|
MacCready Gossamer Condor
The MacCready ''Gossamer Condor'' was the first human-powered aircraft capable of controlled and sustained flight; as such, it won the Kremer prize in 1977. Its design was led by Paul MacCready of AeroVironment, Inc. Design and development The Kremer Prize had been set up in 1959 by Henry Kremer, a British industrialist, and offered £50,000 in prize money to the first group that could fly a human-powered aircraft over a figure-eight course covering a total of one mile (1.6 kilometers). The course also included a ten-foot pole that the aircraft had to fly over at the start and at the end. Early attempts to build human-powered aircraft had focused on wooden designs, which proved too heavy. Very early attempts – notably the ' and ''Pedaliante'' – used catapult launches. In 1961, Southampton University's Man Powered Aircraft SUMPAC took to the air at Lasham Airfield on 9 November, piloted by Derek Piggott, achieving a maximum flight of 650 metres. One week later, on 16 N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Aircraft
An experimental aircraft is an aircraft intended for testing new aerospace technologies and design concepts. The term ''research aircraft'' or ''testbed aircraft'', by contrast, generally denotes aircraft modified to perform scientific studies, such as weather research or geophysical surveying, similar to a research vessel. United States The term "experimental aircraft" also has specific legal meaning in Australia, the United States and some other countries; usually used to refer to aircraft flown with an experimental certificate. In the United States, this also includes most homebuilt aircraft, many of which are based on conventional designs and hence are experimental only in name because of certain restrictions in operation. US Federal Aviation Administration. Retrieved 2018-01 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canard (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, a canard is a wing configuration in which a small forewing or foreplane is placed forward of the main wing of a fixed-wing aircraft or a weapon. The term "canard" may be used to describe the aircraft itself, the wing configuration, or the foreplane.. Canard wings are also extensively used in guided missiles and smart bombs. The term "canard" arose from the appearance of the Santos-Dumont 14-bis of 1906, which was said to be reminiscent of a duck (''canard'' in French) with its neck stretched out in flight. Despite the use of a canard surface on the first powered aeroplane, the Wright Flyer of 1903, canard designs were not built in quantity until the appearance of the Saab Viggen jet fighter in 1967. The aerodynamics of the canard configuration are complex and require careful analysis. Rather than use the conventional tailplane configuration found on most aircraft, an aircraft designer may adopt the canard configuration to reduce the main wing loading, to better ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Flight Of The Gossamer Condor
''The Flight of the Gossamer Condor'' is a 1978 American short documentary film directed by Ben Shedd, about the development of the Gossamer Condor, the first human-powered aircraft, by a team led by Paul MacCready. The Academy Film Archive preserved ''The Flight of the Gossamer Condor'' in 2007. Reception In the education magazine ''Media & Methods'', David Mallery called ''Flight of the Gossamer Condor'' "a film or extraordinary appeal", writing that "the Shedds' most subtle achievement - least flashy, most serving to their subject - is that we are thoroughly caught up in the work of the MacCready group, are intimately a part of their struggles, their determination, their energy." Mallery concludes "It's a joyous experience. I recommend it with special enthusiasm." ''The Flight of the Gossamer Condor'' won an Oscars at the 51st Academy Awards in 1979 for Documentary Short Subject. Cast * Bryan Allen as Himself - Final Pilot * Paul B. MacCready as Himself (as Paul MacCready ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacCready Gossamer Albatross
The ''Gossamer Albatross'' is a human-powered aircraft built by American aeronautical engineer Dr Paul B MacCready's company AeroVironment. On June 12, 1979, it completed a successful crossing of the English Channel to win the second Kremer prize worth £100,000 (). Design and development The aircraft was designed and built by a team led by Paul B. MacCready, a noted American aeronautics engineer, designer, and world soaring champion. ''Gossamer Albatross'' was his second human-powered aircraft, the first being the ''Gossamer Condor'', which had won the first Kremer prize on August 23, 1977, by completing a -long figure-eight course. The second Kremer challenge was then announced as a flight across the English Channel recalling Louis Blériot's crossing of 1909. The aircraft is of " canard" configuration, using a large horizontal stabilizer forward of the wing in a manner similar to the Wright brothers' successful ''Wright Flyer'' aircraft and powered using pedals to drive a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gossamer Condor
The MacCready ''Gossamer Condor'' was the first human-powered aircraft capable of controlled and sustained flight; as such, it won the Kremer prize in 1977. Its design was led by Paul MacCready of AeroVironment, Inc. Design and development The Kremer Prize had been set up in 1959 by Henry Kremer, a British industrialist, and offered £50,000 in prize money to the first group that could fly a human-powered aircraft over a figure-eight course covering a total of one mile (1.6 kilometers). The course also included a ten-foot pole that the aircraft had to fly over at the start and at the end. Early attempts to build human-powered aircraft had focused on wooden designs, which proved too heavy. Very early attempts – notably the ' and ''Pedaliante'' – used catapult launches. In 1961, Southampton University's Man Powered Aircraft SUMPAC took to the air at Lasham Airfield on 9 November, piloted by Derek Piggott, achieving a maximum flight of 650 metres. One week later, on 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
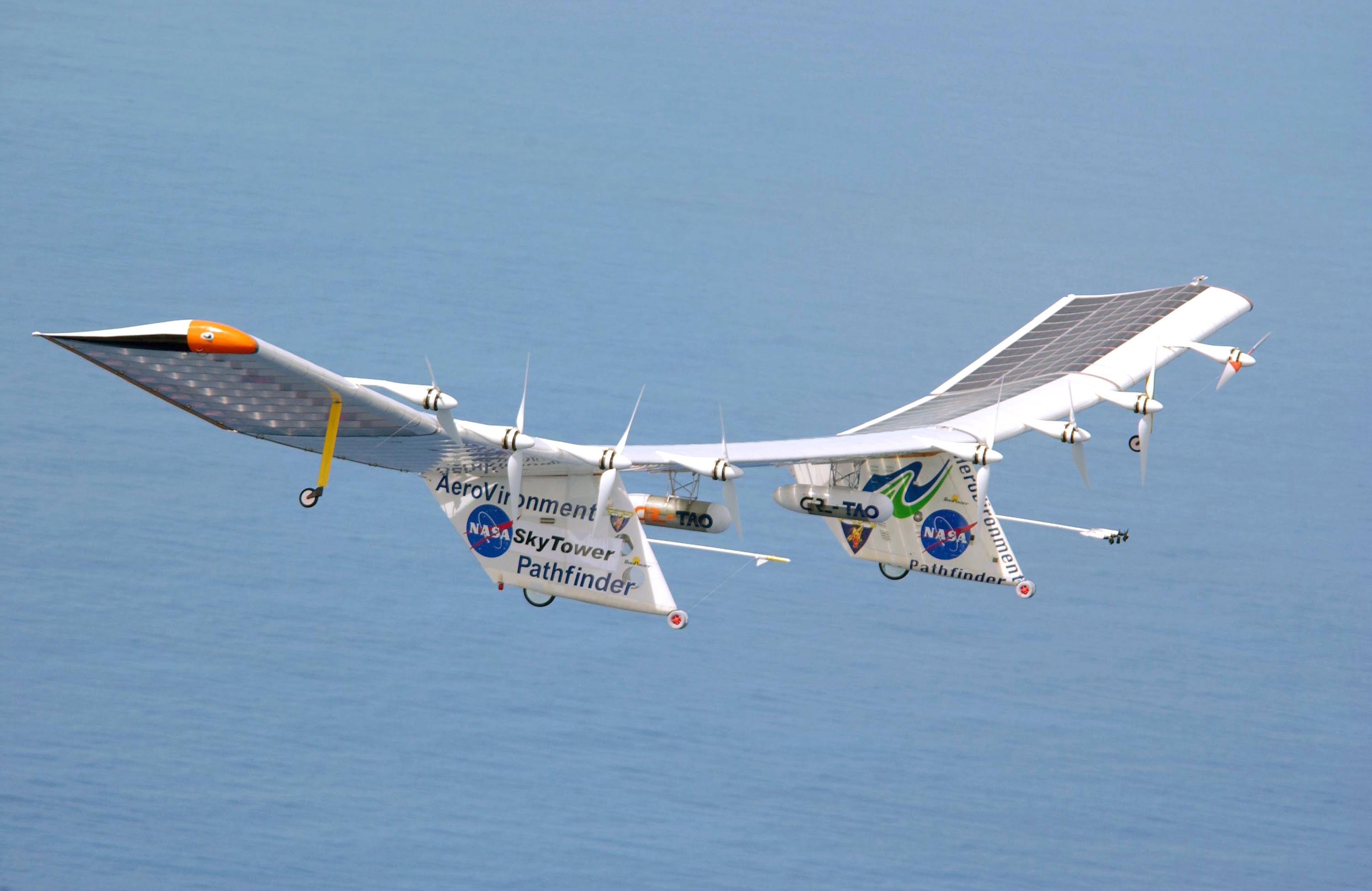
NASA Pathfinder
The NASA Pathfinder and NASA Pathfinder Plus were the first two aircraft developed as part of an evolutionary series of solar- and fuel-cell-system-powered unmanned aerial vehicles. AeroVironment, Inc. developed the vehicles under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program. They were built to develop the technologies that would allow long-term, high-altitude aircraft to serve as atmospheric satellites, to perform atmospheric research tasks as well as serve as communications platforms. They were developed further into the NASA Centurion and NASA Helios aircraft. Pathfinder AeroVironment initiated its development of full-scale solar-powered aircraft with the Gossamer Penguin and Solar Challenger vehicles in the late 1970s and early 1980s, following the pioneering work of Robert Boucher, who built the first solar-powered flying models in 1974. As part of the ERAST program, AeroVironment built four generations of long endurance unmanned aerial ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Challenger
The Solar Challenger was a solar-powered electric aircraft designed by Paul MacCready's AeroVironment. The aircraft was designed as an improvement on the Gossamer Penguin, which in turn was a solar-powered variant of the human-powered Gossamer Albatross. It was powered entirely by the photovoltaic cells on its wing and stabilizer, without even reserve batteries, and was the first such craft capable of long-distance flight. In 1981, it successfully completed a 163-mile (262 km) demonstration flight from France to England. History The Solar Challenger was designed by a team led by Paul MacCready as a more airworthy improvement on the Gossamer Penguin, directly incorporating lessons learned from flight testing the earlier aircraft.Solar Challenger - E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kanaal, "The Channel"; german: Ärmelkanal, "Sleeve Channel" ( French: ''la Manche;'' also called the British Channel or simply the Channel) is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world. It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some . The Channel was a key factor in Britain becoming a naval superpower and has been utilised by Britain as a natural def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Air And Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum of the Smithsonian Institution, also called the Air and Space Museum, is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States. Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, it opened its main building on the National Mall near L'Enfant Plaza in 1976. In 2018, the museum saw about 6.2 million visitors, making it the fifth-most-visited museum in the world, and the second-most-visited museum in the United States. In 2020, due to long closures and a drop in foreign tourism caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, museum attendance dropped to 267,000. The National Air and Space Museum is a center for research into the history and science of aviation and spaceflight, as well as planetary science and terrestrial geology and geophysics. Almost all spacecraft and aircraft on display are originals or the original backup craft. The museum contains the Apollo 11 Command Module ''Columbia'', the ''Friendship 7'' capsule which was flown by John Glenn, Charles Lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shafter, California
Shafter is a city in Kern County, California, United States. It is located west-northwest of Bakersfield. The population was 16,988 at the 2010 census, up from 12,736 at the 2000 census. The city is located along State Route 43. Suburbs of Shafter include Myricks Corner, North Shafter, Smith Corner, and Thomas Lane. History The city of Shafter began as a loading dock along the Santa Fe Railroad (former San Francisco and San Joaquin Valley Railroad) right-of-way. The community was named for General William Rufus Shafter who commanded US Forces in Cuba during the Spanish–American War. Property was sold beginning in 1914 and the city incorporated on January 11, 1938. The first post office opened in 1898, moved in 1902, closed in 1905. A new postal service started in 1914. Also of historical note, Shafter is home to Minter Field, which began operations in June 1941 and saw heavy use during World War II. Approximately 7,000 troops were stationed at the airstrip which hosted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minter Field
Minter may refer to: Places in the United States *Minter, Alabama, an unincorporated community *Minter Village, California, an unincorporated community *Minter City, Mississippi Minter City is an unincorporated community in Leflore County and Tallahatchie County, Mississippi. It is part of the Greenwood, Mississippi micropolitan area, and is within the Mississippi Delta. Mississippi Highway 8 intersects U.S. Route 49E ... * Minter, Washington State, Hendersen Bay's northwest shore, Carr Inlet, southern Salish Sea Other uses * Minter (surname) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
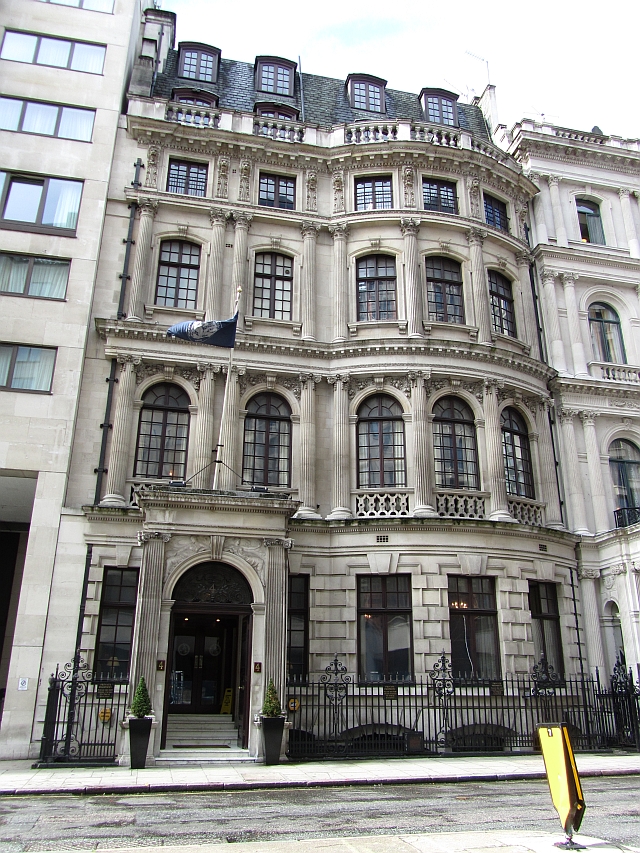
Royal Aeronautical Society
The Royal Aeronautical Society, also known as the RAeS, is a British multi-disciplinary professional institution dedicated to the global aerospace community. Founded in 1866, it is the oldest aeronautical society in the world. Members, Fellows, and Companions of the society can use the post-nominal letters MRAeS, FRAeS, or CRAeS, respectively. Function The objectives of The Royal Aeronautical Society include: to support and maintain high professional standards in aerospace disciplines; to provide a unique source of specialist information and a local forum for the exchange of ideas; and to exert influence in the interests of aerospace in the public and industrial arenas, including universities. The Royal Aeronautical Society is a worldwide society with an international network of 67 branches. Many practitioners of aerospace disciplines use the Society's designatory post-nominals such aFRAeS CRAeS, MRAeS, AMRAeS, and ARAeS (incorporating the former graduate grade, GradRAeS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(9256079273).jpg)