|
Madison Parish, Louisiana
Madison Parish (French: ''Paroisse de Madison'') is a parish located on the northeastern border of the U.S. state of Louisiana, in the delta lowlands along the Mississippi River. As of the 2010 census, the population was 12,093. Its parish seat is Tallulah. The parish was formed in 1839. With a history of cotton plantations and pecan farms, the parish economy continues to be primarily agricultural. It has a majority African-American population. For years a ferry connected Delta, Louisiana (and traffic from the parish) to Vicksburg, Mississippi. The Vicksburg Bridge now carries U.S. Route 80 and Interstate 20 across the river into Madison Parish. History Prehistory Madison Parish was the home to many succeeding Native American groups in the thousands of years before European settlement. Peoples of the Marksville culture, Troyville culture, Coles Creek culture and Plaquemine culture built villages and earthwork mound complexes throughout the area. Notable examples incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana Parishes
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is bordered by the state of Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, Mississippi to the east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. A large part of its eastern boundary is demarcated by the Mississippi River. Louisiana is the only U.S. state with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are equivalent to counties, making it one of only two U.S. states not subdivided into counties (the other being Alaska and its boroughs). The state's capital is Baton Rouge, and its largest city is New Orleans, with a population of roughly 383,000 people. Some Louisiana urban environments have a multicultural, multilingual heritage, being so strongly influenced by a mixture of 18th century Louisiana French, Dominican Creole, Spanish, French Canadian, Acadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
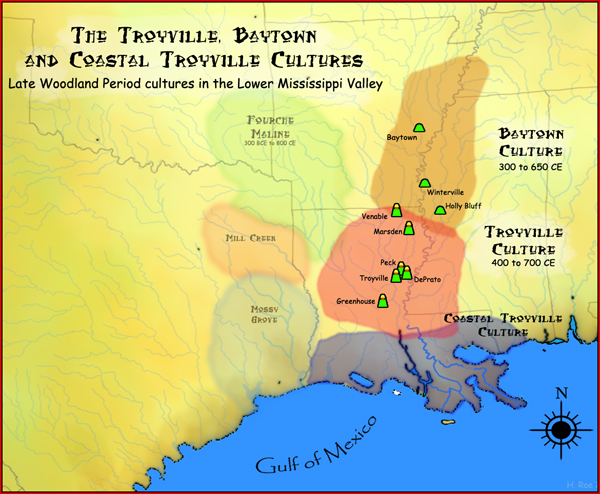
Troyville Culture
The Troyville culture is an archaeological culture in areas of Louisiana and Arkansas in the Lower Mississippi valley in the Southeastern Woodlands. It was a Baytown Period culture and lasted from 400 to 700 CE during the Late Woodland period. It was contemporaneous with the Coastal Troyville and Baytown cultures (all three had evolved from the Marksville Hopewellian peoples) and was succeeded by the Coles Creek culture Coles Creek culture is a Late Woodland archaeological culture in the Lower Mississippi valley in the Southeastern Woodlands. It followed the Troyville culture. The period marks a significant change in the cultural history of the area. Population .... Where the Baytown peoples built dispersed settlements, the Troyville people instead continued building major earthwork centers. Subsistence The Troyville-Coles Creek people lived on gathered wild plants and local domesticates, and maize was of only minor importance. Acorns, persimmons, palmetto, maygrass, and squ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John D
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy comprised U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky and Missouri also declared secession and had full representation in the Confederate Congress, though their territory was largely controlled by Union forces. The Confederacy was formed on February 8, 1861, by seven slave states: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. All seven were in the Deep South region of the United States, whose economy was heavily dependent upon agriculture—particularly cotton—and a plantation system that relied upon enslave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilization, as well as fabric remnants dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia (U
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are shaped by the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Chesapeake Bay, which provide habitat for much of its flora and fauna. The capital of the Commonwealth is Richmond; Virginia Beach is the most-populous city, and Fairfax County is the most-populous political subdivision. The Commonwealth's population was over 8.65million, with 36% of them living in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The area's history begins with several indigenous groups, including the Powhatan. In 1607, the London Company established the Colony of Virginia as the first permanent English colony in the New World. Virginia's state nickname, the Old Dominion, is a reference to this status. Slave labor and land acquired from displaced native tribes fueled the growing p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natchez Language
The Natchez language is the ancestral language of the Natchez people who historically inhabited Mississippi and Louisiana, and who now mostly live among the Muscogee and Cherokee peoples in Oklahoma. The language is considered to be either unrelated to other indigenous languages of the Americas or distantly related to the Muskogean languages. The phonology of Natchez is atypical in having voicing distinction in its sonorants but not in its obstruents; it also has a wide range of morphophonemic processes. Morphologically, it has complex verbal inflection and a relatively simple nominal inflection (the ergative case marks nouns in transitive clauses), and its syntax is characterized by active-stative alignment and subject-object-verb word order (or more accurately Agent-Object-Verb and Subject-Verb). Natchez storytellers used a specific register (sociolinguistics), register, "cannibal speech" to impersonate cannibals, a recurring character in Natchez oral literature. The Natchez chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natchez People
The Natchez (; Natchez pronunciation ) are a Native American people who originally lived in the Natchez Bluffs area in the Lower Mississippi Valley, near the present-day city of Natchez, Mississippi in the United States. They spoke a language with no known close relatives, although it may be very distantly related to the Muskogean languages of the Creek Confederacy.Geoffrey Kimball, "Natchez" in ''Native Languages of the Southeastern United States'', ed. Janine Scancarelli and Heath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taensa
The Taensa (also Taënsas, Tensas, Tensaw, and ''Grands Taensas'' in French) were a Native American people whose settlements at the time of European contact in the late 17th century were located in present-day Tensas Parish, Louisiana. The meaning of the name, which has the further spelling variants of ''Taenso'', ''Tinsas'', ''Tenza'' or ''Tinza'', ''Tahensa'' or ''Takensa'', and ''Tenisaw'', is unknown. It is believed to be an autonym. The Taensa should not be confused with the Avoyel (or Avoyelles), known by the French as the ''petits Taensas'' (English: Little Taensa), who were mentioned in writings by explorer Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville in 1699. The Taensa are more closely related to the Natchez people and both are considered descendants of the late prehistoric Plaquemine culture. The Taensa migrated as a result of Chickasaw and Yazoo hostilities, first lower down the Mississippi River. In 1715, protected by the French, they migrated to lands near the now eponymously nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raffman Site
The Raffman site ( 16 MA 20 ) is an archaeological site located in Madison Parish, Louisiana and constructed between 700 and 1200 CE. It has components from the Tchefuncte culture and the Coles Creek culture, whose main period of occupation was during the Balmoral phase (1000-1100 CE) of the Tensas Basin and Natchez Bluffs chronology and which was virtually deserted by the end of the Preston phase (1100–1200 CE). Description The site is quite large with nine platform mounds arranged around a central plaza. The plaza is by , with Mounds A, B, C, D, E, and G closely crowded around it. Mounds H and I are located adjacent to Mound A just to the southeast of the plaza. Located on the southern boundary of the plaza is Mound A, the largest at the site. It is in height and by at its base. Chronology Testing of the site revealed Early Woodland period deposits from the Tchefuncte period (600 BCE to 200 CE) underlying the Coles Creek period mounds (700 to 1200 CE). After the Early Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
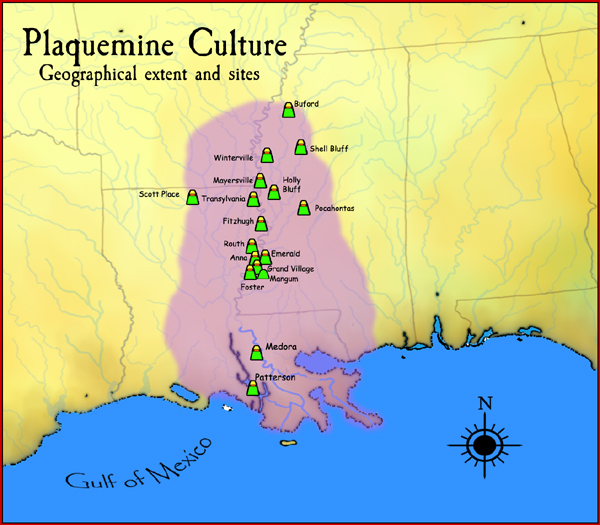
Fitzhugh Mounds
Fitzhugh Mounds is an archaeological site in Madison Parish, Louisiana from the Plaquemine culture, Plaquemine\Mississippian culture, Mississippian period dating to approximately 1200–1541 CE. It is the type site for the ''Fitzhugh Phase(1350-1500)'' of the Tensas Basin Plaquemine Mississippian chronology. Description The site was once an impressive seven-mound complex, with four of the platform mounds surrounding a central plaza. The site is first mentioned in E. G. Squier and Edwin Hamilton Davis, E. H. Davis' ''Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley'' in 1848. The largest mound at the site, at in height, was bulldozed and carted away to use as fill during the construction of Interstate 20#Louisiana, Interstate 20. Other of the mounds have been extensively plowed by local farmers and only two of the original seven mounds remain. Mound B is in height. Mound D serves as an active historic cemetery and is approximately in height. Location The site is located on La 602 so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |