|
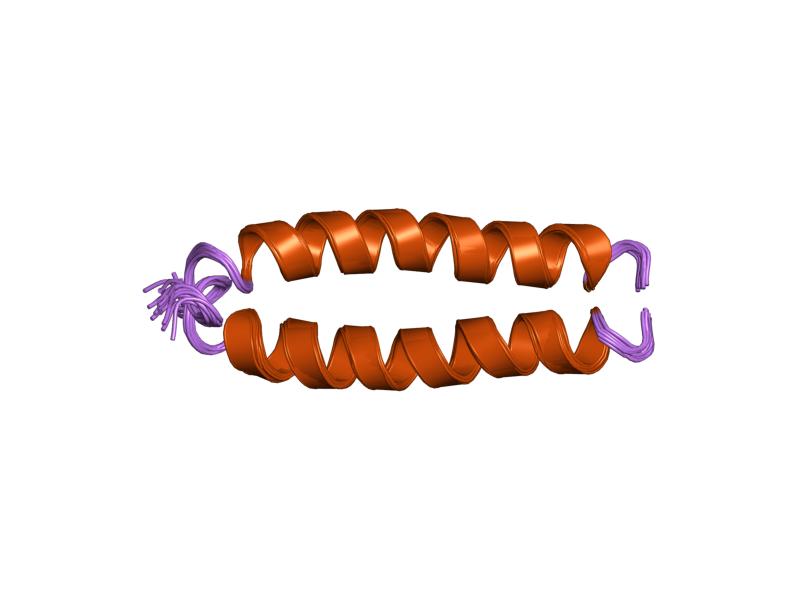
MYO15A
Myosin-XV is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYO15A'' gene. Gene Read-through transcript containing an upstream gene and this gene have been identified, but they are not thought to encode a fusion protein. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, but their full length sequences have not been determined. Function This gene encodes an unconventional myosin. This protein differs from other myosins in that it has a long N-terminal extension preceding the conserved motor domain. Studies in mice suggest that this protein is necessary for actin organization in the hair cells of the cochlea. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene have been associated with profound, congenital, neurosensory, nonsyndromic deafness. This gene is located within the Smith–Magenis syndrome Smith–Magenis Syndrome (SMS), also known as 17p- syndrome, is a microdeletion syndrome characterized by an abnormality in the short (p) arm of chromosome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsyndromic Deafness
Nonsyndromic deafness is hearing loss that is not associated with other signs and symptoms. In contrast, syndromic deafness involves hearing loss that occurs with abnormalities in other parts of the body. Genetic changes are related to the following types of nonsyndromic deafness. * DFNA: nonsyndromic deafness, autosomal dominant * DFNB: nonsyndromic deafness, autosomal recessive * DFNX: nonsyndromic deafness, X-linked * nonsyndromic deafness, mitochondrial Each type is numbered in the order in which it was described. For example, DFNA1 was the first described autosomal dominant type of nonsyndromic deafness. Mitochondrial nonsyndromic deafness involves changes to the small amount of DNA found in mitochondria, the energy-producing centers within cells. Most forms of nonsyndromic deafness are associated with permanent hearing loss caused by damage to structures in the inner ear. The inner ear consists of three parts: a snail-shaped structure called the cochlea that helps process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myosin
Myosins () are a superfamily of motor proteins best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are ATP-dependent and responsible for actin-based motility. The first myosin (M2) to be discovered was in 1864 by Wilhelm Kühne. Kühne had extracted a viscous protein from skeletal muscle that he held responsible for keeping the tension state in muscle. He called this protein ''myosin''. The term has been extended to include a group of similar ATPases found in the cells of both striated muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Following the discovery in 1973 of enzymes with myosin-like function in '' Acanthamoeba castellanii'', a global range of divergent myosin genes have been discovered throughout the realm of eukaryotes. Although myosin was originally thought to be restricted to muscle cells (hence '' myo-''(s) + '' -in''), there is no single "myosin"; rather it is a very large superfamily of genes whose p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjoined Gene
A conjoined gene (CG) is defined as a gene, which gives rise to transcripts by combining at least part of one exon from each of two or more distinct known (parent) genes which lie on the same chromosome, are in the same orientation, and often (95%) translate independently into different proteins. In some cases, the transcripts formed by CGs are translated to form chimeric or completely novel proteins. Several alternative names are used to address conjoined genes, including combined gene and complex gene, fusion gene, fusion protein, read-through transcript, co-transcribed genes, bridged genes, spanning genes, hybrid genes, locus-spanning transcripts, etc. At present, 800 CGs have been identified in the entire human genome by different research groups across the world including Prakash et al., Akiva et al., Parra et al., Kim et al., and in the 1% of the human genome in the ENCODE pilot project. 36% of all these CGs could be validated experimentally using RT-PCR and sequencing tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Protein
Fusion proteins or chimeric (kī-ˈmir-ik) proteins (literally, made of parts from different sources) are proteins created through the joining of two or more genes that originally coded for separate proteins. Translation of this ''fusion gene'' results in a single or multiple polypeptides with functional properties derived from each of the original proteins. ''Recombinant fusion proteins'' are created artificially by recombinant DNA technology for use in biological research or therapeutics. '' Chimeric'' or ''chimera'' usually designate hybrid proteins made of polypeptides having different functions or physico-chemical patterns. ''Chimeric mutant proteins'' occur naturally when a complex mutation, such as a chromosomal translocation, tandem duplication, or retrotransposition creates a novel coding sequence containing parts of the coding sequences from two different genes. Naturally occurring fusion proteins are commonly found in cancer cells, where they may function as oncoproteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different (alternative) mRNA strands. Consequently, the proteins translated from alternatively spliced mRNAs will contain differences in their amino acid sequence and, often, in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle movement, cell sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing, which is distributed along the partition separating the fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea. The name cochlea derives . Structure The cochlea (plural is cochleae) is a spiraled, hollow, conical chamber of bone, in which waves propagate from the base (near the middle ear and the oval window) to the apex (the top or center of the spiral). The spiral canal of the cochlea is a section of the bony labyrinth of the inner ear that is approximately 30 mm long and makes 2 turns about the modiolus. The cochlear structures include: * Three ''scalae'' or chambers: ** the vestibular duct or ''scala vestibuli'' (containing perilymph), which lies superior to the cochlear duct and abuts the oval window ** the ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |