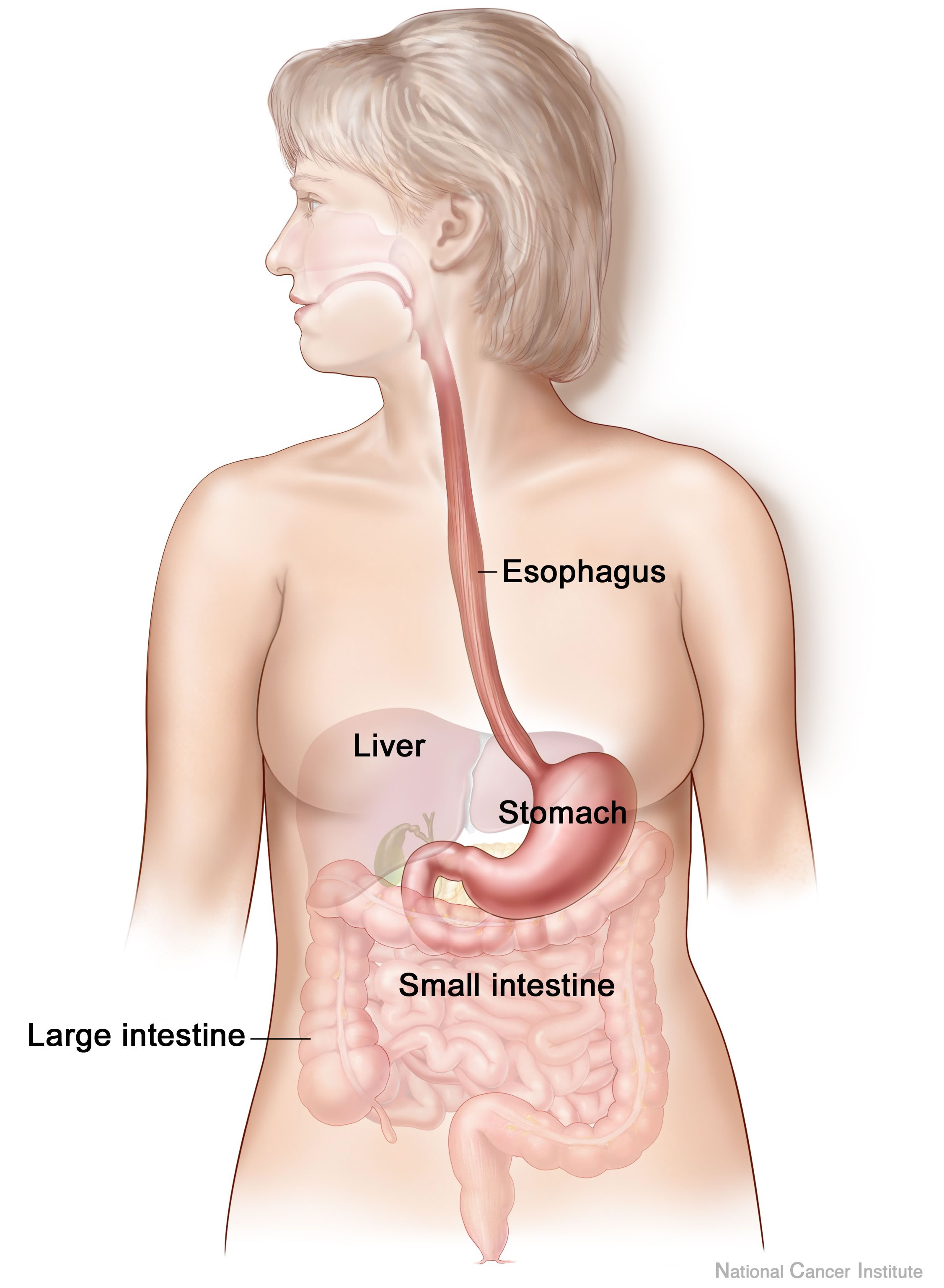
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycinate
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a ''Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by the French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelates
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate) ligands for the same metal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea are: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and persistent diarrhea (lasting more than two weeks, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypomagnesemia
Magnesium deficiency is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is a low level of magnesium in the body. It can result in multiple symptoms. Symptoms include tremor, poor coordination, muscle spasms, loss of appetite, personality changes, and nystagmus. Complications may include seizures or cardiac arrest such as from torsade de pointes. Those with low magnesium often have low potassium. Causes include low dietary intake, alcoholism, diarrhea, increased urinary loss, poor absorption from the intestines, and diabetes mellitus. A number of medications may also cause low magnesium, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and furosemide. The diagnosis is typically based on finding low blood magnesium levels (hypomagnesemia). Normal magnesium levels are between 0.6 and 1.1 mmol/L (1.46–2.68 mg/dL) with levels less than 0.6 mmol/L (1.46 mg/dL) defining hypomagnesemia. Specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes may be seen. Treatment is with magnesium either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |