|
MYL7
Atrial Light Chain-2 (ALC-2) also known as Myosin regulatory light chain 2, atrial isoform (MLC2a) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYL7'' gene. ALC-2 expression is restricted to cardiac muscle atria in healthy individuals, where it functions to modulate cardiac development and contractility. In human diseases, including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, ischemic cardiomyopathy and others, ALC-2 expression is altered. Structure Human ALC-2 protein has a molecular weight of 19.4 kDa and is composed of 175 amino acids. ALC-2 is an EF hand protein that binds to the neck region of alpha myosin heavy chain. ALC-2 and the ventricular isoform, VLC-2, share 59% homology, showing significant differences at their N-termini and at the regulatory phosphorylation site(s), Serine-15 and Serine/Asparagine-14. Function ALC-2 expression has proven to be a useful marker of cardiac muscle chamber distinction, development and differentiation. ALC-2 shows a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYH6
Myosin heavy chain, α isoform (MHC-α) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYH6'' gene. This isoform is distinct from the ventricular/slow myosin heavy chain isoform, MYH7, referred to as MHC-β. MHC-α isoform is expressed predominantly in human cardiac atria, exhibiting only minor expression in human cardiac ventricles. It is the major protein comprising the cardiac muscle thick filament, and functions in cardiac muscle contraction. Mutations in ''MYH6'' have been associated with late-onset hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, atrial septal defects and sick sinus syndrome. Structure MHC-α is a 224 kDa protein composed of 1939 amino acids. The ''MYH6'' gene is located on chromosome 14q12, approximately ~4kb downstream of the ''MYH7'' gene encoding the other major cardiac muscle isoform of myosin heavy chain, MHC-β. MHC-α is a hexameric, asymmetric motor forming the bulk of the thick filament in cardiac muscle; it is the predominant isoform expressed in human cardiac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EF Hand
The EF hand is a helix–loop–helix structural domain or ''motif'' found in a large family of calcium-binding proteins. The EF-hand motif contains a helix–loop–helix topology, much like the spread thumb and forefinger of the human hand, in which the Ca2+ ions are coordinated by ligands within the loop. The motif takes its name from traditional nomenclature used in describing the protein parvalbumin, which contains three such motifs and is probably involved in muscle relaxation via its calcium-binding activity. The EF-hand consists of two alpha helices linked by a short loop region (usually about 12 amino acids) that usually binds calcium ions. EF-hands also appear in each structural domain of the signaling protein calmodulin and in the muscle protein troponin-C. Calcium ion binding site The calcium ion is coordinated in a pentagonal bipyramidal configuration. The six residues involved in the binding are in positions 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 12; these residues are denoted by X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYL4
Atrial Light Chain-1 (ALC-1), also known as Essential Light Chain, Atrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYL4'' gene. ALC-1 is expressed in fetal cardiac ventricular and fetal skeletal muscle, as well as fetal and adult cardiac atrial tissue. ALC-1 expression is reactivated in human ventricular myocardium in various cardiac muscle diseases, including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, ischemic cardiomyopathy and congenital heart diseases. Structure ALC-1 is a 21.6 kDa protein composed of 197 amino acids. ALC-1 is expressed in fetal cardiac ventricular and fetal skeletal muscle, as well as fetal and adult cardiac atrial tissue. ALC-1 binds the neck region of muscle myosin in adult atria. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. Relative to ventricular essential light chain VLC-1, ALC-1 has an additional ~40 amino-acid N-terminal region that contains four to eleven residues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYL2
Myosin regulatory light chain 2, ventricular/cardiac muscle isoform (MLC-2) also known as the regulatory light chain of myosin (RLC) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYL2'' gene. This cardiac ventricular RLC isoform is distinct from that expressed in skeletal muscle ( MYLPF), smooth muscle ( MYL12B) and cardiac atrial muscle (MYL7). Ventricular myosin light chain-2 (MLC-2v) refers to the ventricular cardiac muscle form of myosin light chain 2 (Myl2). MLC-2v is a 19-KDa protein composed of 166 amino acids, that belongs to the EF-hand Ca2+ binding superfamily. MLC-2v interacts with the neck/tail region of the muscle thick filament protein myosin to regulate myosin motility and function. Structure Cardiac, ventricular RLC is an 18.8 kDa protein composed of 166 amino acids. RLC and the second ventricular light chain, essential light chain (ELC, MYL3), are non-covalently bound to IQXXXRGXXXR motifs in the 9 nm S1-S2 lever arm of the myosin head, both alpha (MYH6) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate. Examples Human anatomy * Interatrial septum, the wall of tissue that is a sectional part of the left and right atria of the heart * Interventricular septum, the wall separating the left and right ventricles of the heart * Lingual septum, a vertical layer of fibrous tissue that separates the halves of the tongue. *Nasal septum: the cartilage wall separating the nostrils of the nose * Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the alveoli from each other in the lungs * Orbital septum, a palpebral ligament in the upper and lower eyelids * Septum pellucidum or septum lucidum, a thin structure separating two fluid pockets in the brain * Uterine septum, a malformation of the uterus * Vaginal septum, a lateral or transverse partition inside the vagina * Intermuscular sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called muscle fibers or myofibers) which are formed during embryonic myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes. The costamere is a different component that connects the sarcomere to the sarcolemma. Two of the important proteins are myosin, which forms the thick filament, and actin, which forms the thin filament. Myosin has a long, fibrous tail and a globular head, which binds to actin. The myosin head also binds to ATP, which is the source of energy for muscle movement. Myos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocytes
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Muscle cells (including myocytes and muscle fibers) develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Myoblasts fuse to form multinucleated skeletal muscle cells known as syncytia in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac muscle fiber''. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the esophagus and stomach. Sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
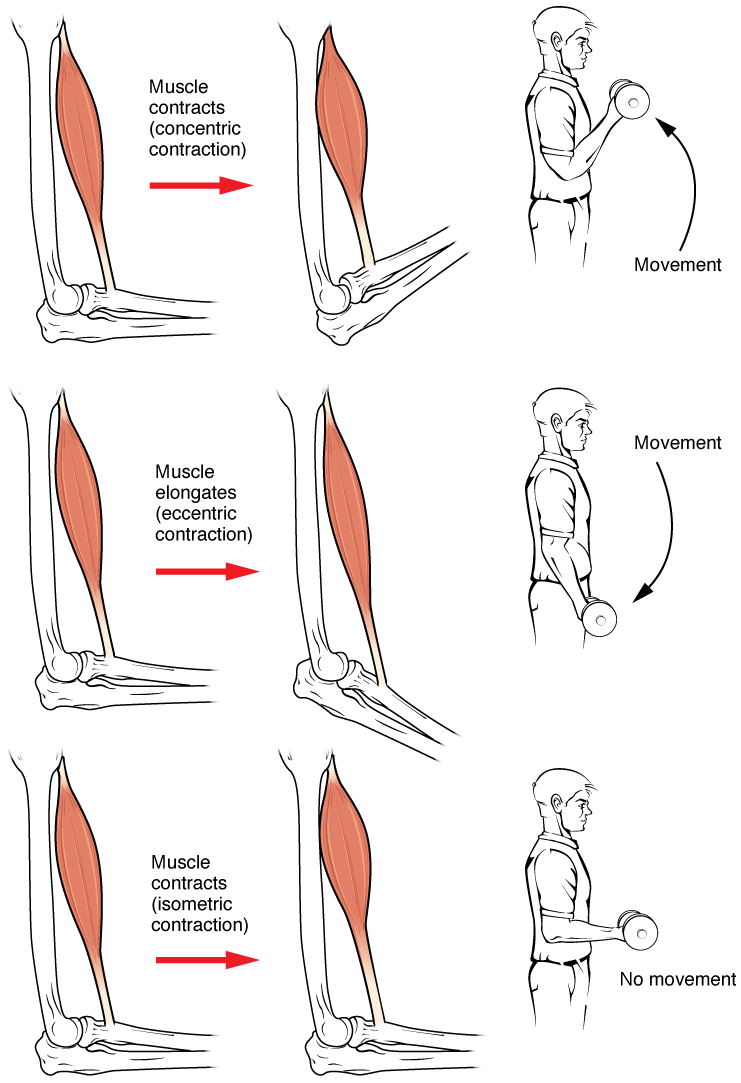
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the interaction of two types of filaments which are the thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are two strands of actin coiled around each, and thick filaments consist of mostly elongated proteins called myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils which are important organelles in the skeletal muscle system. Muscle contraction can also be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, is a narrow part known as the isthmus that connects to the cervix, leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes, at the uterine horns, and the rounded part above the openings to the fallopian tubes is the fundus. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the uterotubal junction. The fertilized egg is carried to the uterus along the fallopian tube. It will have divided on its journey to form a blastocyst that will implant itself into the lining of the uterus – the endometrium, where it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following a period of robust contraction and pumping of blood, called systole. After emptying, the heart immediately relaxes and expands to receive another influx of blood returning from the lungs and other systems of the body, before again contracting to pump blood to the lungs and those systems. A normally performing heart must be fully expanded before it can efficiently pump again. Assuming a healthy heart and a typical rate of 70 to 75 beats per minute, each cardiac cycle, or heartbeat, takes about 0.8 second to complete the cycle. There are two atrial and two ventricle chambers of the heart; they are paired as the left heart and the right heart—that is, the left atrium with the left ventricle, the right atrium with the right ventricle—and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomyocytes
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's my ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |