|
MPLS VPN
MPLS VPN is a family of methods for using Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) to create virtual private networks (VPNs). MPLS VPN is a flexible method to transport and route several types of network traffic using an MPLS backbone. There are three types of MPLS VPNs deployed in networks today: 1. Point-to-point ( Pseudowire) 2. Layer 2 (VPLS) 3. Layer 3 (VPRN) Point-to-point (pseudowire) Point-to-point MPLS VPNs employ VLL ( virtual leased lines) for providing Layer 2 point-to-point connectivity between two sites. Ethernet, TDM, and ATM frames can be encapsulated within these VLLs. Some examples of how point-to-point VPNs might be used by utilities include: * encapsulating TDM T1 circuits attached to Remote Terminal Units * forwarding non-routed DNP3 traffic across the backbone network to the SCADA master controller. Layer 2 VPN (VPLS) Layer 2 MPLS VPNs, or VPLS (virtual private LAN service), offers a “switch in the cloud” style service. VPLS provides the ability to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiprotocol Label Switching
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that directs data from one node to the next based on labels rather than network addresses. Whereas network addresses identify endpoints the labels identify established paths between endpoints. MPLS can encapsulate packets of various network protocols, hence the ''multiprotocol'' component of the name. MPLS supports a range of access technologies, including T1/ E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL. Role and functioning In an MPLS network, labels are assigned to data packets. Packet-forwarding decisions are made solely on the contents of this label, without the need to examine the packet itself. This allows one to create end-to-end circuits across any type of transport medium, using any protocol. The primary benefit is to eliminate dependence on a particular OSI model data link layer (layer 2) technology, and eliminate the need for multiple layer-2 networks to satisfy different types of traf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
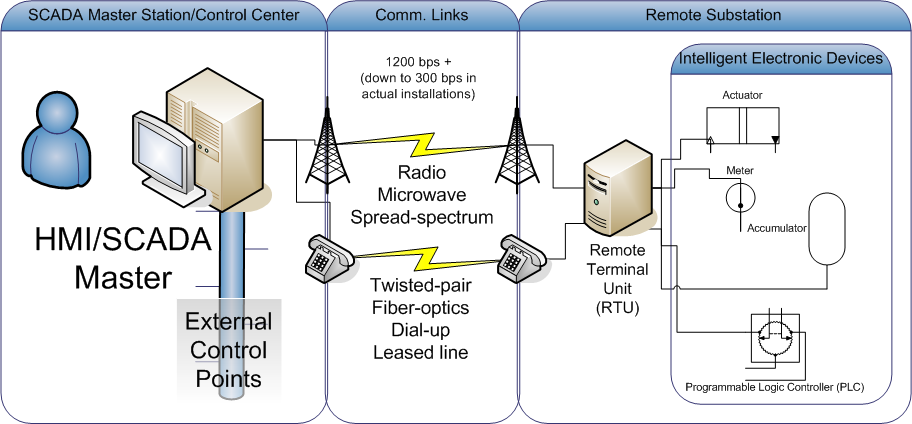
SCADA
Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) is a control system architecture comprising computers, networked data communications and graphical user interfaces for high-level supervision of machines and processes. It also covers sensors and other devices, such as programmable logic controllers, which interface with process plant or machinery. Explanation The operator interfaces which enable monitoring and the issuing of process commands, like controller set point changes, are handled through the SCADA computer system. The subordinated operations, e.g. the real-time control logic or controller calculations, are performed by networked modules connected to the field sensors and actuators. The SCADA concept was developed to be a universal means of remote-access to a variety of local control modules, which could be from different manufacturers and allowing access through standard automation protocols. In practice, large SCADA systems have grown to become very similar to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet VPN
Ethernet VPN (EVPN) is a technology for carrying layer 2 Ethernet traffic as a virtual private network using wide area network protocols. EVPN technologies include Ethernet over MPLS and Ethernet over VXLAN. EVPNs are covered by a number of Internet RFCs, including: * "Requirements for Ethernet VPN (EVPN)", * "BGP MPLS-Based Ethernet VPN", * "A Network Virtualization Overlay Solution Using Ethernet VPN (EVPN)", * "Ethernet-Tree (E-Tree) Support in Ethernet VPN (EVPN) and Provider Backbone Bridging EVPN (PBB-EVPN)". References See also * Virtual Private LAN Service Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) is a way to provide Ethernet-based multipoint to multipoint communication over IP or MPLS networks. It allows geographically dispersed sites to share an Ethernet broadcast domain by connecting sites through p ... Ethernet Tunneling protocols {{network-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segment Routing
Segment routing, a form of computer networking, is a modern variant of source routing that is being developed within thSPRINGand IPv6 working groups of the IETF. In a segment routed network, an ingress node may prepend a header to packets that contain a list of segments, which are instructions that are executed on subsequent nodes in the network. These instructions may be forwarding instructions, such as an instruction to forward a packet to a specific destination or interface. Segment routing works either on top of a MPLS network or on an IPv6 network. In an MPLS network, segments are encoded as MPLS labels. Under IPv6, a new header called a Segment Routing Header (SRH) is used. Segments in a SRH are encoded in a list of IPv6 addresses. See also * Bang path * Dynamic Source Routing * Policy-based routing can also be used to route packets using their source addresses. * Scalable Source Routing Scalable Source Routing (SSR) is a routing protocol for unstructured networks suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiprotocol BGP
Multiprotocol Extensions for BGP (MBGP or MP-BGP), sometimes referred to as Multiprotocol BGP or Multicast BGP and defined in IETF RFC 4760, is an extension to Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) that allows different types of addresses (known as address families) to be distributed in parallel. Whereas standard BGP supports only IPv4 unicast addresses, Multiprotocol BGP supports IPv4 and IPv6 addresses and it supports unicast and multicast variants of each. Multiprotocol BGP allows information about the topology of IP multicast-capable routers to be exchanged separately from the topology of normal IPv4 unicast routers. Thus, it allows a multicast routing topology different from the unicast routing topology. Although MBGP enables the exchange of inter-domain multicast routing information, other protocols such as the Protocol Independent Multicast family are needed to build trees and forward multicast traffic. As an enhancement of BGP-4, MP-BGP provides routing information for various prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L3 MPLS VPN En
L3, L03, L.3 or L-3 may refer to: In arts and media * Live, Loud & Local, a show launched by band The Matches in the Oakland, California region * '' Leprechaun 3'', a film * L3-37, a droid in ''Solo: A Star Wars Story'' * Lower third, in television and film a graphic overlay placed in the title-safe lower area of the screen. Businesses * L3 Technologies, a company that provided intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance systems prior to a merger with Harris Corporation to form L3Harris Technologies in 2019 * DHL De Guatemala (IATA code L3), a cargo airline based in Guatemala * LTU Austria (IATA code L3), an airline based in Austria In science and technology Biology and medicine * L3, the third lumbar vertebra, in human anatomy * the third larval stage in the ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' worm development * ATC code L03 ''Immunostimulants'', a subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System * Haplogroup L3 (mtDNA), a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Layer 2 MPLS VPN
A Layer 2 MPLS VPN is a term in computer networking. It is a method that Internet service providers use to segregate their network for their customers, to allow them to transmit data over an IP network. This is often sold as a service to businesses. Layer 2 VPNs are a type of Virtual Private Network (VPN) that uses MPLS labels to transport data. The communication occurs between routers that are known as ''Provider Edge'' routers (PEs), as they sit on the edge of the provider's network, next to the customer's network. Internet providers who have an existing Layer 2 network (such as ATM or Frame Relay) may choose to use these VPNs instead of the other common MPLS VPN, Layer 3. There is no one IETF standard for Layer 2 MPLS VPNs. Instead, two methodologies may be used. Both methods use a standard MPLS header to encapsulate data. However, they differ in their signaling protocols. Types of Layer 2 MPLS VPNs BGP-based The BGP-based type is based on a draft specification by Kire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L2 MPLS VPN En
L, or l, is the twelfth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''el'' (pronounced ), plural ''els''. History Lamedh may have come from a pictogram of an ox goad or cattle prod. Some have suggested a shepherd's staff. Use in writing systems Phonetic and phonemic transcription In phonetic and phonemic transcription, the International Phonetic Alphabet uses to represent the lateral alveolar approximant. English In English orthography, usually represents the phoneme , which can have several sound values, depending on the speaker's accent, and whether it occurs before or after a vowel. The alveolar lateral approximant (the sound represented in IPA by lowercase ) occurs before a vowel, as in ''lip'' or ''blend'', while the velarized alveolar lateral approximant (IPA ) occurs in ''bell'' and ''milk''. This velarization does not occur in many Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNP3
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. Its main use is in utilities such as electric and water companies. Usage in other industries is not common. It was developed for communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It plays a crucial role in SCADA systems, where it is used by SCADA Master Stations (a.k.a. Control Centers), Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). It is primarily used for communications between a master station and RTUs or IEDs. ICCP, the Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol (a part of IEC 60870-6), is used for inter-master station communications. Competing standards include the older Modbus protocol and the newer IEC 61850 protocol. History While IEC 60870-5 was still under development and had not been standardized, there was a need to create a standard that would allow interoperability be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Private Network
A virtual private network (VPN) extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network. The benefits of a VPN include increases in functionality, security, and management of the private network. It provides access to resources that are inaccessible on the public network and is typically used for remote workers. Encryption is common, although not an inherent part of a VPN connection. A VPN is created by establishing a virtual point-to-point connection through the use of dedicated circuits or with tunneling protocols over existing networks. A VPN available from the public Internet can provide some of the benefits of a wide area network (WAN). From a user perspective, the resources available within the private network can be accessed remotely. Types Virtual private networks may be classified into several categories: ;Remote ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
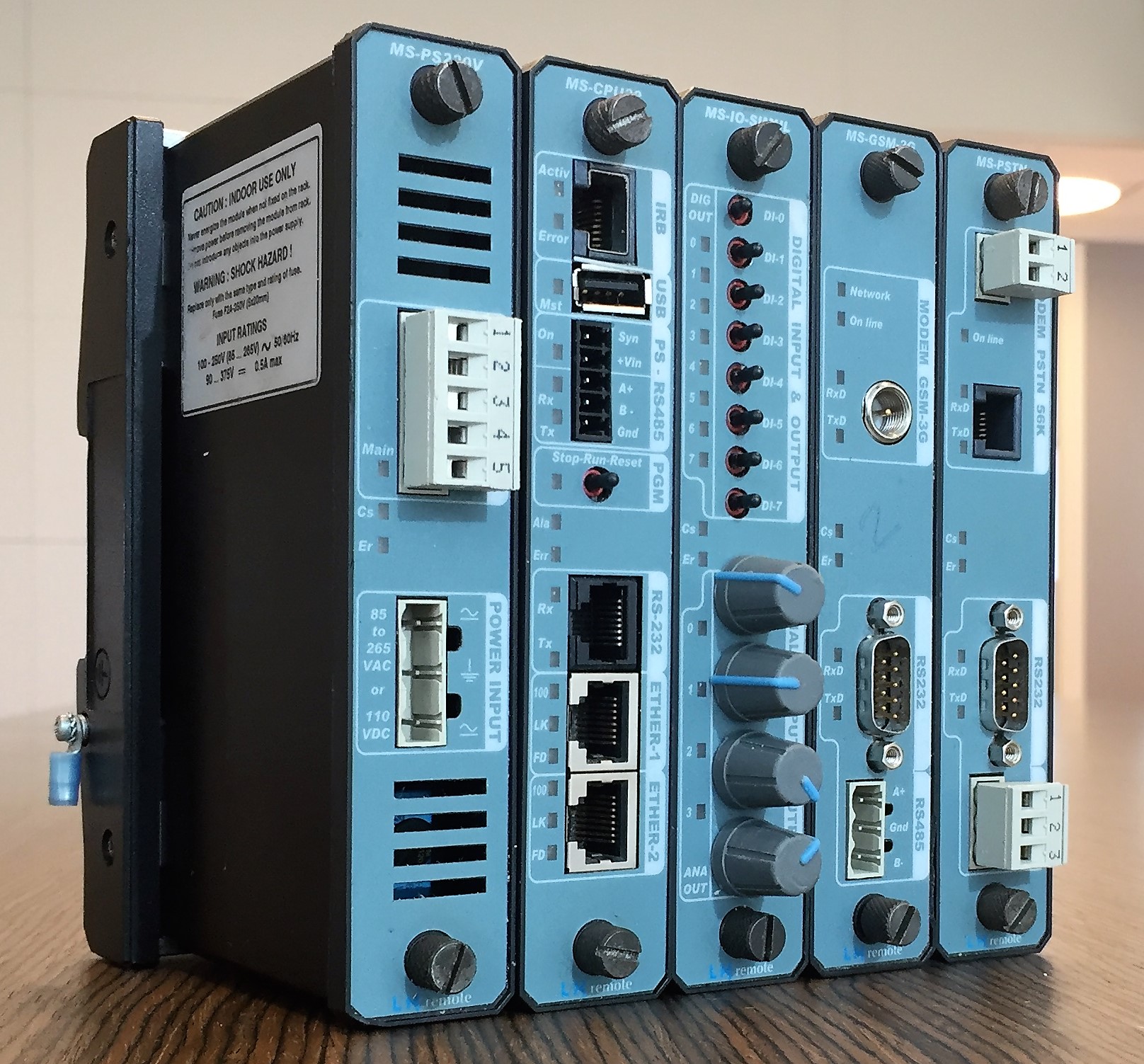
Remote Terminal Unit
A remote terminal unit(RTU) is a microprocessor-controlled electronic device that interfaces objects in the physical world to a distributed control system or SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) system by transmitting telemetry data to a master system, and by using messages from the master supervisory system to control connected objects.Gordon R. Clarke, Deon Reynders, Edwin Wright,'' Practical modern SCADA Protocols: DNP3, 60870.5 and related systems'' Newnes, 2004 pages 19-21 Other terms that may be used for RTU are remote telemetry unit and remote telecontrol unit. Architecture An RTU monitors the field digital and analog parameters and transmits data to a SCADA Master Station. It runs setup software to connect data input streams to data output streams, define communication protocols, and troubleshoot installation problems in the field. An RTU may consist of one complex circuit card consisting of various sections needed to do a custom-fitted function, or may cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T1 Circuit
Digital Signal 1 (DS1, sometimes DS-1) is a T-carrier signaling scheme devised by Bell Labs. DS1 is the primary digital telephone standard used in the United States, Canada and Japan and is able to transmit up to 24 multiplexed voice and data calls over telephone lines. E-carrier is used in place of T-carrier outside the United States, Canada, Japan, and South Korea. DS1 is the logical bit pattern used over a physical T1 line; in practice, the terms ''DS1'' and ''T1'' are often used interchangeably. Overview T1 refers to the primary digital telephone carrier system used in North America. T1 is one line type of the PCM T-carrier hierarchy. T1 describes the cabling, signal type, and signal regeneration requirements of the carrier system. The signal transmitted on a T1 line, referred to as the DS1 signal, consists of serial bits transmitted at the rate of 1.544 Mbit/s. The type of line code used is called Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI). Digital Signal Designation is the classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |