|
Musical Transposition
In music, transposition refers to the process or operation of moving a collection of notes ( pitches or pitch classes) up or down in pitch by a constant interval. For example, one might transpose an entire piece of music into another key. Similarly, one might transpose a tone row or an unordered collection of pitches such as a chord so that it begins on another pitch. The transposition of a set ''A'' by ''n'' semitones is designated by ''T''''n''(''A''), representing the addition ( mod 12) of an integer ''n'' to each of the pitch class integers of the set ''A''. Thus the set (''A'') consisting of 0–1–2 transposed by 5 semitones is 5–6–7 (''T''5(''A'')) since , , and . Scalar transpositions In scalar transposition, every pitch in a collection is shifted up or down a fixed number of scale steps within some scale. The pitches remain in the same scale before and after the shift. This term covers both chromatic and diatonic transpositions as follows. Chromatic transpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposition Example From Koch
Transposition may refer to: Logic and mathematics * Transposition (mathematics), a permutation which exchanges two elements and keeps all others fixed * Transposition, producing the transpose of a matrix ''A''T, which is computed by swapping columns for rows in the matrix ''A'' * Transpose of a linear map * Transposition (logic), a rule of replacement in philosophical logic * Transpose relation, another name for converse relation Games * Transposition (chess), different moves or a different move order leading to the same position, especially during the openings * Transposition table, used in computer games to speed up the search of the game tree Biology * Transposition (birth defect), a group of congenital defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of tissue or organ ** Transposition of the great vessels, cardiac transposition, a congenital heart defect with malformation of any of the major vessels ** Transposition of teeth ** Penoscrotal transposition * T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Math
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" when reaching a certain value, called the modulus. The modern approach to modular arithmetic was developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss in his book ''Disquisitiones Arithmeticae'', published in 1801. A familiar use of modular arithmetic is in the 12-hour clock, in which the day is divided into two 12-hour periods. If the time is 7:00 now, then 8 hours later it will be 3:00. Simple addition would result in , but clocks "wrap around" every 12 hours. Because the hour number starts over at zero when it reaches 12, this is arithmetic ''modulo'' 12. In terms of the definition below, 15 is ''congruent'' to 3 modulo 12, so "15:00" on a 24-hour clock is displayed "3:00" on a 12-hour clock. Congruence Given an integer , called a modulus, two integers and are said to be congruent modulo , if is a divisor of their difference (that is, if there is an integer such that ). Congruence modulo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enharmonic Equivalence
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written note, interval, or chord is an alternative way to write that note, interval, or chord. The term is derived from Latin ''enharmonicus'', from Late Latin ''enarmonius'', from Ancient Greek ἐναρμόνιος (''enarmónios''), from ἐν (''en'') and ἁρμονία (''harmonía''). Definition For example, in any twelve-tone equal temperament (the predominant system of musical tuning in Western music), the notes C and D are ''enharmonic'' (or ''enharmonically equivalent'') notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard, and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressions. Arbitrary amounts of accidentals can produce further enharmonic equivalents, such as B ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpositionally Equivalent
In music, transposition refers to the process or operation of moving a collection of notes ( pitches or pitch classes) up or down in pitch by a constant interval. For example, one might transpose an entire piece of music into another key. Similarly, one might transpose a tone row or an unordered collection of pitches such as a chord so that it begins on another pitch. The transposition of a set ''A'' by ''n'' semitones is designated by ''T''''n''(''A''), representing the addition ( mod 12) of an integer ''n'' to each of the pitch class integers of the set ''A''. Thus the set (''A'') consisting of 0–1–2 transposed by 5 semitones is 5–6–7 (''T''5(''A'')) since , , and . Scalar transpositions In scalar transposition, every pitch in a collection is shifted up or down a fixed number of scale steps within some scale. The pitches remain in the same scale before and after the shift. This term covers both chromatic and diatonic transpositions as follows. Chromatic transp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree (music)
In music theory, the scale degree is the position of a particular note on a scale relative to the tonic, the first and main note of the scale from which each octave is assumed to begin. Degrees are useful for indicating the size of intervals and chords and whether an interval is major or minor. In the most general sense, the scale degree is the number given to each step of the scale, usually starting with 1 for tonic. Defining it like this implies that a tonic is specified. For instance, the 7-tone diatonic scale may become the major scale once the proper degree has been chosen as tonic (e.g. the C-major scale C–D–E–F–G–A–B, in which C is the tonic). If the scale has no tonic, the starting degree must be chosen arbitrarily. In set theory, for instance, the 12 degrees of the chromatic scale usually are numbered starting from C=0, the twelve pitch classes being numbered from 0 to 11. In a more specific sense, scale degrees are given names that indicate their parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
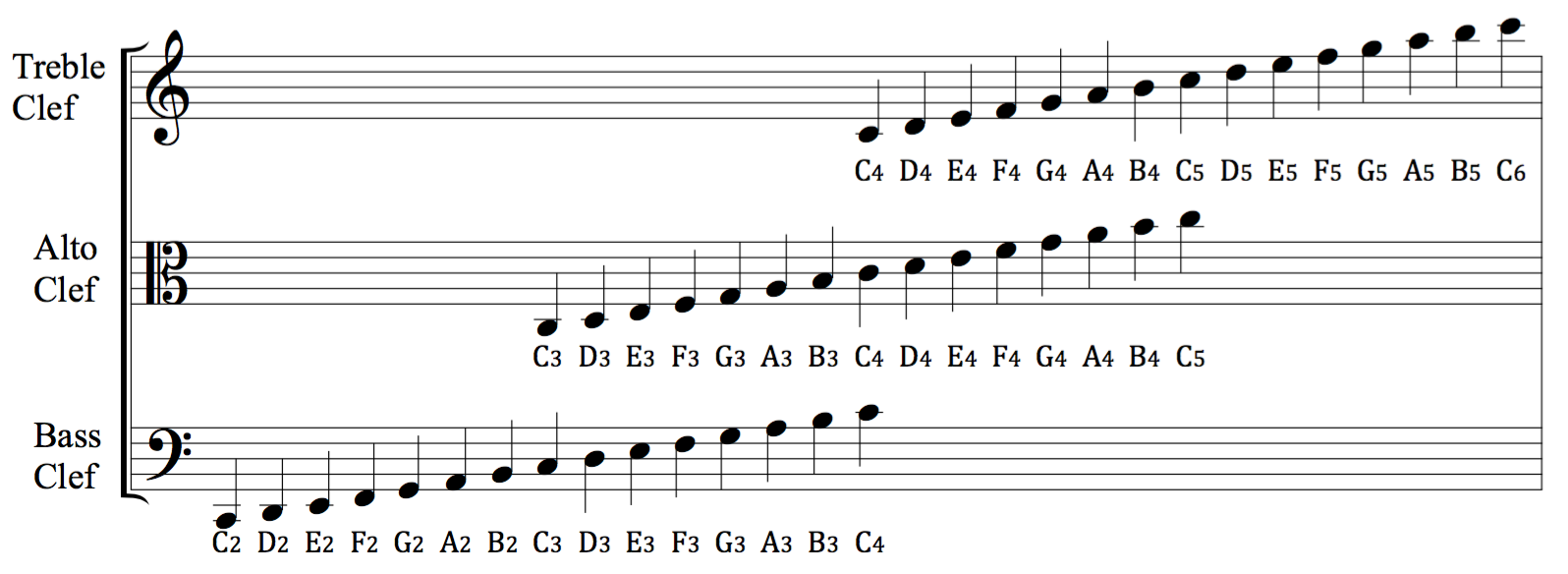
Staff Position
In Western musical notation, the staff (US and UK)"staff" in the Collins English Dictionary "in British English: also called: stave; plural: staffs or staves""staff" in the Merriam-Webster Dictionary /ref> or stave (UK) (: staffs or staves) is a set of five horizontal lines and four spaces that each represent a different musical pitch or in the case of a percussion staff, diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces. The three clef symbols used in modern music notation are the G-clef, F-clef, and C-clef. Placing these clefs on a line fixes a reference note to that line—an F-clef fixes the F below middle C C or Do is the first note and semitone of the C major scale, the third note of the A minor scale (the relative minor of C major), and the fourth note (G, A, B, C) of the Guidonian hand, commonly pitched around 261.63 Hz. The actual frequen ..., a C-clef fixes middle C, and a G-clef fixes the G above middle C. In modern music notation, the G-clef is most frequently seen as treble clef (placing Scientific pitch notation, G4 on the second line of the stave), and the F-clef as bass clef (placing F3 on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposing Instrument
A transposing instrument is a musical instrument for which music notation is not written at concert pitch (concert pitch is the pitch on a non-transposing instrument such as the piano). For example, playing a written middle C on a transposing instrument produces a pitch other than middle C; that sounding pitch identifies the interval of transposition when describing the instrument. Playing a written C on clarinet or soprano saxophone produces a concert B (i.e. B at concert pitch), so these are referred to as B instruments. Providing transposed music for these instruments is a convention of musical notation. The instruments do not transpose the music; rather, their music is written at a transposed pitch. Where chords are indicated for improvisation they are also written in the appropriate transposed form. For some instruments, a written C sounds as a C, but is in a different octave; these instruments are said to transpose "at the octave". Pitches on the piccolo sound an oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvorak 9, Trumpet Part Exerpt
Dvořák (feminine Dvořáková) is a Czech surname, originally referring to a servant or an official of manorial estate or royal court. Notable people include: People Dvořák or Dvorak Arts * Ann Dvorak (1912–1979), American film actress (stage name) * Antonín Dvořák (1841–1904), Czech composer * František Dvořák (painter), (1862-1927), Czech painter * Josef Dvořák (born 1942), Czech actor * Max Dvořák (1874–1921), Austrian art historian * Tomáš Dvořák (1978–), Czech composer Science * August Dvorak (1894–1975), co-creator of the Dvorak keyboard layout * John C. Dvorak (born 1952), computer-industry columnist and new-media personality * Vernon Dvorak (1928–2022), meteorologist, developer of method to estimate tropical-cyclone intensity Sports * Bedřich Dvořák canoeist * Ben Dvorak, NFL football player * Bill Dvořák (born 1958), American pioneering whitewater rafter * Christian Dvorak (born 1996), American ice hockey player * David Dvoř� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Signature
In Western musical notation, a key signature is a set of sharp (), flat (), or rarely, natural () symbols placed on the staff at the beginning of a section of music. The initial key signature in a piece is placed immediately after the clef at the beginning of the first line. If the piece contains a section in a different key, the new key signature is placed at the beginning of that section. In a key signature, a sharp or flat symbol on a line or space of the staff indicates that the note represented by that line or space is to be played a semitone higher (sharp) or lower (flat) than it would otherwise be played. This applies through the end of the piece or until another key signature is indicated. Each symbol applies to all notes in the same pitch class—for example, a flat on the third line of the treble staff (as in the diagram) indicates that all notes appearing as Bs are played as B-flats. This convention was not universal until the late Baroque and early Classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |