|
MOSIX
MOSIX is a proprietary distributed operating system. Although early versions were based on older UNIX systems, since 1999 it focuses on Linux clusters and grids. In a MOSIX cluster/grid there is no need to modify or to link applications with any library, to copy files or login to remote nodes, or even to assign processes to different nodes – it is all done automatically, like in an SMP. History MOSIX has been researched and developesince 1977at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem by the research team of Prof. Amnon Barak. So far, ten major versions have been developed. The first version, called MOS, for ''Multicomputer OS'', (1981–83) was based on Bell Lab's Seventh Edition Unix and ran on a cluster of PDP-11 computers. Later versions were based on Unix System V Release 2 (1987–89) and ran on a cluster of VAX and NS32332-based computers, followed by a BSD/OS-derived version (1991–93) for a cluster of 486/Pentium computers. Since 1999 MOSIX is tuned to Linux for x86 pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosix
MOSIX is a proprietary distributed operating system. Although early versions were based on older UNIX systems, since 1999 it focuses on Linux clusters and grids. In a MOSIX cluster/grid there is no need to modify or to link applications with any library, to copy files or login to remote nodes, or even to assign processes to different nodes – it is all done automatically, like in an SMP. History MOSIX has been researched and developesince 1977at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem by the research team of Prof. Amnon Barak. So far, ten major versions have been developed. The first version, called MOS, for ''Multicomputer OS'', (1981–83) was based on Bell Lab's Seventh Edition Unix and ran on a cluster of PDP-11 computers. Later versions were based on Unix System V Release 2 (1987–89) and ran on a cluster of VAX and NS32332-based computers, followed by a BSD/OS-derived version (1991–93) for a cluster of 486/Pentium computers. Since 1999 MOSIX is tuned to Linux for x86 pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single System Image
In distributed computing, a single system image (SSI) cluster is a cluster of machines that appears to be one single system. The concept is often considered synonymous with that of a distributed operating system, but a single image may be presented for more limited purposes, just job scheduling for instance, which may be achieved by means of an additional layer of software over conventional operating system images running on each node. The interest in SSI clusters is based on the perception that they may be simpler to use and administer than more specialized clusters. Different SSI systems may provide a more or less complete illusion of a single system. Features of SSI clustering systems Different SSI systems may, depending on their intended usage, provide some subset of these features. Process migration Many SSI systems provide process migration. Processes may start on one node and be moved to another node, possibly for resource balancing or administrative reasons.for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Cluster
A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software. The components of a cluster are usually connected to each other through fast local area networks, with each node (computer used as a server) running its own instance of an operating system. In most circumstances, all of the nodes use the same hardware and the same operating system, although in some setups (e.g. using Open Source Cluster Application Resources (OSCAR)), different operating systems can be used on each computer, or different hardware. Clusters are usually deployed to improve performance and availability over that of a single computer, while typically being much more cost-effective than single computers of comparable speed or availability. Computer clusters emerged as a result of convergence of a number of computing trends including t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Cluster
A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software. The components of a cluster are usually connected to each other through fast local area networks, with each node (computer used as a server) running its own instance of an operating system. In most circumstances, all of the nodes use the same hardware and the same operating system, although in some setups (e.g. using Open Source Cluster Application Resources (OSCAR)), different operating systems can be used on each computer, or different hardware. Clusters are usually deployed to improve performance and availability over that of a single computer, while typically being much more cost-effective than single computers of comparable speed or availability. Computer clusters emerged as a result of convergence of a number of computing trends including t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster (computing)
A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software. The components of a cluster are usually connected to each other through fast local area networks, with each node (computer used as a server) running its own instance of an operating system. In most circumstances, all of the nodes use the same hardware and the same operating system, although in some setups (e.g. using Open Source Cluster Application Resources (OSCAR)), different operating systems can be used on each computer, or different hardware. Clusters are usually deployed to improve performance and availability over that of a single computer, while typically being much more cost-effective than single computers of comparable speed or availability. Computer clusters emerged as a result of convergence of a number of computing trends including th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nano-technology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. A more generalized description of nanotechnology was subsequently established by the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which defined nanotechnology as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). This definition reflects the fact that quantum mechanical effects are important at this quantum-realm scale, and so the definition shifted from a particular technological goal to a research category inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with the special properties of matter which occur below the given size threshold. It is therefore common to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-performance Computing
High-performance computing (HPC) uses supercomputers and computer clusters to solve advanced computation problems. Overview HPC integrates systems administration (including network and security knowledge) and parallel programming into a multidisciplinary field that combines digital electronics, computer architecture, system software, programming languages, algorithms and computational techniques. HPC technologies are the tools and systems used to implement and create high performance computing systems. Recently, HPC systems have shifted from supercomputing to computing clusters and grids. Because of the need of networking in clusters and grids, High Performance Computing Technologies are being promoted by the use of a collapsed network backbone, because the collapsed backbone architecture is simple to troubleshoot and upgrades can be applied to a single router as opposed to multiple ones. The term is most commonly associated with computing used for scientific research or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
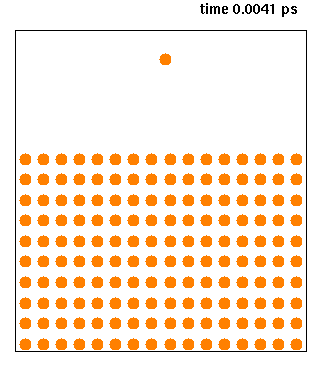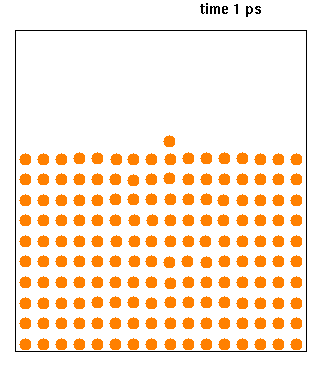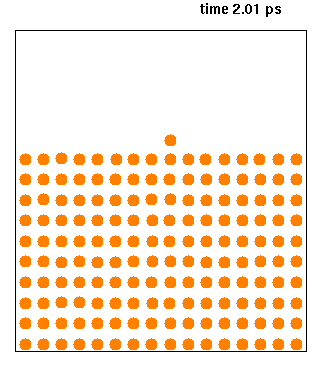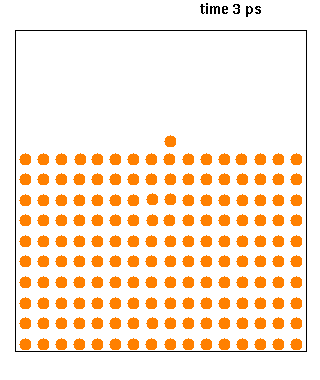
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by numerically solving Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where forces between the particles and their potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanical force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analytically; MD simulation circumvents this problem by using numerical methods. However, long MD simulations are mathematically ill-conditioned, generating cumulative errors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology forecasting, to predict the conditions of the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere for a given location and time. People have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia and formally since the 19th century. Weather forecasts are made by collecting quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere, land, and ocean and using meteorology to project how the atmosphere will change at a given place. Once calculated manually based mainly upon changes in atmospheric pressure, barometric pressure, current weather conditions, and sky condition or cloud cover, weather forecasting now relies on numerical weather prediction, computer-based models that take many atmospheric factors into account. Human input is still required to pick the best possible forecast model to base the forecast upon, which involves pattern recognition skills, teleconnections, knowledge of model performance, and knowledge of model biases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomic
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dimensional structural configuration. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of ''individual'' genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of ''all'' of an organism's genes, their interrelations and influence on the organism. Genes may direct the production of proteins with the assistance of enzymes and messenger molecules. In turn, proteins make up body structures such as organs and tissues as well as control chemical reactions and carry signals between cells. Genomics also involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes through uses of high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. Advances in gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Load Balancing (computing)
In computing, load balancing is the process of distributing a set of tasks over a set of resources (computing units), with the aim of making their overall processing more efficient. Load balancing can optimize the response time and avoid unevenly overloading some compute nodes while other compute nodes are left idle. Load balancing is the subject of research in the field of parallel computers. Two main approaches exist: static algorithms, which do not take into account the state of the different machines, and dynamic algorithms, which are usually more general and more efficient but require exchanges of information between the different computing units, at the risk of a loss of efficiency. Problem overview A load-balancing algorithm always tries to answer a specific problem. Among other things, the nature of the tasks, the algorithmic complexity, the hardware architecture on which the algorithms will run as well as required error tolerance, must be taken into account. Therefore c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input/output
In computing, input/output (I/O, or informally io or IO) is the communication between an information processing system, such as a computer, and the outside world, possibly a human or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system and outputs are the signals or data sent from it. The term can also be used as part of an action; to "perform I/O" is to perform an input or output operation. are the pieces of hardware used by a human (or other system) to communicate with a computer. For instance, a keyboard or computer mouse is an input device for a computer, while monitors and printers are output devices. Devices for communication between computers, such as modems and network cards, typically perform both input and output operations. Any interaction with the system by a interactor is an input and the reaction the system responds is called the output. The designation of a device as either input or output depends on perspective. Mice a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |