|
M2-PK Test
The M2-PK Test is a non-invasive screening (medicine), screening method for the early detection of colorectal cancers and Polyp (medicine), polyps which are known to be the precursors of colorectal cancer. The M2-PK Test which is used for stool analysis is available either as fully quantitative ELISA Test or as a rapid test that can be performed by any general practitioner without the need of a laboratory or any additional equipment. The enzyme biomarker (medicine), biomarker Tumor M2-PK, M2-PK has been identified as a key enzyme in colorectal cancers and polyps. The detection of M2-PK does not depend on blood in the stool and is specifically related on changes in the Tumor metabolome, tumor metabolism. False positive results by unspecific blood sources in the bowel are excluded and the test is able to detect both bleeding as well as non-bleeding colorectal cancers and polyps. The M2-PK Test is able to detect 80.3% of colorectal cancers. Testing for M2-PK allows for colorectal ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screening (medicine)
Screening, in medicine, is a strategy used to look for as-yet-unrecognised conditions or risk markers. This testing can be applied to individuals or to a whole population. The people tested may not exhibit any signs or symptoms of a disease, or they might exhibit only one or two symptoms, which by themselves do not indicate a definitive diagnosis. Screening interventions are designed to identify conditions which could at some future point turn into disease, thus enabling earlier intervention and management in the hope to reduce mortality and suffering from a disease. Although screening may lead to an earlier diagnosis, not all screening tests have been shown to benefit the person being screened; overdiagnosis, misdiagnosis, and creating a false sense of security are some potential adverse effects of screening. Additionally, some screening tests can be inappropriately overused. For these reasons, a test used in a screening program, especially for a disease with low incidence, must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to old age and lifestyle factors, with only a small number of cases due to underlying genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a benign tumor, often in the form of a polyp, which over time becomes cancerous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyp (medicine)
In anatomy, a polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be ''pedunculated''; if it is attached without a stalk, it is said to be ''sessile''. Polyps are commonly found in the colon, stomach, nose, ear, sinus(es), urinary bladder, and uterus. They may also occur elsewhere in the body where there are mucous membranes, including the cervix, vocal folds, and small intestine. Some polyps are tumors (neoplasms) and others are non-neoplastic, for example hyperplastic or dysplastic, which are benign. The neoplastic ones are usually benign, although some can be pre-malignant, or concurrent with a malignancy. The name is of ancient origin, in use in English from about 1400 for a nasal polyp, from Latin ''polypus'' through Greek. The animal of similar appearance called polyp is attested from 1742, although the word was earlier used for an octopus. Digestive polyps Relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand (commonly a protein) in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries. In the most simple form of an ELISA, antigens from the sample to be tested are attached to a surface. Then, a matching antibody is applied over the surface so it can bind the antigen. This antibody is linked to an enzyme and then any unbound antibodies are removed. In the final step, a substance containing the enzyme's substrate is added. If there was binding, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable signal, most commonly a color change. Performing an ELISA involves at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomarker (medicine)
In medicine, a biomarker is a measurable indicator of the severity or presence of some disease state. More generally a biomarker is anything that can be used as an indicator of a particular disease state or some other physiological state of an organism. According to the WHO, the indicator may be chemical, physical, or biological in nature - and the measurement may be functional, physiological, biochemical, cellular, or molecular. A biomarker can be a substance that is introduced into an organism as a means to examine organ function or other aspects of health. For example, rubidium chloride is used in isotopic labeling to evaluate perfusion of heart muscle. It can also be a substance whose detection indicates a particular disease state, for example, the presence of an antibody may indicate an infection. More specifically, a biomarker indicates a change in expression or state of a protein that correlates with the risk or progression of a disease, or with the susceptibility of the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
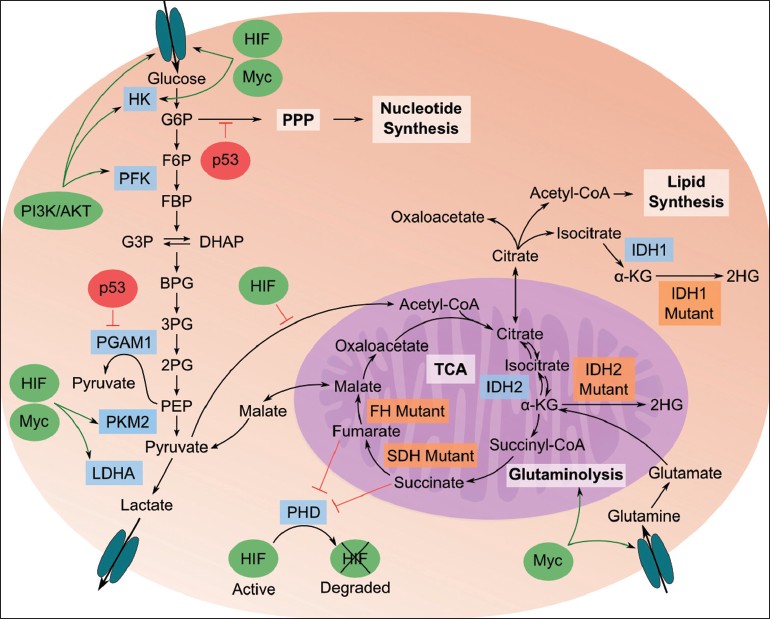
Tumor M2-PK
Tumor M2-PK is a synonym for the Dimer (chemistry), dimeric form of the pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 (PKM2), a key enzyme within tumor metabolome, tumor metabolism. Tumor M2-PK can be elevated in many tumor types, rather than being an organ-specific tumor marker such as prostate specific antigen, PSA. Increased stool (fecal) levels are being investigated as a method of screening for colorectal cancer, colorectal tumors, and EDTA blood plasma, plasma levels are undergoing testing for possible application in the follow-up of various cancers. Sandwich ELISAs based on two monoclonal antibodies which specifically recognize Tumor M2-PK (the dimeric form of M2-PK) are available for the quantification of Tumor M2-PK in stool and EDTA-plasma samples respectively. As a biomarker, the amount of Tumor M2-PK in stool and EDTA-plasma reflects the specific metabolic status of the tumors. Early detection of colorectal tumors and polyps M2-PK, as measured in feces, is a potential tumor marke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood In The Stool
Blood in stool looks different depending on how early it enters the digestive tract—and thus how much digestive action it has been exposed to—and how much there is. The term can refer either to melena, with a black appearance, typically originating from upper gastrointestinal bleeding; or to hematochezia, with a red color, typically originating from lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Evaluation of the blood found in stool depends on its characteristics, in terms of color, quantity and other features, which can point to its source, however, more serious conditions can present with a mixed picture, or with the form of bleeding that is found in another section of the tract. The term "blood in stool" is usually only used to describe visible blood, and not fecal occult blood, which is found only after physical examination and chemical laboratory testing. In infants, the Apt test can be used to distinguish fetal hemoglobin from maternal blood based on the differences in composition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Metabolome
The study of the tumor metabolism, also known as tumor metabolome describes the different characteristic metabolic changes in tumor cells. The characteristic attributes of the tumor metabolome are high glycolytic enzyme activities, the expression of the pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2, increased channeling of glucose carbons into synthetic processes, such as nucleic acid, amino acid and phospholipid synthesis, a high rate of pyrimidine and purine de novo synthesis, a low ratio of Adenosine triphosphate and Guanosine triphosphate to Cytidine triphosphate and Uridine triphosphate, low Adenosine monophosphate levels, high glutaminolytic capacities, release of immunosuppressive substances and dependency on methionine. Although the link between the cancer and metabolism was observed in the early days of cancer research by Otto Heinrich Warburg, which is also known as Warburg hypothesis, not much substantial research was carried out until the late 1990s because of the lack of ''in vit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Positive
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test result incorrectly indicates the absence of a condition when it is actually present. These are the two kinds of errors in a binary test, in contrast to the two kinds of correct result (a and a ). They are also known in medicine as a false positive (or false negative) diagnosis, and in statistical classification as a false positive (or false negative) error. In statistical hypothesis testing the analogous concepts are known as type I and type II errors, where a positive result corresponds to rejecting the null hypothesis, and a negative result corresponds to not rejecting the null hypothesis. The terms are often used interchangeably, but there are differences in detail and interpretation due to the differences between medical testing and statist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Screening
Cancer screening aims to detect cancer before symptoms appear. This may involve blood tests, urine tests, DNA tests, other tests, or medical imaging. The benefits of screening in terms of cancer prevention, early detection and subsequent treatment must be weighed against any harms. Universal screening, also known as mass screening or population screening, involves screening everyone, usually within a specific age group. Selective screening identifies people who are known to be at higher risk of developing cancer, such as people with a family history of cancer. Screening can lead to false positive results and subsequent invasive procedures. Screening can also lead to false negative results, where an existing cancer is missed. Controversy arises when it is not clear if the benefits of screening outweigh the risks of the screening procedure itself, and any follow-up diagnostic tests and treatments. Screening tests must be effective, safe, well tolerated with acceptably low rates o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)