|
Mycena Alcalina
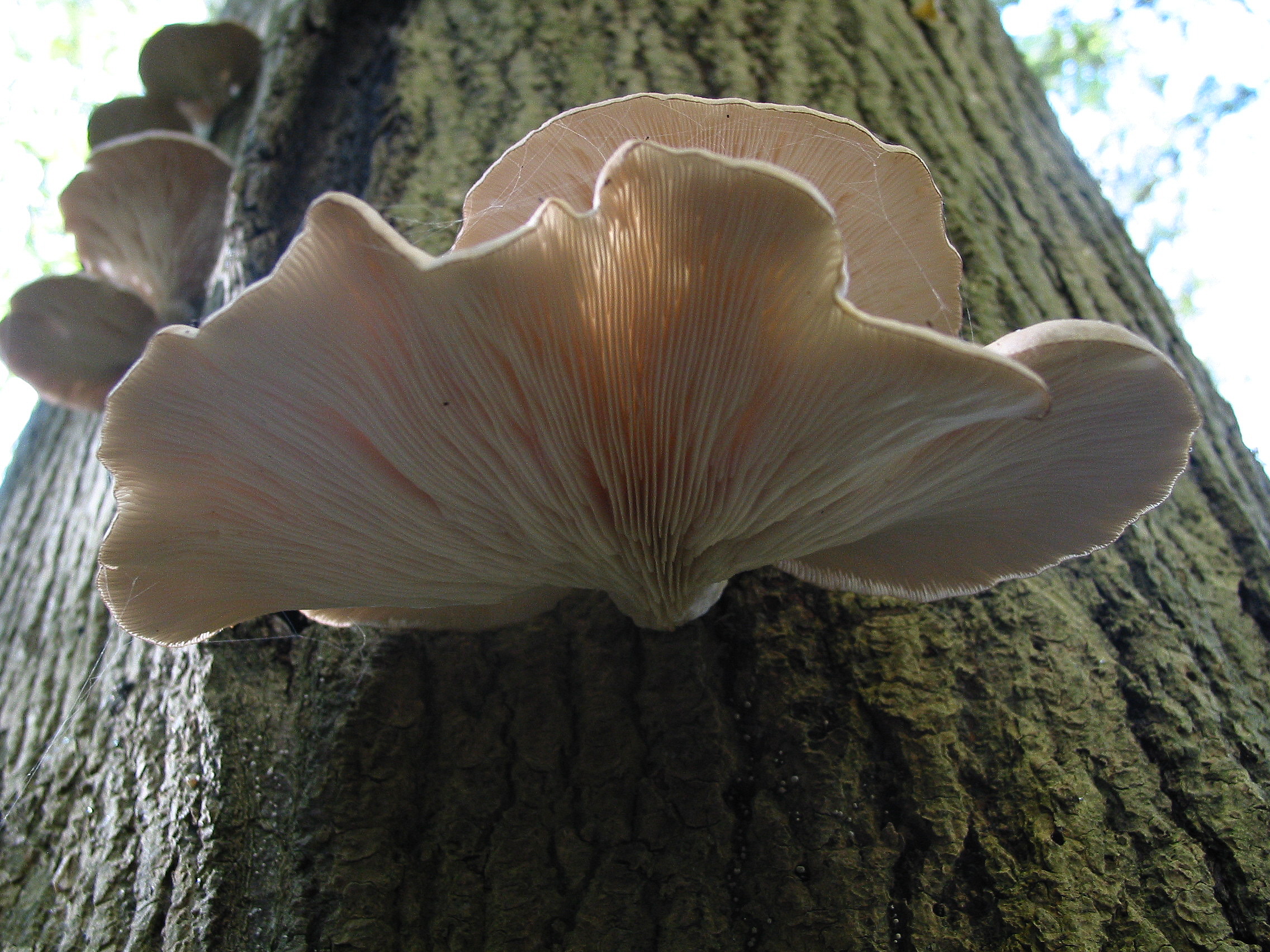
''Mycena alcalina'', commonly known as the stump fairy helmet mushroom, is a species of fungus in the family Mycenaceae. It grows widely, ranging from North America to Europe. Taxonomy ''Mycena'' is a genus of saprotrophic mushroom. The name "''Mycena''" comes from the Ancient Greek μύκης, or , meaning "mushroom." It is characterized by a white/grey spore print, small conical (bell-shaped) cap, and very thin stem. The genus ''Mycena'' is fairly large and includes many species including ''Mycena alcalina'', Mycena leptocephala, Mycena austera, and Mycena brevipes. Species found in the genus ''Mycena'' are typically known as ''bonnets''. Description The cap of ''Mycena alcalina'' ranges from conical to bell shaped and is generally 1–4 cm in diameter. The cap is supported by a thin, hollow stem growing anywhere from 20–65mm long. The cap appears black at first, but fades to a grey-brown colour around the edges, with the stem generally being the same colour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Hendrik Persoon
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon (1 February 1761 – 16 November 1836) was a German mycologist who made additions to Linnaeus' mushroom taxonomy. Early life Persoon was born in South Africa at the Cape of Good Hope, the third child of an immigrant Pomeranian father and Dutch mother. His mother died soon after he was born; at the age of thirteen his father (who died a year later) sent him to Europe for his education. Education Initially studying theology at Halle, at age 22 (in 1784) Persoon switched to medicine at Leiden and Göttingen. He received a doctorate from the "Kaiserlich-Leopoldinisch-Carolinische Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher" in 1799. Later years He moved to Paris in 1802, where he spent the rest of his life, renting an upper floor of a house in a poor part of town. He was apparently unemployed, unmarried, poverty-stricken and a recluse, although he corresponded with botanists throughout Europe. Because of his financial difficulties, Persoon agreed to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude-Casimir Gillet
Claude Casimir Gillet (19 May 1806 in Dormans, department of Marne – 1 September 1896 in Alençon), was a French botanist and mycologist. He initially trained as a medical doctor and veterinarian. As a veterinarian, he worked for four years in Africa. Around 1853 he developed a passion for mycology, subsequently publishing a number of works on the subject. In 1867 he became a corresponding member of the ''Société Linnéenne de Normandie''. Gillet was the taxonomic authority of the genera ''Tubaria'' (initially named a subgenus of ''Agaricus'' by Worthington George Smith) and ''Microglossum''. MycoBank. International Mycological Association He was honoured in 1899, when botanists P.A.Saccardo & P.Sydow published '' |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenaceae
The Mycenaceae are a family of fungi in the order Agaricales. According to the ''Dictionary of the Fungi'' (10th edition, 2008), the family contains 10 genera and 705 species. This is one of several families that were separated from the Tricholomataceae as a result of phylogenetic analyses. Taxa in the Mycenaceae are saprobic, have a cosmopolitan distribution, and are found in almost all ecological zones. The family was circumscribed by Caspar van Overeem in 1926. The extinct genus ''Protomycena'', described from Burdigalian age Dominican amber found on the island of Hispaniola is one of four known agaric genera in the fossil record. Phylogeny A large-scale phylogenetic analysis study of the Agaricales published by a consortium of mycologists in 2002 adopted the name Mycenaceae for a strongly supported clade consisting of ''Dictyopanus'', '' Favolaschia'', ''Mycena ''Mycena'' is a large genus of small saprotrophic mushrooms that are rarely more than a few centimeters in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saprotrophic
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi (for example ''Mucor'') and soil bacteria. Saprotrophic microscopic fungi are sometimes called saprobes; saprotrophic plants or bacterial flora are called saprophytes ( sapro- 'rotten material' + -phyte 'plant'), although it is now believed that all plants previously thought to be saprotrophic are in fact parasites of microscopic fungi or other plants. The process is most often facilitated through the active transport of such materials through endocytosis within the internal mycelium and its constituent hyphae. states the purpose of saprotrophs and their internal nutrition, as well as the main two types of fungi that are most often referred to, as well as describes, visually, the process of saprotrophic nutrition through a diagram of hyph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycena Leptocephala
''Mycena leptocephala'', commonly known as the nitrous bonnet, is a species of fungus in the family Mycenaceae. The mushrooms have conical grayish caps that reach up to in diameter, and thin fragile stems up to long. The gills are gray and distantly spaced. The spores are elliptical, typically measure 7–10 by 4–6 μm, and are white in deposit. When viewed under a light microscope, the gills have abundant spindle-shaped cystidia on the gill edges, but few on the gill faces. The mushroom is found in North America, Asia, and Europe where it grows singly or in groups on conifer needles, cones and sticks on the forest floor. It has a distinctive odor of bleach; the edibility is unknown. Similar species include ''Mycena alcalina'', '' M. austera'', and '' M. brevipes''. Taxonomy The species was first called ''Agaricus leptocephalus'' by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1800, and was transferred to the genus ''Mycena'' in 1876 by French mycologist Claude-Casimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycena Austera
''Mycena'' is a large genus of small saprotrophic mushrooms that are rarely more than a few centimeters in width. They are characterized by a white spore print, a small conical or bell-shaped cap, and a thin fragile stem. Most are gray or brown, but a few species have brighter colors. Most have a translucent and striate cap, which rarely has an incurved margin. The gills are attached and usually have cystidia. Some species, like '' Mycena haematopus'', exude a latex when the stem is broken, and many species have a chlorine or radish-like odor. Overview ''Mycenas'' are hard to identify to species and some are distinguishable only by microscopic features such as the shape of the cystidia. Some species are edible, while others contain toxins, but the edibility of most is not known, as they are likely too small to be useful in cooking. ''Mycena pura'' contains the mycotoxin muscarine, but the medical significance of this is unknown. Over 58 species are known to be bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycena Brevipes
''Mycena'' is a large genus of small saprotrophic mushrooms that are rarely more than a few centimeters in width. They are characterized by a white spore print, a small conical or bell-shaped cap, and a thin fragile stem. Most are gray or brown, but a few species have brighter colors. Most have a translucent and striate cap, which rarely has an incurved margin. The gills are attached and usually have cystidia. Some species, like '' Mycena haematopus'', exude a latex when the stem is broken, and many species have a chlorine or radish-like odor. Overview ''Mycenas'' are hard to identify to species and some are distinguishable only by microscopic features such as the shape of the cystidia. Some species are edible, while others contain toxins, but the edibility of most is not known, as they are likely too small to be useful in cooking. ''Mycena pura'' contains the mycotoxin muscarine, but the medical significance of this is unknown. Over 58 species are known to be bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
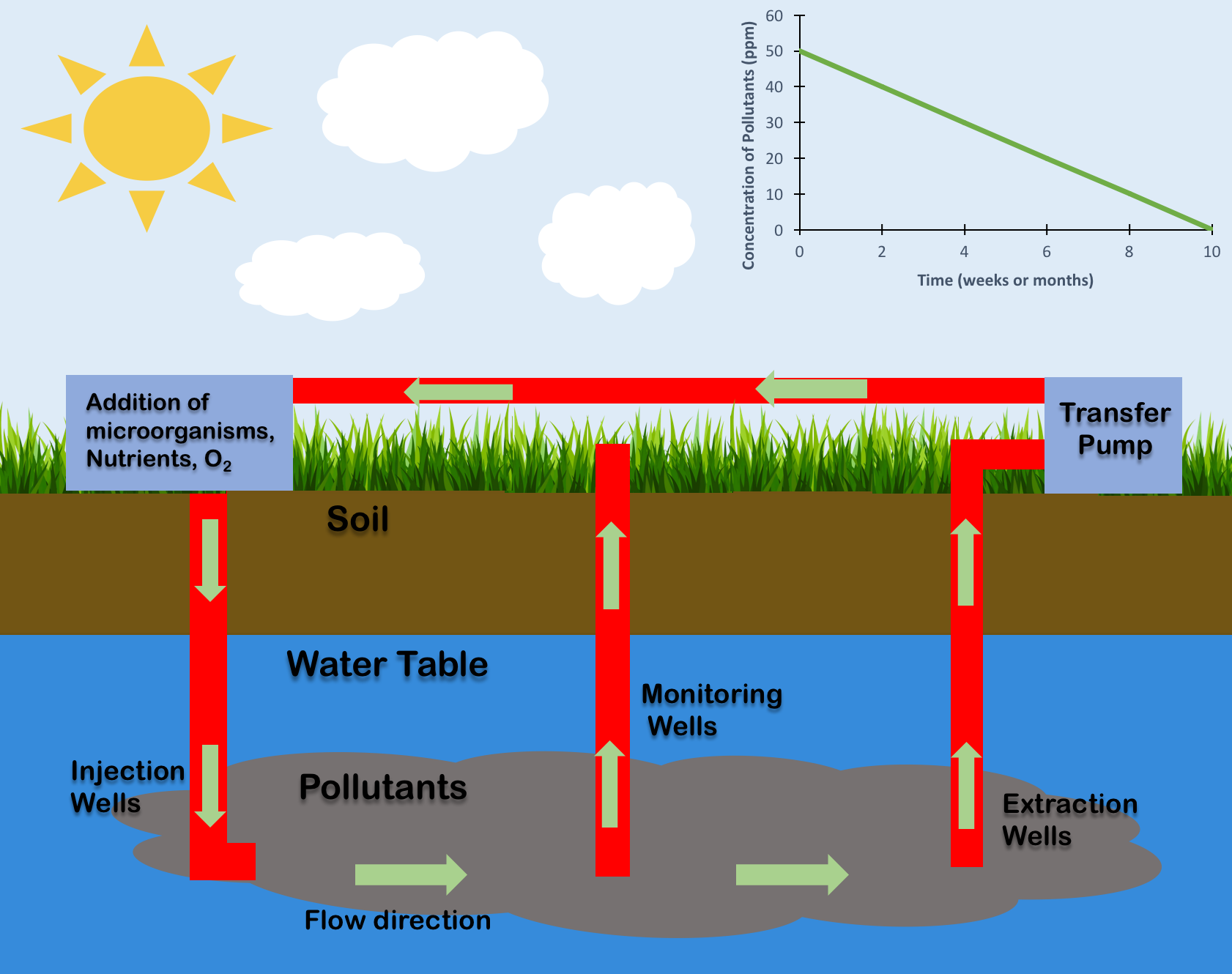
Mycoremediation
Mycoremediation (from ancient Greek ''μύκης (mukēs)'', meaning "fungus" and the suffix ''-remedium'', in Latin meaning 'restoring balance') is a form of bioremediation in which fungi-based remediation methods are used to decontaminate the environment. Fungi have been proven to be a cheap, effective and environmentally sound way for removing a wide array of contaminants from damaged environments or wastewater. These contaminants include heavy metals, organic pollutants, textile dyes, leather tanning chemicals and wastewater, petroleum fuels, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, pharmaceuticals and personal care products, pesticides and herbicides in land, fresh water, and marine environments. The byproducts of the remediation can be valuable materials themselves, such as enzymes (like laccase), edible or medicinal mushrooms, making the remediation process even more profitable. Some fungi are useful in the biodegradation of contaminants in extremely cold or radioactive environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer considerable advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote the growth. In principle, bioremediation could be used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperaccumulators
A hyperaccumulator is a plant capable of growing in soil or water with very high concentrations of metals, absorbing these metals through their roots, and concentrating extremely high levels of metals in their tissues. The metals are concentrated at levels that are toxic to closely related species not adapted to growing on the metalliferous soils. Compared to non-hyperaccumulating species, hyperaccumulator roots extract the metal from the soil at a higher rate, transfer it more quickly to their shoots, and store large amounts in leaves and roots. The ability to hyperaccumulate toxic metals compared to related species has been shown to be due to differential gene expression and regulation of the same genes in both plants. Hyperaccumulating plants are of interest for their ability to extract metals from the soils of contaminated sites (phytoremediation) to return the ecosystem to a less toxic state. The plants also hold potential to be used to mine metals from soils with very high c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |