|
MAC (chemotherapy)
"7+3" in the context of chemotherapy is an acronym for a chemotherapy regimen that is most often used today (as of 2014) as first-line induction therapy (to induce remission) in acute myelogenous leukemia, excluding the acute promyelocytic leukemia form, which is better treated with ATRA and/or arsenic trioxide and requires less chemotherapy (if requires it at all, which is not always the case). The name "7+3" comes from the duration of chemotherapy course, which consists of 7 days of standard-dose cytarabine, and 3 days of an anthracycline antibiotic or an anthracenedione, most often daunorubicin (can be substituted for doxorubicin or idarubicin or mitoxantrone). Dosing regimen Standard-dose cytarabine plus daunorubicin (DA or DAC chemotherapy) Standard-dose cytarabine plus idarubicin (IA or IAC chemotherapy) Standard-dose cytarabine plus mitoxantrone (MA or MAC chemotherapy) Intensified versions There were attempts to intensify the "7+3" regimen in order to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daunorubicin
Daunorubicin, also known as daunomycin, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Specifically it is used for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and Kaposi's sarcoma. It is administered by injection into a vein. A liposomal formulation known as liposomal daunorubicin also exists. Common side effects include hair loss, vomiting, bone marrow suppression, and inflammation of the inside of the mouth. Other severe side effects include heart disease and tissue death at the site of injection. Use in pregnancy may harm the fetus. Daunorubicin is in the anthracycline family of medication. It works in part by blocking the function of topoisomerase II. Daunorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1979. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It was originally isolated from bacteria of the '' Streptomyces'' type. Medical uses It slows or stops the gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADE (chemotherapy)
ADE is a chemotherapy regimen most often used as an induction or consolidation regimen in acute myelogenous leukemia, especially in poor-risk patients or those refractory to the standard first-line induction with standard " 7+3" regimen or who are relapsed after the standard chemotherapy. ADE regimen consists of three drugs: # Ara-C (cytarabine) - an antimetabolite; # Daunorubicin - an anthracycline antibiotic that is able to intercalate DNA and thus disrupt the cell division cycle, preventing mitosis In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is mainta ...; # Etoposide - a topoisomerase inhibitor. Dosing regimen References {{Reflist Chemotherapy regimens used in acute myeloid leukemia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etoposide
Etoposide, sold under the brand name Vepesid among others, is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatments of a number of types of cancer including testicular cancer, lung cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. It is also used for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. It is used by mouth or injection into a vein. Side effects are very common. They can include low blood cell counts, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, hair loss, and fever. Other severe side effects include allergic reactions and low blood pressure. Use during pregnancy will likely harm the fetus. Etoposide is in the topoisomerase inhibitor family of medication. It is believed to work by damaging DNA. Etoposide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1983. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Etoposide is used as a form of chemotherapy for cancers such as Kaposi’s sarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, lung cancer, testicular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melphalan
Melphalan, sold under the brand name Alkeran among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat multiple myeloma, ovarian cancer, melanoma, and AL amyloidosis. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. Common side effects include nausea and bone marrow suppression. Other severe side effects may include anaphylaxis and the development of other cancers. Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the fetus. Melphalan belongs to the class of nitrogen mustard alkylating agents. It works by interfering with the creation of DNA and RNA. Melphalan was approved for medical use in the United States in 1964. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. Medical uses It is used to treat multiple myeloma, ovarian cancer, AL amyloidosis, and occasionally malignant melanoma. The agent was first investigated as a possible drug for use in melanoma, it was not found to be effective. In 2016, it was approve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
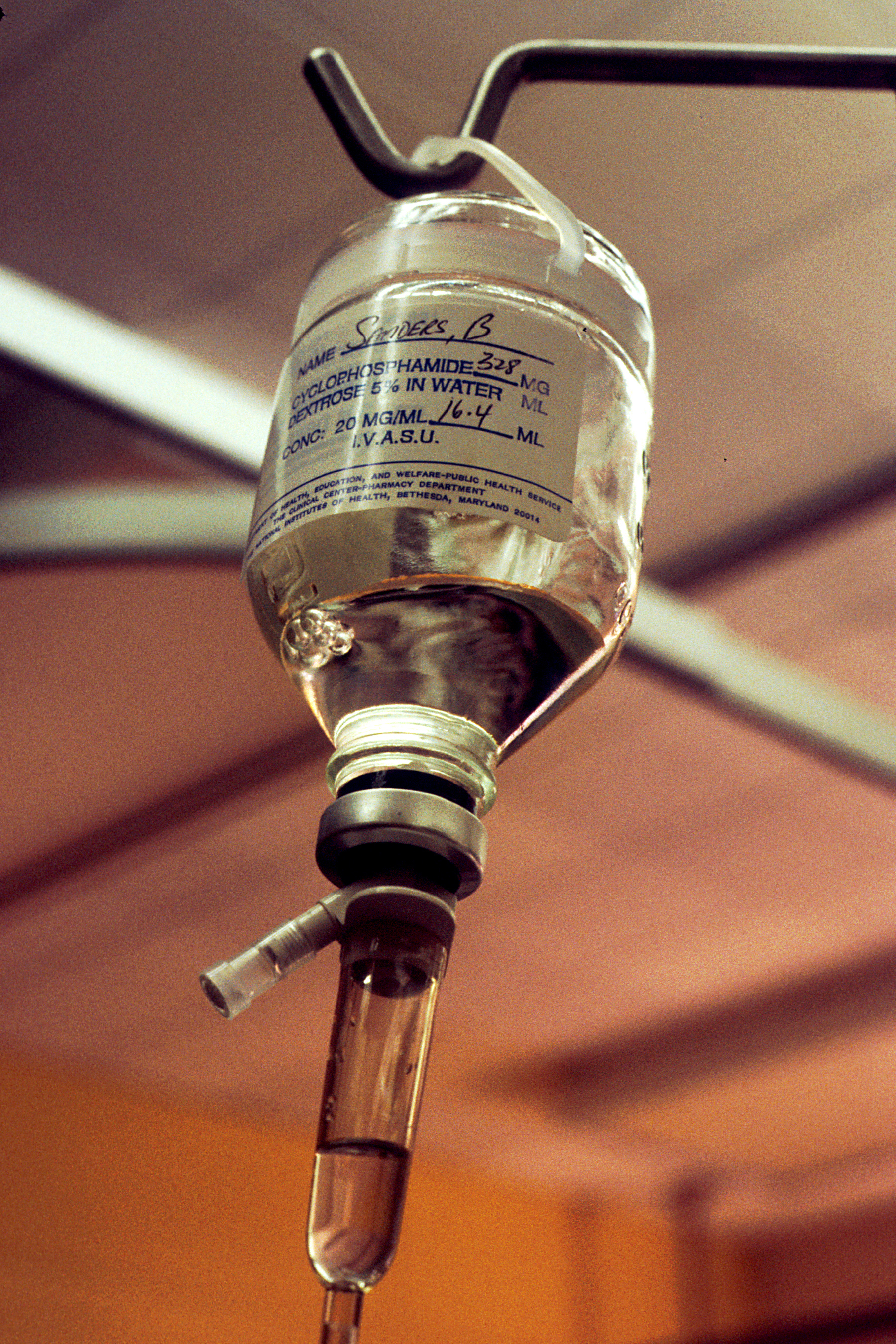
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to immunosuppressant, suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or intravenous, injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include leukopenia, low white blood cell counts, loss of appetite, vomiting, hair loss, and hemorrhagic cystitis, bleeding from the bladder. Other severe side effects include an increased future risk of cancer, infertility, allergic reactions, and pulmonary fibrosis. Cyclophosphamide is in the alkylating antineoplastic agent, alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It is believed to work by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, gestational trophoblastic disease, and osteosarcoma. Types of autoimmune diseases it is used for include psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It can be given by mouth or by injection. Common side effects include nausea, feeling tired, fever, increased risk of infection, low white blood cell counts, and breakdown of the skin inside the mouth. Other side effects may include liver disease, lung disease, lymphoma, and severe skin rashes. People on long-term treatment should be regularly checked for side effects. It is not safe during breastfeeding. In those with kidney problems, lower doses may be needed. It acts by blocking the body's use of folic acid. Methotrexate was first made in 1947 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prednisolone
Prednisolone is a steroid medication used to treat certain types of allergies, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders, and cancers. Some of these conditions include adrenocortical insufficiency, high blood calcium, rheumatoid arthritis, dermatitis, eye inflammation, asthma, and multiple sclerosis. It can be taken by mouth, injected into a vein, used topically as a skin cream, or as eye drops. Side effects with short-term use include nausea and feeling tired. More severe side effects include psychiatric problems, which may occur in about 5% of people. Common side effects with long term use include bone loss, weakness, yeast infections, and easy bruising. While short-term use in the later part of pregnancy is safe, long-term use or use in early pregnancy is occasionally associated with harm to the baby. It is a glucocorticoid made from hydrocortisone (cortisol). Prednisolone was discovered and approved for medical use in 1955. It is on the World Health Organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. The name "glucocorticoid" is a portmanteau (glucose + cortex + steroid) and is composed from its role in regulation of glucose metabolism, synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and its steroidal structure (see structure below). Glucocorticoids are part of the feedback mechanism in the immune system, which reduces certain aspects of immune function, such as inflammation. They are therefore used in medicine to treat diseases caused by an overactive immune system, such as allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and sepsis. Glucocorticoids have many diverse ( pleiotropic) effects, including potentially harmful side effects. They also interfere with some of the abnormal mechanisms in cancer cells, so they are used in high doses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloperoxidase
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a peroxidase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MPO'' gene on chromosome 17. MPO is most abundantly expressed in neutrophil granulocytes (a subtype of white blood cells), and produces hypohalous acids to carry out their antimicrobial activity, including hypochlorous acid, the sodium salt of which is the chemical in bleach. It is a lysosomal protein stored in azurophilic granules of the neutrophil and released into the extracellular space during degranulation. Neutrophil myeloperoxidase has a heme pigment, which causes its green color in secretions rich in neutrophils, such as mucus and sputum. The green color contributed to its outdated name verdoperoxidase. Structure The 150- kDa MPO protein is a cationic heterotetramer consisting of two 15-kDa light chains and two variable-weight glycosylated heavy chains bound to a prosthetic heme group complex with calcium ions, arranged as a homodimer of heterodimers. The light chains are glycosylated an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' Chemical specificity, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinblastine
Vinblastine (VBL), sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, brain cancer, melanoma, and testicular cancer. It is given by injection into a vein. Most people experience some side effects. Commonly it causes a change in sensation, constipation, weakness, loss of appetite, and headaches. Severe side effects include low blood cell counts and shortness of breath. It should not be given to people who have a current bacterial infection. Use during pregnancy will likely harm the baby. Vinblastine works by blocking cell division. Vinblastine was isolated in 1958. An example of a natural herbal remedy that has since been developed into a conventional medicine, vinblastine was originally obtained from the Madagascar periwinkle. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |