|
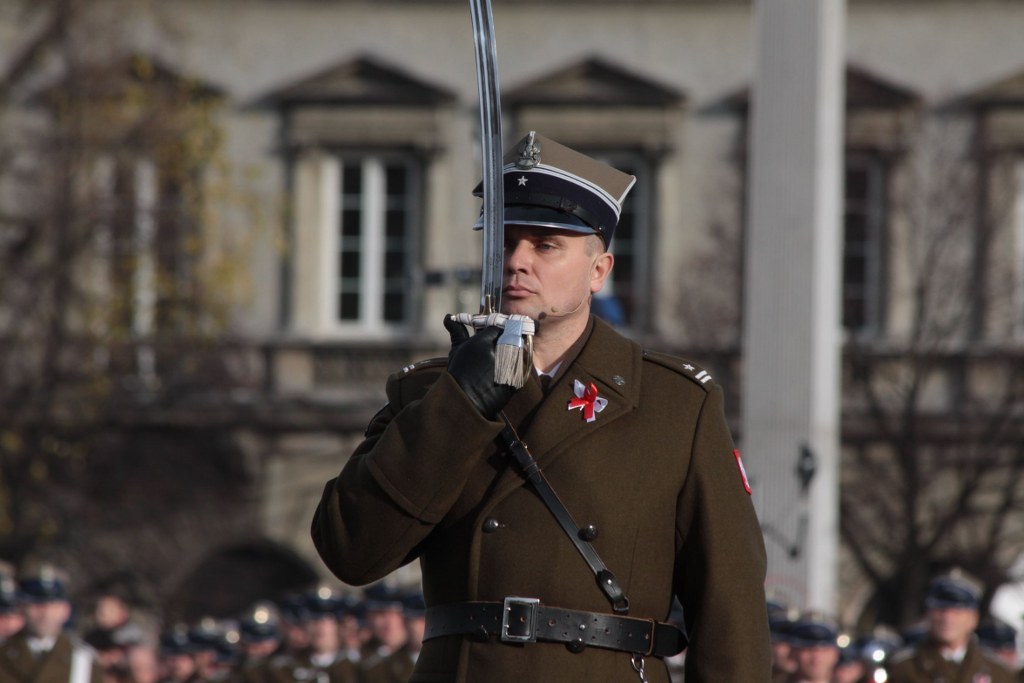
Mace-bearer
{{Short description, Royal court official with a ceremonial or real mace A mace-bearer, or macebearer, is a person who carries a mace, either a real weapon or ceremonial. Armed When the mace was still in actual use as a weapon, it was deemed fit for close-protection, and hence a mace-bearer could be a bodyguard. Thus in French and Dutch, a ''massier'' (armed with a ''masse d'armes'' 'weapon-mace') could be a member of a formally so-styled guard corps, as in the court of the Dukes of Brabant. In Spain, a macero were originally an armed guard protecting the King of Castile; they were called ''macero'' due to the weapon they wielded, a ''maza'' (i.e., a mace). Otherwise, a normally more domestic servant could double (arming trusted household staff was not unusual) as macebearer, as in the case of the prophet Mohammed's first muezzin, Bilal ibn Ribah Ceremonial As for ceremonial maces, which symbolise the power or status of a monarch, institution or high dignitary, the duty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swordbearer (ceremonial)
{{Short description, Royal court official with a ceremonial or real mace A mace-bearer, or macebearer, is a person who carries a mace, either a real weapon or ceremonial. Armed When the mace was still in actual use as a weapon, it was deemed fit for close-protection, and hence a mace-bearer could be a bodyguard. Thus in French and Dutch, a ''massier'' (armed with a ''masse d'armes'' 'weapon-mace') could be a member of a formally so-styled guard corps, as in the court of the Dukes of Brabant. In Spain, a macero were originally an armed guard protecting the King of Castile; they were called ''macero'' due to the weapon they wielded, a ''maza'' (i.e., a mace). Otherwise, a normally more domestic servant could double (arming trusted household staff was not unusual) as macebearer, as in the case of the prophet Mohammed's first muezzin, Bilal ibn Ribah Ceremonial As for ceremonial maces, which symbolise the power or status of a monarch, institution or high dignitary, the duty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceremonial Mace
A ceremonial mace is a highly ornamented staff of metal or wood, carried before a sovereign or other high officials in civic ceremonies by a mace-bearer, intended to represent the official's authority. The mace, as used today, derives from the original mace used as a weapon. Processions often feature maces, as on parliamentary or formal academic occasions. History Ancient Near East Ceremonial maces originated in the Ancient Near East, where they were used as symbols of rank and authority across the region during the late Stone Age, Bronze Age, and early Iron Age. Among the oldest known ceremonial maceheads are the Ancient Egyptian Scorpion Macehead and Narmer Macehead; both are elaborately engraved with royal scenes, although their precise role and symbolism are obscure. In later Mesopotamian art, the mace is more clearly associated with authority; by the Old Babylonian period the most common figure on cylinder seals (a type of seal used to authenticate clay documents) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceremonial Mace
A ceremonial mace is a highly ornamented staff of metal or wood, carried before a sovereign or other high officials in civic ceremonies by a mace-bearer, intended to represent the official's authority. The mace, as used today, derives from the original mace used as a weapon. Processions often feature maces, as on parliamentary or formal academic occasions. History Ancient Near East Ceremonial maces originated in the Ancient Near East, where they were used as symbols of rank and authority across the region during the late Stone Age, Bronze Age, and early Iron Age. Among the oldest known ceremonial maceheads are the Ancient Egyptian Scorpion Macehead and Narmer Macehead; both are elaborately engraved with royal scenes, although their precise role and symbolism are obscure. In later Mesopotamian art, the mace is more clearly associated with authority; by the Old Babylonian period the most common figure on cylinder seals (a type of seal used to authenticate clay documents) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mace (bludgeon)
A mace is a blunt weapon, a type of club or virge that uses a heavy head on the end of a handle to deliver powerful strikes. A mace typically consists of a strong, heavy, wooden or metal shaft, often reinforced with metal, featuring a head made of stone, bone, copper, bronze, iron, or steel. The head of a military mace can be shaped with flanges or knobs to allow greater penetration of plate armour. The length of maces can vary considerably. The maces of foot soldiers were usually quite short (two or three feet, or sixty to ninety centimetres). The maces of cavalrymen were longer and thus better suited for blows delivered from horseback. Two-handed maces could be even larger. Maces are rarely used today for actual combat, but many government bodies (for instance, the British House of Commons and the U.S. Congress), universities and other institutions have ceremonial maces and continue to display them as symbols of authority. They are often paraded in academic, parliamentary or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mace (bludgeon)
A mace is a blunt weapon, a type of club or virge that uses a heavy head on the end of a handle to deliver powerful strikes. A mace typically consists of a strong, heavy, wooden or metal shaft, often reinforced with metal, featuring a head made of stone, bone, copper, bronze, iron, or steel. The head of a military mace can be shaped with flanges or knobs to allow greater penetration of plate armour. The length of maces can vary considerably. The maces of foot soldiers were usually quite short (two or three feet, or sixty to ninety centimetres). The maces of cavalrymen were longer and thus better suited for blows delivered from horseback. Two-handed maces could be even larger. Maces are rarely used today for actual combat, but many government bodies (for instance, the British House of Commons and the U.S. Congress), universities and other institutions have ceremonial maces and continue to display them as symbols of authority. They are often paraded in academic, parliamentary or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodyguard
A bodyguard (or close protection officer/operative) is a type of security guard, government law enforcement officer, or servicemember who protects a person or a group of people — usually witnesses, high-ranking public officials or officers, wealthy people, and celebrities — from danger: generally theft, assault, kidnapping, assassination, harassment, loss of confidential information, threats, or other criminal offences. The personnel team that protects a VIP is often referred to as the VIP's security detail. Most important public figures, such as heads of state, heads of government, and governors are protected by several bodyguards or by a team of bodyguards from a government agency, security forces, or police forces (e.g., in the United States, the Secret Service or the Diplomatic Security Service of the State Department). In most countries where the head of state is also their military leader, the leader's bodyguards have traditionally been royal guards, republican guar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedel
The bedel (from medieval Latin ''pedellus'' or ''bidellus'', occasionally ''bidellus generalis'', from Old High German ''bital'', ''pital'', "the one who invites, calls"; cognate with beadle) was, and is to some extent still, an administrative official at universities in several European countries, and often had a policiary function at the time when universities had their own jurisdiction over students. History of the bedel The office can be traced back as far as 1245, and originated in Paris. In French universities, the position was frequently open to purchase. In the medieval English universities in Oxford and Cambridge, the ''bedel'' was an administrative assistant of the chancellor and the proctors. The bedel was, among other things, to collect fines and fees, keep rolls of scholars with the license to teach, and participate in ceremonial dress in academic processions and on other similar occasions. There were six bedels at Oxford, one superior and one inferior bedel for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Augé
Paul Augé (4 July 1881, L'Isle-Jourdain – 23 July 1951, Cabourg) was a 20th-century French publisher, romanist and lexicographer. In 1920, Paul Augé took over the publishing of the dictionary and lexicum of the Éditions Larousse from his father Claude Augé Claude Augé (; 31 October 1854 – 22 July 1924) was a French pedagogue, publisher, and lexicographer. Biography First a school master, he married a grand niece of Pierre Larousse's wife, joined the Librairie Larousse as bookkeeper in 1885 an .... Editions * from 1927 to 1933: édition du deuxième grand dictionnaire du XXe, ''Larousse du XX'', six volumes édition * 1936: ''Grand Mémento'' * 1948: ''Nouveau Larousse universel'' References External links {{DEFAULTSORT:Auge, Paul French publishers (people) French lexicographers French encyclopedists 1881 births People from Gers 1951 deaths 20th-century lexicographers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Augé
Claude Augé (; 31 October 1854 – 22 July 1924) was a French pedagogue, publisher, and lexicographer. Biography First a school master, he married a grand niece of Pierre Larousse's wife, joined the Librairie Larousse as bookkeeper in 1885 and became quickly one of the directors. Until his death, he continued to pursue the work of the famous lexicographer. In 1920, while continuing his work, he chose to be replaced in his editorial functions, by his son Paul Augé. Personal works *From 1891 to 1895: ''Cours d'histoire de France'' (levels: first grade, elementary and middle course), in collaboration with Maxime Petit. Works that have been republished many times until 1923. *From 1890 to 1912 : ''Cours de grammaire'' in 4 volumes (from preparatory courses to higher education): this brilliant collection trained generations of French people (certificat d'étude;brevet élémentaire ; brevet supérieur) until the eve of World War II. * Around 1895: ''Le Livre de Musique''. Many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serjeant-at-arms
A serjeant-at-arms, or sergeant-at-arms, is an officer appointed by a deliberative body, usually a legislature, to keep order during its meetings. The word "serjeant" is derived from the Latin ''serviens'', which means "servant". Historically, serjeants-at-arms were armed men retained by English lords and monarchs, and the ceremonial maces which they are associated with were originally a type of weapon. Origins The term "sergeant" can be given two main definitions; the first being a military rank and the other a governmental role. Whereas technically the two roles were not mutually exclusive, they were very different in roles and duties. The soldier sergeant was a man of what would now be thought of as the 'middle class', fulfilling a junior role to the knight in the medieval hierarchy. Sergeants could fight either as heavy to light cavalry, or as well-trained professional infantry, either spearmen or crossbowmen. Most notable medieval mercenaries fell into the 'sergeant' class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceremonial Sword
A ceremonial weapon is an object used for ceremonial purposes to display power or authority. They are often used in parades and as part of dress uniforms. Although they are descended from weapons used in actual combat, they are not normally used as such. Their form and, especially, their finishing and decoration are typically designed to show status and power and to be an impressive sight, rather than for practicality as a weapon. Quite often, ceremonial weapons are constructed with precious metals or other materials that make them too delicate for combat use. With ceremonial swords, an example of this is that the sword may be poorly balanced. Historically, however, many ceremonial weapons were also capable of actual combat, most notably in the military. Maces, halberds, daggers and swords are the most common form of ceremonial weapons, but in theory almost any weapon can become ceremonial. The Sergeant at Arms in some parliaments carries a ceremonial mace. The Swiss Guard in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |