|
Māori Potatoes
Māori potatoes or taewa are varieties of potatoes, potato (''Solanum tuberosum'' subsp. ''tuberosum'' and ''andigena'') cultivated by Māori people, especially those grown before New Zealand was colonised by the British. Māori have grown potatoes for at least 200 years, and "taewa" refers collectively to some traditional varieties, including Karuparerā, Huakaroro, Raupī, Moemoe, and Tūtae-kurī. These are smaller, knobblier, and more colourful than modern potato varieties, which are referred to by the loanword ''pārete''. Other collective names for traditional Māori potatoes are ''rīwai'', ''parareka'' and ''mahetau.'' Māori potatoes are commonly used as a base ingredient in rewena bread. Origins and history Potatoes originate in the Andes and temperate, and were introduced into Europe in the second half of the 16th century, part of the Columbian exchange. Māori traditions maintain that taewa were cultivated well before Europeans first visited Aotearoa. Despite t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piper Excelsum
''Piper excelsum'' (formerly known as ''Macropiper excelsum''), of the Pepper Family (Piperaceae) commonly known as kawakawa, is a small tree to 20 feet (six meters)of which the subspecies ''P. excelsum'' subsp. ''excelsum'' is endemic to New Zealand; the subspecies ''P. e.'' subsp. ''psittacorum'' is found on Lord Howe Island, Norfolk Island and the Kermadec Islands. Description Kawakawa is found throughout the North Island, and as far south as Okarito (43.20 °S) on the West Coast, and Banks Peninsula (43.5 °S) on the east coast of the South Island. The leaves are often covered with holes caused by the caterpillar of the kawakawa looper moth (''Cleora scriptaria''). The images depict the variety ''majus'' which has larger and more glossy leaves than ''P. excelsum''. The name ''kawakawa'' comes from the Māori language, where it refers to the bitter taste of the leaves, from ''kawa'' or bitter. Leaves Kawakawa leaves are about 5–10 cm long by 6–12 cm wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
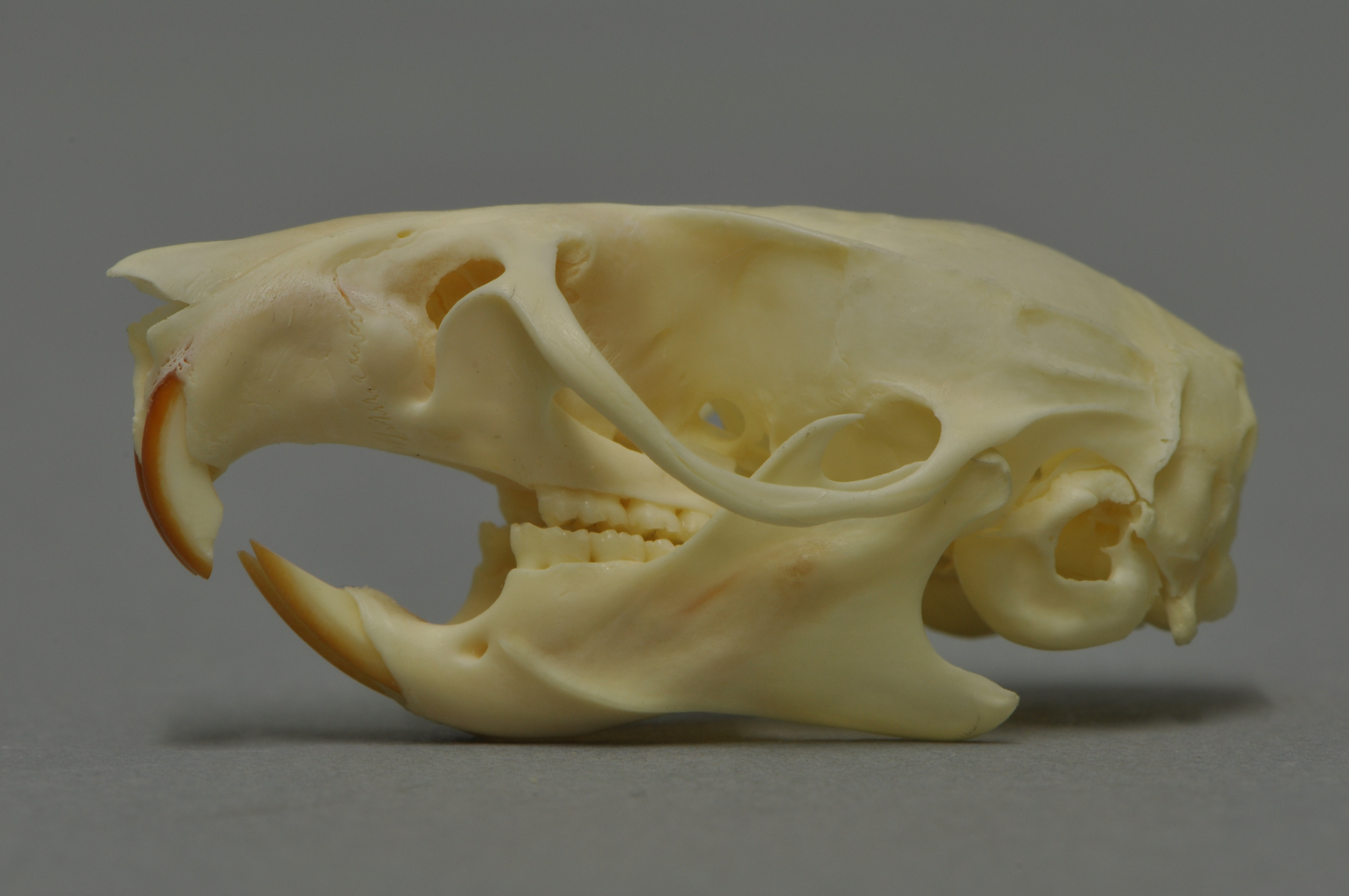
European Rabbit
The European rabbit (''Oryctolagus cuniculus'') or coney is a species of rabbit native to the Iberian Peninsula (including Spain, Portugal, and southwestern France), western France, and the northern Atlas Mountains in northwest Africa. It has been widely introduced elsewhere, often with devastating effects on local biodiversity. Its decline in its native range due to myxomatosis, rabbit calicivirus, overhunting and habitat loss has caused the decline of the Iberian lynx (''Lynx pardinus'') and Spanish imperial eagle (''Aquila adalberti''). It is known as an invasive species because it has been introduced to countries on all continents with the exception of Antarctica, and has caused many problems within the environment and ecosystems; in particular, European rabbits in Australia have had a devastating impact, due in part to the lack of natural predators there. The European rabbit is well known for digging networks of burrows, called warrens, where it spends most of its tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasian Swamphen
The Australasian swamphen (''Porphyrio melanotus'') is a species of swamphen (''Porphyrio'') occurring in eastern Indonesia (the Moluccas, Aru and Kai Islands), Papua New Guinea, Australia and New Zealand. In New Zealand, it is known as the pukeko (from the Māori ). The species used to be considered a subspecies of the purple swamphen. Distribution The Australasian swamphen occurs in mainland Australia, eastern Indonesia, the Moluccas, Aru and Kai Islands, and in Papua New Guinea. It is also found on New Zealand's main islands and in the Chatham and Kermadec Islands. It has a small shield, black upperparts, and a purple throat and breast. ''P. p. pelewensis'' (Hartlaub & Finsch, 1872) from Palau, resembles ''melanotus'' but has greener upperparts and is smaller. ''P. p. melanopterus'' (Bonaparte, 1856) is found from the Lesser Sundas and Moluccas to New Guinea. It is as ''melanotus'' but smaller, more variable and less blue in the upperparts. ''P. p. bellus'' (Gould, 182 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is now one of the widest-ranging mammals in the world, as well as the most widespread suiform. It has been assessed as least concern on the IUCN Red List due to its wide range, high numbers, and adaptability to a diversity of habitats. It has become an invasive species in part of its introduced range. Wild boars probably originated in Southeast Asia during the Early Pleistocene and outcompeted other suid species as they spread throughout the Old World. , up to 16 subspecies are recognized, which are divided into four regional groupings based on skull height and lacrimal bone length. The species lives in matriarchal societies consisting of interrelated females and their young (both male and female). Fully grown males are usually solitary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Rat
The brown rat (''Rattus norvegicus''), also known as the common rat, street rat, sewer rat, wharf rat, Hanover rat, Norway rat, Norwegian rat and Parisian rat, is a widespread species of common rat. One of the largest muroids, it is a brown or grey rodent with a head and body length of up to long, and a tail slightly shorter than that. It weighs between . Thought to have originated in northern China and neighbouring areas, this rodent has now spread to all continents except Antarctica, and is the dominant rat in Europe and much of North America. With rare exceptions, the brown rat lives wherever humans live, particularly in urban areas. Selective breeding of the brown rat has produced the fancy rat (rats kept as pets), as well as the laboratory rat (rats used as model organisms in biological research). Both fancy rats and laboratory rats are of the domesticated subspecies ''Rattus norvegicus domestica''. Studies of wild rats in New York City have shown that populations livi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide. The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore and a serious pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple in Deshnoke. Taxonomy ''Mus rattus'' was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the black rat. Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually color morphs: *''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat *''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat *''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat Characteristics A typical adult black rat is long, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactericera Cockerelli
''Bactericera cockerelli'', also known as the potato psyllid, is a species of Psylloidea, psyllid native to southern North America. Its range extends from Central America north to the American Pacific Northwest and parts of Manitoba, in Canada. It is restricted to the western part of the continent. As its name suggests, it is commonly found on potato and tomato crops, but has a species range that encompasses over 40 species of Solanaceae, solanaceous plants and as many as 20 genera. Breeding hosts are generally recognised as being restricted primarily to Solanaceae, including important crop and common weed species, and a few species of Convolvulaceae, including bindweed and sweet potato. On some plants, especially potato, feeding of the nymphs causes a condition called psyllid yellows, presumed to be the result of a toxin. Both nymphs and adults can transmit the bacterium Candidatus Liberibacter. Zebra chip is a recently diagnosed disease of potatoes associated with psyll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henosepilachna Vigintioctopunctata
''Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata '' is a species of beetle in the family Coccinellidae. It is commonly known as the 28-spotted potato ladybird or the Hadda beetle. It feeds on the foliage of potatoes and other solanaceous crops. It was previously called ''Epilachna vigintioctopunctata'' and is a cryptic species complex. It is very often confused with a closely related species, '' Henosepilachna vigintioctomaculata'', which occurs in Russia, China, Japan, and Korea, and is given the same "common name". Distribution This species is native to southeastern Asia, primarily India, but has been accidentally introduced to other parts of the world, including Australia and New Zealand. It has also been recorded from Brazil and Argentina, beginning in 1996. Economic significance This species causes damage to agricultural crops primarily in the family Solanaceae, especially potatoes; other crops include pumpkin, turnips, radishes, beans and spinach Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysodeixis Eriosoma
''Chrysodeixis eriosoma'', the green garden looper, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. Mostly cosmopolitan in distribution, it is a pest in Japan, China, India, Sri Lanka, the Malay Peninsula and Australasia. It is present in Hawaii and recorded as an incursion in mainland North America and Russia. It is morphologically identical to ''Chrysodeixis chalcites'' and the two may be sibling species. Description Adult ''Chrysodeixis eriosoma'' has a wingspan of 42 mm. Some specimens are much darker than others. ''Chrysodeixis eriosoma'' differs from '' C. signata'' in the head, thorax, and forewing having a reddish tinge; abdomen with the lateral and anal tufts often black in the male. Forewing with much more gilding on the basal, medial, and outer areas; the antemedial line more oblique, the postmedial more oblique and sinuous; the Y mark large, prominent, and golden, the arms often filled in with golden and occasionally joined to the tail. ''Chrysodeixis eriosoma'' and ''Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrosiphum Euphorbiae
''Macrosiphum euphorbiae'', the potato aphid, is a sap-sucking pest insect in the family Aphididae. It infests potatoes and a number of other commercially important crops. Distribution ''Macrosiphum euphorbiae'' originated in North America but it has spread to the temperate parts of Europe and Asia and is found in all areas in which potatoes are grown. Description The wingless female potato aphid is green or occasionally pink, often with a darker dorsal stripe. It has a pear-shaped body reaching about four millimetres long. The antennae are dark at the joints between the segments and are longer than the body. They are set on outward facing tubercles. The legs are longer than in other aphids, pale green but darker at the apices. The siphunculi are pale coloured, cylindrical with dark tips and operculi, and are about one third the length of the body. The tail is sword-shaped and bears 6 to 12 hairs and is much shorter than the siphunculi. The winged female has a uniform darker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulacorthum Solani
The foxglove aphid, (''Aulacorthum solani''), also known as glasshouse-potato aphid, is an aphid in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from plants. Host It has one of the broadest host ranges of any aphid in the world, where they both hosts on dicots and monocots. Economic importance It is known to be a major insect pest on tomato, peppers, tobacco, celery, carrots, tulip bulbs, cucurbits and legume A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock f ...s. References External links * http://influentialpoints.com/Gallery/Aulacorthum_solani_Glasshouse-potato_aphid_Foxglove_aphid.htm * * * Macrosiphini Agricultural pest insects {{Aphididae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(Sylvilagus_palustris).jpg)