|
Macular Hypoplasia
Macular hypoplasia (or foveal hypoplasia) is a rare medical condition involving the underdevelopment of the macula, a small area on the retina (the eye's internal surface) responsible for seeing in detail and sensing light. Macular hypoplasia is often associated with albinism. When the foveal area of the eye is compromised, visual clarity and color perception are reduced. Diagnosing is done by an ophthalmologist. The foveal area of the eye is located in the back of the eyeball. It is placed in front of the optic nerve and is responsible for light sensory and visual perceptiveness. Other diseases with foveal hypoplasia besides albinism include aniridia, retinopathy of prematurity, and Alport syndrome. Causes Macular hypoplasia occurs the most in people that have a diagnosis of albinism. There are four gene mutations that occur in albinism and are linked to macular hypoplasia. The four mutations can occur on the phenotypes of FH, PAX6, SLC38A8, and AHR. The most common gene mutat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
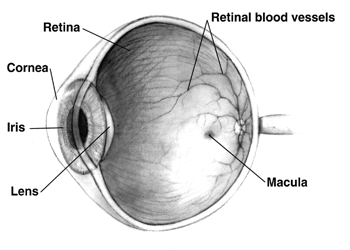
Human Eye Cross-sectional View Grayscale
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Color
Eye color is a polygenic phenotypic character determined by two distinct factors: the pigmentation of the eye's iris and the frequency-dependence of the scattering of light by the turbid medium in the stroma of the iris. In humans, the pigmentation of the iris varies from light brown to black, depending on the concentration of melanin in the iris pigment epithelium (located on the back of the iris), the melanin content within the iris stroma (located at the front of the iris), and the cellular density of the stroma. The appearance of blue, green, and hazel eyes results from the Tyndall scattering of light in the stroma, a phenomenon similar to that which accounts for the blueness of the sky called Rayleigh scattering. Neither blue nor green pigments are ever present in the human iris or ocular fluid. Eye color is thus an instance of structural color and varies depending on the lighting conditions, especially for lighter-colored eyes. The brightly colored eyes of many bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrective Lens
A corrective lens is a lens (i.e. a transmissive optical device) that is typically worn in front of the eye to improve daily vision. The most common use is to treat refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are worn on the face a short distance in front of the eye. Contact lenses are worn directly on the surface of the eye. Intraocular lenses are surgically implanted most commonly after cataract removal but can be used for purely refractive purposes. Prescription of corrective lenses Corrective lenses are typically prescribed by an ophthalmologist or an optometrist. The prescription consists of all the specifications necessary to make the lens. Prescriptions typically include the power specifications of each lens (for each eye). Strengths are generally prescribed in quarter-diopter steps (0.25 D) because most people cannot generally distinguish between smaller increments (e.g., eighth-diopter steps / 0.125 D). The use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy is therapy using pharmaceutical drugs, as distinguished from therapy using surgery (surgical therapy), radiation (radiation therapy), movement ( physical therapy), or other modes. Among physicians, sometimes the term ''medical therapy'' refers specifically to pharmacotherapy as opposed to surgical or other therapy; for example, in oncology, medical oncology is thus distinguished from surgical oncology. Pharmacists are experts in pharmacotherapy and are responsible for ensuring the safe, appropriate, and economical use of pharmaceutical drugs. The skills required to function as a pharmacist require knowledge, training and experience in biomedical, pharmaceutical and clinical sciences. Pharmacology is the science that aims to continually improve pharmacotherapy. The pharmaceutical industry and academia use basic science, applied science, and translational science to create new pharmaceutical drugs. As pharmacotherapy specialists and pharmacists have responsibil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinopathy
Retinopathy is any damage to the retina of the eyes, which may cause vision impairment. Retinopathy often refers to retinal vascular disease, or damage to the retina caused by abnormal blood flow. Age-related macular degeneration is technically included under the umbrella term retinopathy but is often discussed as a separate entity. Retinopathy, or retinal vascular disease, can be broadly categorized into proliferative and non-proliferative types. Frequently, retinopathy is an ocular manifestation of systemic disease as seen in diabetes or hypertension. Diabetes is the most common cause of retinopathy in the U.S. as of 2008. Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in working-aged people. It accounts for about 5% of blindness worldwide and is designated a priority eye disease by the World Health Organization. Signs and symptoms Many people often do not have symptoms until very late in their disease course. Patients often become symptomatic when there is irreversible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual hallucinations may also occur. Macular degeneration typically occurs in older people. Genetic factors and smoking also play a role. It is due to damage to the macula of the retina. Diagnosis is by a complete eye exam. The severity is divided into early, intermediate, and late types. The late type is additionally divided into "dry" and "wet" forms with the dry form making up 90% of cases. The difference between the two forms is the change of macula. Those with dry form AMD have drusen, ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medication. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Eye Syndrome
Dry eye syndrome (DES), also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS), is the condition of having dry eyes. Other associated symptoms include irritation, redness, discharge, and easily fatigued eyes. Blurred vision may also occur. Symptoms range from mild and occasional to severe and continuous. Scarring of the cornea may occur in untreated cases. Dry eye occurs when either the eye does not produce enough tears or when the tears evaporate too quickly. This can result from contact lens use, meibomian gland dysfunction, pregnancy, Sjögren syndrome, vitamin A deficiency, omega-3 fatty acid deficiency, LASIK surgery, and certain medications such as antihistamines, some blood pressure medication, hormone replacement therapy, and antidepressants. Chronic conjunctivitis such as from tobacco smoke exposure or infection may also lead to the condition. Diagnosis is mostly based on the symptoms, though a number of other tests may be used. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimally Invasive Procedure
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as ''open surgery''. Incisions made during open surgery can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. Advancements in medical technologies have enabled the development and regular use of minimally invasive procedures. For example, endovascular aneurysm repair, a minimally invasive surgery, has become the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in the US as of 2003. The procedure involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery. Interventional radiologists were the forerunners of minimally invasive procedures. Using imaging techniques, radiologists wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that uses low-coherence light to capture micrometer-resolution, two- and three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). It is used for medical imaging and industrial nondestructive testing (NDT). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution. Depending on the properties of the light source ( superluminescent diodes, ultrashort pulsed lasers, and supercontinuum lasers have been employed), optical coherence tomography has achieved sub-micrometer resolution (with very wide-spectrum sources emitting over a ~100 nm wavelength range). Optical coherence tomography is one of a class of optical tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescein Angiography
Fluorescein angiography (FA), fluorescent angiography (FAG), or fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) is a technique for examining the circulation of the retina and choroid (parts of the fundus) using a fluorescent dye and a specialized camera. Sodium fluorescein is added into the systemic circulation, the retina is illuminated with blue light at a wavelength of 490 nanometers, and an angiogram is obtained by photographing the fluorescent green light that is emitted by the dye. The fluorescein is administered intravenously in intravenous fluorescein angiography (IVFA) and orally in oral fluorescein angiography (OFA). The test is a dye tracing method. The fluorescein dye also reappears in the patient urine, causing the urine to appear darker, and sometimes orange. It can also cause discolouration of the saliva. Fluorescein angiography is one of several health care applications of this dye, all of which have a risk of severe adverse effects. See fluorescein safety in health care a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes". In normal eyesight, while the head rotates about an axis, distant visual images are sustained by rotating eyes in the opposite direction of the respective axis. The semicircular canals in the vestibule of the ear sense angular acceleration, and send signals to the nuclei for eye movement in the brain. From here, a signal is relayed to the extraocular muscles to allow one's gaze to fix on an object as the head moves. Nystagmus occurs when the semicircular canals are stimulated (e.g., by means of the caloric test, or by disease) while the head is stationary. The direction of ocular movement is related to the semicircular canal that is being stimulated. There are two key form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

..jpg)