|
Magicicada Tredecim
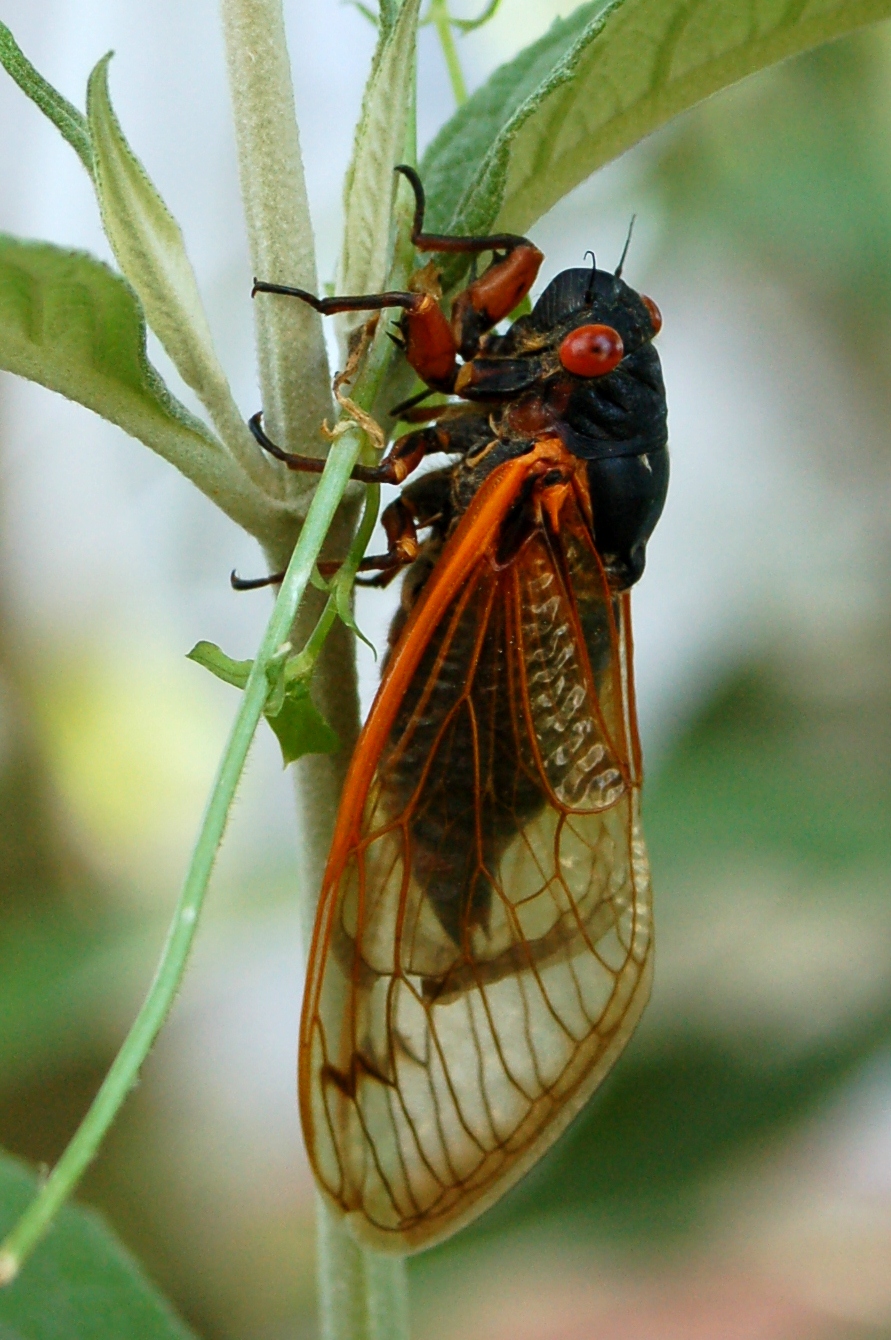
''Magicicada tredecim'' is a 13-year species of periodical cicada, closely related to the newly discovered 13-year species '' Magicicada neotredecim'', from which it differs in male song pitch, female song pitch preferences, abdomen color, and mitochondrial DNA. Both ''M. tredecim'' and ''M. neotredecim'' are closely related to the 17-year species '' M. septendecim'', which was identified by Linnaeus in 1758; these three species are often grouped together under the name decim periodical cicadas. Description Like other species included in its genus, ''M. tredicim'' has reddish eyes and wing veins. Its dorsal thorax is black. The underside of the abdomen of ''M. tredecim'' is light orange or caramel colored, lacking the dark bands seen in ''M. neotredicim'' and ''M. septendecim''. Life cycle Their median life cycle from egg to natural adult death is around thirteen years. However, their life cycle can range from nine years to seventeen years. Habitat, distribution, and cicada "br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodical Cicada
The term periodical cicada is commonly used to refer to any of the seven species of the genus ''Magicicada'' of eastern North America, the 13- and 17-year cicadas. They are called periodical because nearly all individuals in a local population are developmentally synchronized and emerge in the same year. Although they are sometimes called "locusts", this is a misnomer, as cicadas belong to the taxonomic order Hemiptera (true bugs), suborder Auchenorrhyncha, while locusts are grasshoppers belonging to the order Orthoptera. ''Magicicada'' belongs to the cicada tribe Lamotialnini, a group of genera with representatives in Australia, Africa, and Asia, as well as the Americas. ''Magicicada'' species spend around 99.5% of their long lives underground in an immature state called a nymph. While underground the nymphs feed on xylem fluids from the roots of deciduous forest trees in the eastern United States. In the spring of their 13th or 17th year mature cicada nymphs emerge between late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magicicada Neotredecim
''Magicicada neotredecim'' is the most recently discovered species of periodical cicada. Like all ''Magicicada'' species, ''M. neotredecim'' has reddish eyes and wing veins and a black dorsal thorax. It has a 13-year life cycle but seems to be most closely related to the 17-year species ''Magicicada septendecim''. Both species are distinguished by broad orange stripes on the abdomen and a unique high-pitched song said to resemble someone calling "weeeee-whoa" or "Pharaoh." They differ only in life cycle length. Another closely related 13-year species ''Magicicada tredecim'' differs very slightly from ''M. neotredecim'', and for many years two were considered one species with slight differences in abdomen color and mitochondrial DNA suggesting a zone of hybridization or introgression between 13-year and 17-year -decim populations. Then in 1998, scientists studying recordings of the chorus sound of Brood XIX recognized that the low-pitch component of the chorus contained two peak f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magicicada Septendecim
''Magicicada septendecim'', sometimes called the Pharaoh cicada or the 17-year locust, is native to Canada and the United States and is the largest and most northern species of periodical cicada with a 17-year lifecycle. Description Like other species included in ''Magicicada'', the insect's eyes and wing veins are reddish and its dorsal thorax is black. It is distinguished by broad orange stripes on its abdomen and a unique, high-pitched song said to resemble someone calling "weeeee-whoa" or "Pharaoh", features it shares with the newly discovered 13-year species ''Magicicada neotredecim''. Because of similarities between ''M. septendecim'' and the two closely related 13-year species ''M. neotredecim'' and '' M. tredecim'', the three species are often described together as " decim periodical cicadas." Life cycle Their median life cycle from egg to natural adult death is around seventeen years. However, their life cycle can range between thirteen and twenty-one years. Histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decim Periodical Cicadas
Decim periodical cicadas is a term used to group three closely related species of periodical cicadas: ''Magicicada septendecim'', ''Magicicada tredecim'', and ''Magicicada neotredecim''. ''M. septendecim'', first described by Carl Linnaeus, has a 17-year life cycle; the name ''septendecim'' is Latin for 17. ''M. tredecim'', first described in 1868, has a similar call and appearance but a 13-year life cycle; ''tredecim'' is Latin for 13. ''M. neotredecim'' (Latin for "new 13"), first described in 2000 by Marshall and Cooley in an article in the journal ''Evolution'', is a 13-year species but otherwise much more similar to ''M. septendecim'' than to ''M. tredecim'' as shown by studies of DNA and abdominal color variation by Chris Simon and colleagues in a companion article in the same journal issue. Description Like other species included in ''Magicicada'', decim periodical cicadas have synchronized development with a long larval period underground (13 or 17 years, depending on spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood XIX
Brood XIX (also known as The Great Southern Brood) is the largest (most widely distributed) brood of 13-year periodical cicadas, last seen in 2011 across a wide stretch of the southeastern United States. Periodical cicadas (''Magicicada spp.'') are often referred to as "17-year locusts" because most of the known distinct broods have a 17-year life cycle. Brood XIX is one of only three surviving broods with a 13-year cycle. It is also notable because it includes four different 13-year species, one of which was discovered in Brood XIX in 1998 by scientists listening to cicada songs. Position among other broods of cicadas Every 13 years, Brood XIX tunnels ''en masse'' to the surface of the ground, mates, lays eggs, and then dies off in several weeks. In 1907, entomologist C. L. Marlatt postulated the existence of 30 different broods of periodical cicadas: 17 distinct broods with a 17-year life cycle, to which he assigned Roman numerals I through XVII (with emerging years 1893 th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood XXII
Brood XXII (also known as The Baton Rouge Brood) is a brood of 13-year periodical cicadas, last seen in 2014 in a geographic region centered on Baton Rouge, Louisiana, as well as other locations in southeast Louisiana and southwest Mississippi. Periodical cicadas (''Magicicada spp.'') are often referred to as "17-year locusts" because most of the known distinct broods have a 17-year life cycle. Brood XXII is one of only three surviving broods with a 13-year cycle. The next emergence of The Baton Rouge Brood is expected in 2027. Position among other broods of cicadas Every 13 years, Brood XXII tunnels ''en masse'' to the surface of the ground, mates, lays eggs, and then dies off in several weeks. In 1907, the entomologist C. L. Marlatt postulated the existence of 30 different broods of periodical cicadas: 17 distinct broods with a 17-year life cycle, to which he assigned Roman numerals I through XVII (with emerging years 1893 through 1909); plus 13 broods with a 13-year cycle, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood XXIII
Brood XXIII (also known as the Mississippi Valley Brood) is a brood of 13-year periodical cicadas that last emerged in 2015 around the Mississippi River in the states of Louisiana, Mississippi, Arkansas, Tennessee, Missouri, Kentucky, and Illinois. The brood was also seen in Southwestern Indiana and Western Kentucky around the Ohio River, and as far north as Weldon Springs State Park in DeWitt County, Illinois. Brood XXIII is one of three extant periodical cicada broods with a 13-year life cycle, and thus is expected to be seen again in 2028. Lifecycle and history Every 13 years Brood XXIII cicadas tunnel ''en masse'' to the surface of the ground in late-April to early-June of emergence years to molt, mate, lay eggs, and subsequently die off over the course of a few weeks. After the eggs hatch, the nymphs burrow back underground to further develop and grow for the next 13 years before emerging again, completing the cycle. The extreme number of emerging cicadas is often give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamotialnini
Lamotialnini is a tribe of cicadas in the family Cicadidae. There are about 19 genera and at least 90 described species in Lamotialnini, occurring worldwide except South America. Genera These 19 genera belong to the tribe Lamotialnini: * '' Abricta'' Stål, 1866 * '' Abroma'' Stål, 1866 * ''Aleeta'' Moulds, 2003 * '' Allobroma'' Duffels, 2011 * '' Chrysolasia'' Moulds, 2003 * '' Hylora'' Boulard, 1971 * '' Lamotialna'' Boulard, 1976 * '' Lemuriana'' Distant, 1905 * ''Magicicada'' Davis, 1925 (periodical cicadas) * '' Monomatapa'' Distant, 1879 * '' Musimoia'' China, 1929 * '' Neomuda'' Distant, 1920 * '' Oudeboschia'' Distant, 1920 * '' Panka'' Distant, 1905 * '' Sundabroma'' Duffels, 2011 * '' Trismarcha'' Karsch, 1891 * '' Tryella'' Moulds, 2003 * '' Unduncus'' Duffels, 2011 * '' Viettealna'' Boulard, 1980 c g - MadagascarBoulard M (1980) Genres nouveaux, espèces nouvelles de cigales malgaches (Homoptera) ''Bulletin de la Société entomologique de France''. 85: 105-110. iet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiptera Of North America
Hemiptera (; ) is an order of insects, commonly called true bugs, comprising over 80,000 species within groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, assassin bugs, bed bugs, and shield bugs. They range in size from to around , and share a common arrangement of piercing-sucking mouthparts. The name "true bugs" is often limited to the suborder Heteroptera. Entomologists reserve the term ''bug'' for Hemiptera or Heteroptera,Gilbert Waldbauer. ''The Handy Bug Answer Book.'' Visible Ink, 1998p. 1. which does not include other arthropods or insects of other orders such as ants, bees, beetles, or butterflies. In some variations of English, all terrestrial arthropods (including non-insect arachnids, and myriapods) also fall under the colloquial understanding of ''bug''. Many insects with "bug" in their common name, especially in American English, belong to other orders; for example, the lovebug is a fly and the Maybug and ladybug are beetles. The term is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |