|
Madonna Di San Biagio
San Biagio is a church outside Montepulciano, Tuscany, central Italy. History The church, which was built between 1518 and 1540, an example of Renaissance Greek cross central plan, was designed by Antonio da Sangallo the Elder, who was inspired by the Basilica of Santa Maria delle Carceri in Prato, which had been designed years before by his brother Giuliano da Sangallo. The same plan, taken from Filippo Brunelleschi's works, was used for the original design by Bramante and Michelangelo for St. Peter's Basilica, as well as for the church of Santa Maria della Consolazione in Todi, of uncertain paternity. The late Renaissance building was constructed on the site of a pre-existing Palaeochristian pieve dedicated to St. Mary and subsequently to St. Blaise. In the early 16th century only remains existed of the pieve, including a wall with a fresco of ''Madonna with Child and St. Francis'', from a 14th-century Sienese painter. The project was supported by Pope Leo X, who had studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Cross
The Christian cross, with or without a figure of Christ included, is the main religious symbol of Christianity. A cross with a figure of Christ affixed to it is termed a ''crucifix'' and the figure is often referred to as the ''corpus'' (Latin for "body"). The term ''Greek cross'' designates a cross with arms of equal length, as in a plus sign, while the Latin cross designates a cross with an elongated descending arm. Numerous other variants have been developed during the medieval period In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a .... Christian crosses are used widely in churches, on top of church buildings, on bibles, in heraldry, in personal jewelry, on hilltops, and elsewhere as an attestation or other symbol of Christianity. Crosses are a prominent feature of Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Churches In Tuscany
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television * Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churches In Montepulciano
Church may refer to: Religion * Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities * Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination * Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship * Christian denomination, a Christian organization with distinct doctrine and practice * Christian Church, either the collective body of all Christian believers, or early Christianity Places United Kingdom * Church (Liverpool ward), a Liverpool City Council ward * Church (Reading ward), a Reading Borough Council ward * Church (Sefton ward), a Metropolitan Borough of Sefton ward * Church, Lancashire, England United States * Church, Iowa, an unincorporated community * Church Lake, a lake in Minnesota Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Church magazine'', a pastoral theology magazine published by the National Pastoral Life Center Fictional entities * Church (''Red vs. Blue''), a fictional character in the video web series ''Red vs. Blue'' * Churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Architecture In Tuscany
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. It occurred after the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages and was associated with great social change. In addition to the standard periodization, proponents of a "long Renaissance" may put its beginning in the 14th century and its end in the 17th century. The traditional view focuses more on the early modern aspects of the Renaissance and argues that it was a break from the past, but many historians today focus more on its medieval aspects and argue that it was an extension of the Middle Ages. However, the beginnings of the period – the early Renaissance of the 15th century and the Italian Proto-Renaissance from around 1250 or 1300 – overlap considerably with the Late Middle Ages, conventionally dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century Roman Catholic Church Buildings In Italy
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Early Modern Period Domes
Domes built in the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries relied primarily on empirical techniques and oral traditions rather than the architectural treatises of the time, but the study of dome structures changed radically due to developments in mathematics and the study of statics. Analytical approaches were developed and the ideal shape for a dome was debated, but these approaches were often considered too theoretical to be used in construction. The Gothic ribbed vault was displaced with a combination of dome and barrel vaults in the Renaissance style throughout the sixteenth century. The use of lantern towers, or timburios, which hid dome profiles on the exterior declined in Italy as the use of windowed drums beneath domes increased, which introduced new structural difficulties. The spread of domes in this style outside of Italy began with central Europe, although there was often a stylistic delay of a century or two. Use of the oval dome spread quickly through Italy, Spain, France, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travertine
Travertine ( ) is a form of terrestrial limestone deposited around mineral springs, especially hot springs. It often has a fibrous or concentric appearance and exists in white, tan, cream-colored, and even rusty varieties. It is formed by a process of rapid precipitation of calcium carbonate, often at the mouth of a hot spring or in a limestone cave. In the latter, it can form stalactites, stalagmites, and other speleothems. It is frequently used in Italy and elsewhere as a building material. Similar (but softer and extremely porous) deposits formed from ambient-temperature water are known as tufa. Definition Travertine is a sedimentary rock formed by the chemical precipitation of calcium carbonate minerals from fresh water, typically in springs, rivers, and lakes; that is, from surface and ground waters. In the broadest sense, travertine includes deposits in both hot and cold springs, including the porous, spongy rock known as tufa, and also the cave features known as speleot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oculus (architecture)
An oculus (; ) is a circular opening in the center of a dome or in a wall. Originating in antiquity, it is a feature of Byzantine and Neoclassical architecture. It is also known as an '' œil-de-boeuf'' from the French, or simply a "bull's-eye". History Classical The oculus was used by the Ancient Romans, one of the finest examples being that in the dome of the Pantheon. Open to the weather, it allows rain and air to enter and fall to the floor, where it is carried away through drains. Though the opening looks small, it actually has a diameter of , allowing it to light the building. Byzantine The oculus was widely used in the architecture of the Byzantine Empire. It was applied to buildings in Syria in the 5th and 6th centuries and again in the 10th century. In Constantinople's Myrelaion Church (c. 920), there are two oculi above the stringcourse on both lateral facades. Renaissance Early examples of the oculus in Renaissance architecture can be seen in Florence Cathedral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds. A pediment is sometimes the top element of a portico. For symmetric designs, it provides a center point and is often used to add grandness to entrances. The tympanum, the triangular area within the pediment, is often decorated with a pedimental sculpture which may be freestanding or a relief sculpture. The tympanum may hold an inscription, or in modern times, a clock face. Pediments are found in ancient Greek architecture as early as 600 BC (e.g. the archaic Temple of Artemis). Variations of the pediment occur in later architectural styles such as Classical, Neoclassical and Baroque. Gable roofs were common in ancient Greek temples with a low pitch (angle of 12.5° to 16°). History The pediment is found in classical Greek temples, Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metope (architecture)
In classical architecture, a metope (μετόπη) is a rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric order, Doric frieze, which is a decorative band of alternating triglyphs and metopes above the architrave of a building of the Doric order. Metopes often had painted or sculptural decoration; the most famous example are the 92 metopes of the Parthenon marbles some of which depict the battle between the Centaurs and the Lapiths. The painting on most metopes has been lost, but sufficient traces remain to allow a close idea of their original appearance. In terms of structure, metopes may be carved from a single block with a triglyph (or triglyphs), or they may be cut separately and slide into slots in the triglyph blocks as at the Temple of Aphaea. Sometimes the metopes and friezes were cut from different stone, so as to provide color contrast. Although they tend to be close to square in shape, some metopes are noticeably larger in heigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
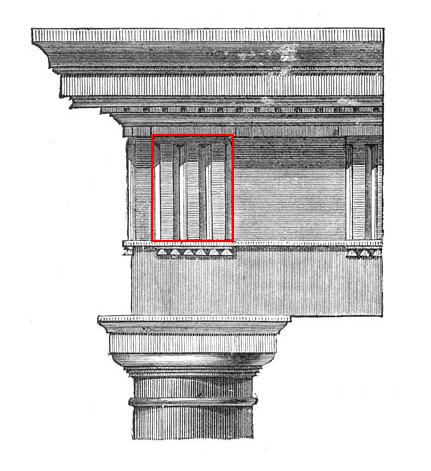
Triglyphs
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)