|
MDS-1
Mission Demonstration Satellite 1 (MDS-1) or Tsubasa (COSPAR 2002-003A, SATCAT 27367) was a Japanese technology test mission. It was launched by the second H-2A on February 4, 2002 from the Tanegashima Space Center. After the launch, MDS-1 was renamed Tsubasa, meaning wings in Japanese. Tsubasa was placed in a geostationary transfer orbit (GTO). It ended its operational phase on 26 February 2003. A similar mission, MDS-2, was cancelled. The purpose of the mission was to test the performance of commercial off-the-shelf components, including solar batteries, semiconductors and computers. MDS-1 also carried instrumentation to observe how changes in the environment as the satellite passed through the Van Allen radiation belts affected the performance of each component. Among these instruments were a dosimeter using radiation-sensitive field effect transistors, a magnetometer, and a device for tracking heavy ions. During the mission, MDS-1 tracked the occurrence of single event ups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the merger, ISA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-2A
H-IIA (H-2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. These liquid fuel rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit; lunar orbiting spacecraft; ''Akatsuki'', which studied the planet Venus; and the Emirates Mars Mission, which was launched to Mars in July 2020. Launches occur at the Tanegashima Space Center. The H-IIA first flew in 2001. , H-IIA rockets were launched 45 times, including 39 consecutive missions without a failure, dating back to 29 November 2003. Production and management of the H-IIA shifted from JAXA to MHI on 1 April 2007. Flight 13, which launched the lunar orbiter SELENE, was the first H-IIA launched after this privatization. The H-IIA is a derivative of the earlier H-II rocket, substantially redesigned to improve reliability and minimize costs. There have been four variants, with two in active service (as of 2020) for various purposes. A deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 2002
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
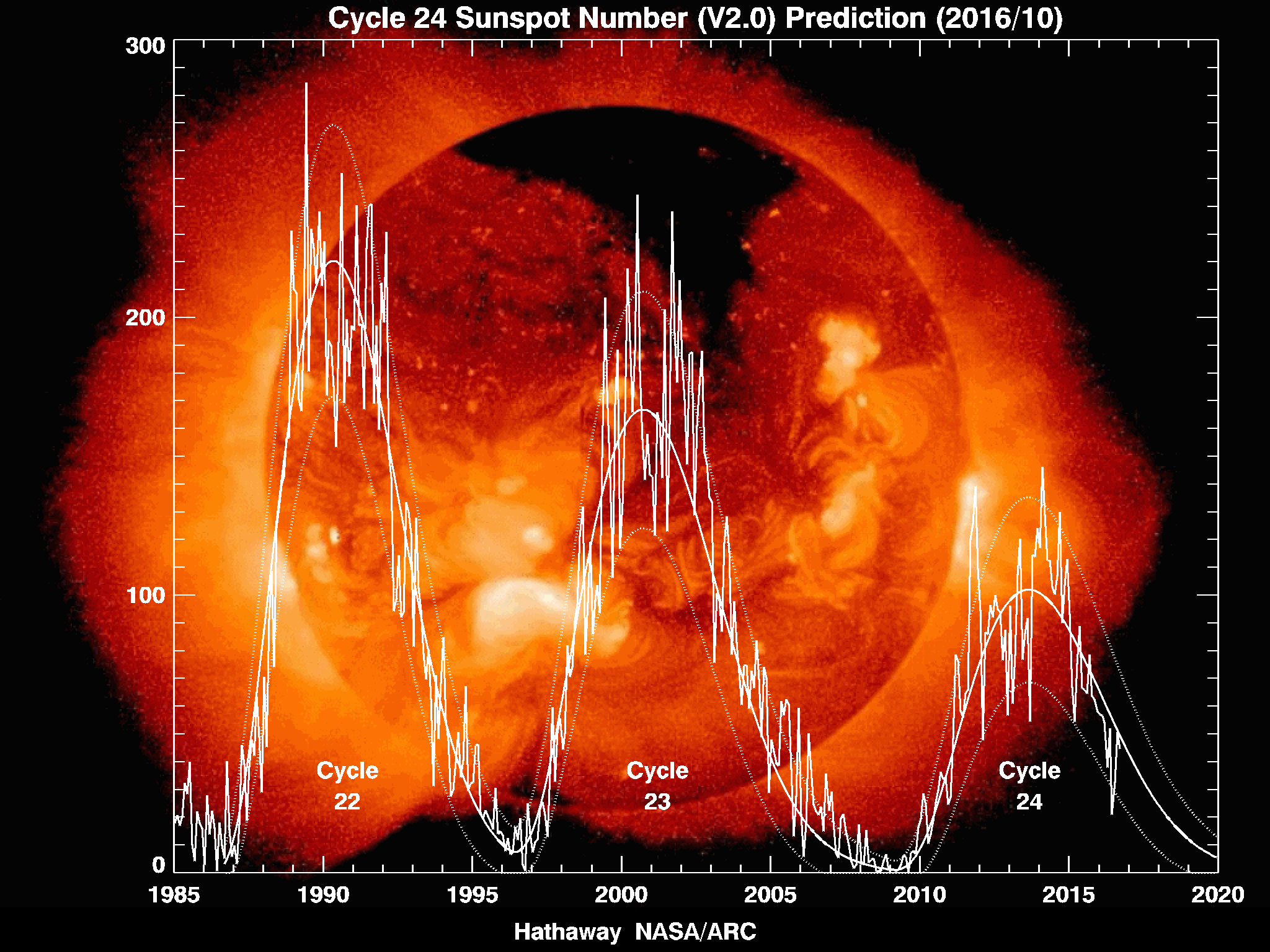
Solar Maximum
Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun's 11-year solar cycle. During solar maximum, large numbers of sunspots appear, and the solar irradiance output grows by about 0.07%. On average, the solar cycle takes about 11 years to go from one solar maximum to the next, with duration observed varying from 9 to 14 years. Large solar storms often occur during solar maximum. For example, the Carrington Event, which took place a few months before the solar maximum of solar cycle 10, was the most intense geomagnetic storm in recorded history and widely considered to have been caused by an equally large solar storm. Predictions Predictions of a future maximum's timing and strength are very difficult; predictions vary widely. There was a solar maximum in 2000. In 2006, NASA initially expected a solar maximum in 2010 or 2011, and thought that it could be the strongest since 1958. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Event Upset
A single-event upset (SEU), also known as a single-event error (SEE), is a change of state caused by one single ionizing particle (ions, electrons, photons...) striking a sensitive node in a live micro-electronic device, such as in a microprocessor, semiconductor memory, or power transistors. The state change is a result of the free charge created by ionization in or close to an important node of a logic element (e.g. memory "bit"). The error in device output or operation caused as a result of the strike is called an SEU or a soft error. The SEU itself is not considered permanently damaging to the transistor's or circuits' functionality unlike the case of single-event latch-up (SEL), single-event gate rupture (SEGR), or single-event burnout (SEB). These are all examples of a general class of radiation effects in electronic devices called ''single-event effects'' (SEEs). History Single-event upsets were first described during above-ground nuclear testing, from 1954 to 1957, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Ion Physics
High-energy nuclear physics studies the behavior of nuclear matter in energy regimes typical of high-energy physics. The primary focus of this field is the study of heavy-ion collisions, as compared to lighter atoms in other particle accelerators. At sufficient collision energies, these types of collisions are theorized to produce the quark–gluon plasma. In peripheral nuclear collisions at high energies one expects to obtain information on the electromagnetic production of leptons and mesons that are not accessible in electron–positron colliders due to their much smaller luminosities. Previous high-energy nuclear accelerator experiments have studied heavy-ion collisions using projectile energies of 1 GeV/nucleon at JINR and LBNL-Bevalac up to 158 GeV/nucleon at CERN-SPS. Experiments of this type, called "fixed-target" experiments, primarily accelerate a "bunch" of ions (typically around 106 to 108 ions per bunch) to speeds approaching the speed of light (0.999' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The first magnetometer capable of measuring the absolute magnetic intensity at a point in space was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall effect, which is still widely used. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
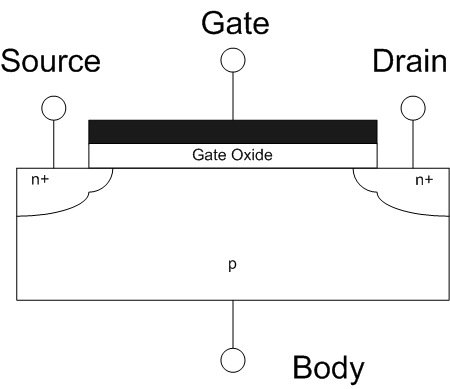
Field Effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dosimeter
A radiation dosimeter is a device that measures dose uptake of external ionizing radiation. It is worn by the person being monitored when used as a personal dosimeter, and is a record of the radiation dose received. Modern electronic personal dosimeters can give a continuous readout of cumulative dose and current dose rate, and can warn the wearer with an audible alarm when a specified dose rate or a cumulative dose is exceeded. Other dosimeters, such as thermoluminescent or film types, require processing after use to reveal the cumulative dose received, and cannot give a current indication of dose while being worn. Personal dosimeters The personal ionising radiation dosimeter is of fundamental importance in the disciplines of radiation dosimetry and radiation health physics and is primarily used to estimate the radiation dose deposited in an individual wearing the device. Ionising radiation damage to the human body is cumulative, and is related to the total dose received, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |