|
Muntz Metal
Muntz metal (also known as yellow metal) is an alpha-beta brass alloy composed of approximately 60% copper, 40% zinc and a trace of iron. It is named after George Fredrick Muntz, a metal-roller of Birmingham, England, who commercialised the alloy following his patent of 1832. The alloy must be worked hot and is used today for corrosion-resistant machine parts. Alpha-beta (also called duplex) metals contain both the α and β phases. The α phase refers to a crystal structure that is face-centered cubic, while the β phase is body-centered cubic. Its original application was as a replacement for copper sheathing on the bottom of boats, as it maintained the anti-fouling abilities of the pure copper at around two thirds of the price. It became the material of choice for this application and Muntz made his fortune. It was found that copper would gradually leach from the alloy in sea water, poisoning any organism that attempted to attach itself to a hull sheathed in the metal. Thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
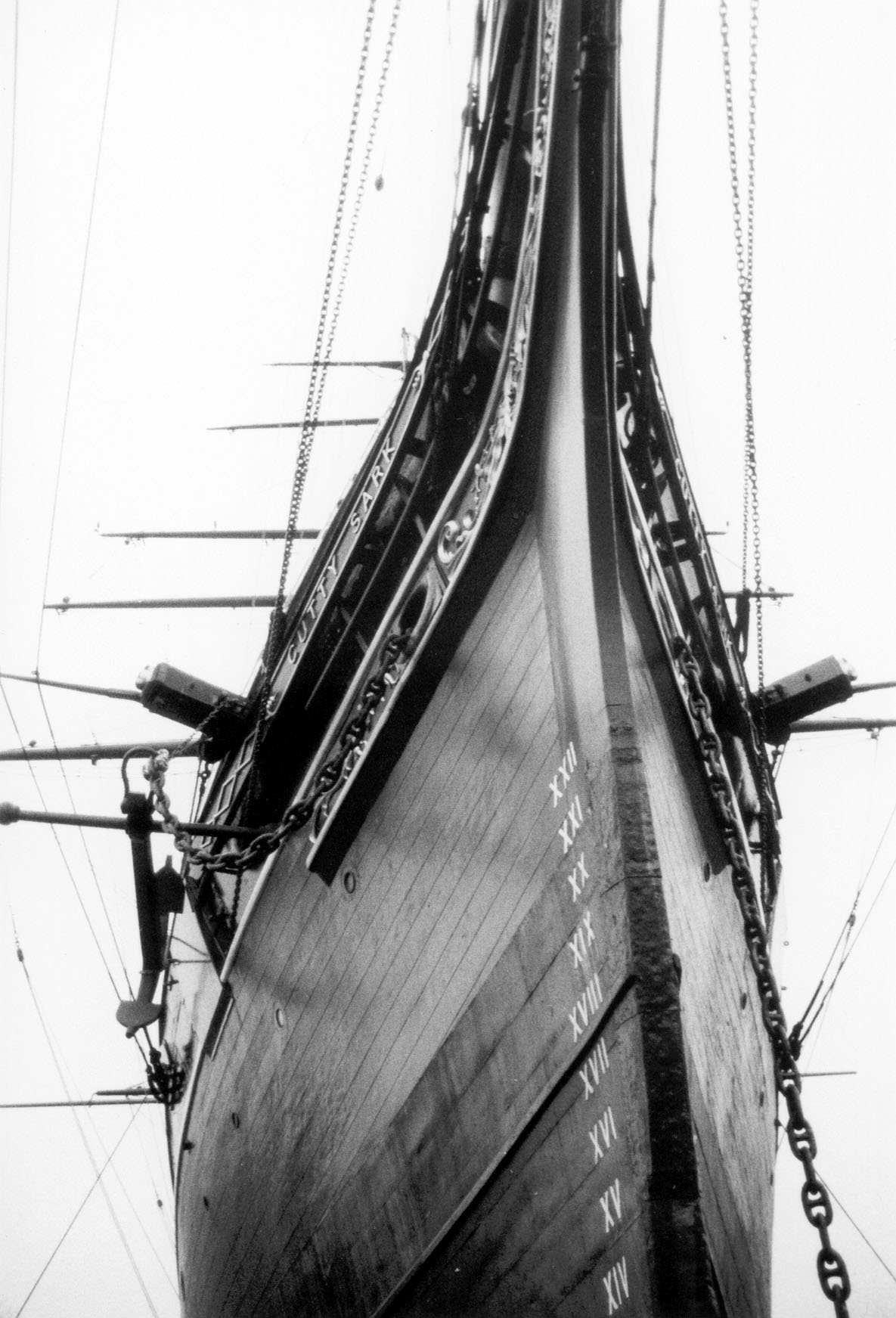
Cutty Sark Detail
Cutty may refer to: People * Cutty Cutshall, American jazz trombonist Robert Cutshall (1911–1968) * Cutty Ranks, Jamaican dancehall musician Philip Thomas (born 1965) * Cutty (rapper), a rapper featured on T.O.K.'s ''Bombrush Hour'' Other uses * Cutty grass, a common name for several grasses * Dennis "Cutty" Wise, a fictional character on the HBO drama ''The Wire'' See also * Cuddy (other) * Cuttie stool A cuttie-stool, or cutty-stool (also -stuil), was a type of three-legged chair used in Scotland. It was a short stool, often having a round seat on the top, but the word also designates a larger piece of furniture associated with public penance in ..., an inexpensive Scottish stool used in milking, and also for church penance * Cutty Sark (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Sheathing
Copper sheathing is the practice of protecting the under-water hull of a ship or boat from the corrosive effects of salt water and biofouling through the use of copper plates affixed to the outside of the hull. It was pioneered and developed by the Royal Navy during the 18th century. In antiquity, ancient Greeks used lead plates to protect the underwater hull. Development Deterioration of the hull of a wooden ship was a significant problem during the Age of Sail. Ships' hulls were under continuous attack by shipworm, barnacles and various marine weeds, all of which had some adverse effect on the ship, be it structurally, in the case of the worm, or affecting speed and handling in the case of the weeds. The most common methods of dealing with these problems were through the use of wood, and sometimes lead, sheathing. Expendable wood sheathing effectively provided a non-structural skin to the hull for the worm to attack, and could be easily replaced in dry dock at regular interva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-fouling Paint
Anti-fouling paint is a specialized category of coatings applied as the outer (outboard) layer to the hull of a ship or boat, to slow the growth of and facilitate detachment of subaquatic organisms that attach to the hull and can affect a vessel's performance and durability. It falls into a category of commercially available underwater hull paints, also known as ''bottom paints''. Anti-fouling paints are often applied as one component of multi-layer coating systems which may have other functions in addition to their antifouling properties, such as acting as a barrier against corrosion on metal hulls that will degrade and weaken the metal, or improving the flow of water past the hull of a fishing vessel or high-performance racing yachts. Although commonly discussed as being applied to ships, antifouling paints are also of benefit in many other sectors such as off-shore structures and fish farms. History In the Age of Sail, sailing vessels suffered severely from the growth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IMI Plc
IMI plc (), formerly Imperial Metal Industries, is a British-based engineering company headquartered in Birmingham, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index. History The company was founded by Scottish entrepreneur George Kynoch who opened a percussion cap factory in Witton, West Midlands in 1862, trading as ''Kynoch''. The business soon diversified, manufacturing goods ranging from soap and bicycle components to non-ferrous metals, but by the early 20th century it had developed particular expertise in metallurgy. After World War I it merged with Nobel Industries. In 1926 the company acquired Eley Brothers, an ammunition business. The company, by then known as ''Nobel Explosives'', was one of the four businesses that merged in 1927 to create Imperial Chemical Industries. The Witton site became the head office of ICI Metals. During the Second World War the Witton site was used for the development and production of uranium for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stour Valley Line
The Stour Valley Line is the present-day name given to the railway line between Birmingham and Wolverhampton, in England. It was authorised as the Birmingham, Wolverhampton and Stour Valley Railway in 1836; the title was often shortened to the Stour Valley Railway. The line opened in 1852, and the line is now the main line between those places. Associated with its construction was the building of the major passenger station that was later named New Street station, and also lines in tunnel each side of the station, connecting to the existing routes. The station was opened in 1854. Before completion, the Company became controlled by the London and North Western Railway, which used dubious methods to harm competitor railways that were to be dependent on its completion. The line was electrified in 1966 and now forms part of the Rugby–Birmingham–Stafford Line, an important and very heavily used part of the railway network. Origins Birmingham's first main railway passenger ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Watt Jr
James Watt junior, FRS (5 February 1769 – 2 June 1848) was a Scottish engineer, businessman and activist. Early life He was born on 5 February 1769, the son of James Watt by his first wife Margaret Miller, and half-brother of Gregory Watt. He was educated at Winson Green near Birmingham, by the Rev. Henry Pickering. His father was unable to find a better school, though dissatisfied with his son's progress. At age 15 Watt spent a year at the Bersham Ironworks of John Wilkinson; and then went to Geneva. There he lodged with Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure, and knew Marc-Auguste Pictet and Jean-André Deluc. Subsequently, he studied German in Eisenach. In Manchester In 1788 Watt returned to England and a position in the textile trade in Manchester. Initially he worked at Taylor & Maxwell, makers of fustian, where Charles Taylor was a partner. Watt worked there in the counting-house. He was then employed by the Manchester radical Thomas Walker, changing jobs just before the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smethwick
Smethwick () is an industrial town in Sandwell, West Midlands, England. It lies west of Birmingham city centre. Historically it was in Staffordshire. In 2019, the ward of Smethwick had an estimated population of 15,246, while the wider built-up area subdivision has a population of 53,653. History It was suggested that the name Smethwick meant "smiths' place of work", but a more recent interpretation has suggested the name means "the settlement on the smooth land". Smethwick was recorded in the Domesday Book as ''Smedeuuich'', the ''d'' in this spelling being the Anglo-Saxon letter eth. Until the end of the 18th century it was an outlying hamlet of the south Staffordshire village of Harborne. Harborne became part of the county borough of Birmingham and thus transferred from Staffordshire to Warwickshire in 1891, leaving Smethwick in the County of Staffordshire. The world's oldest working engine, the Smethwick Engine, made by Boulton & Watt, originally stood near Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
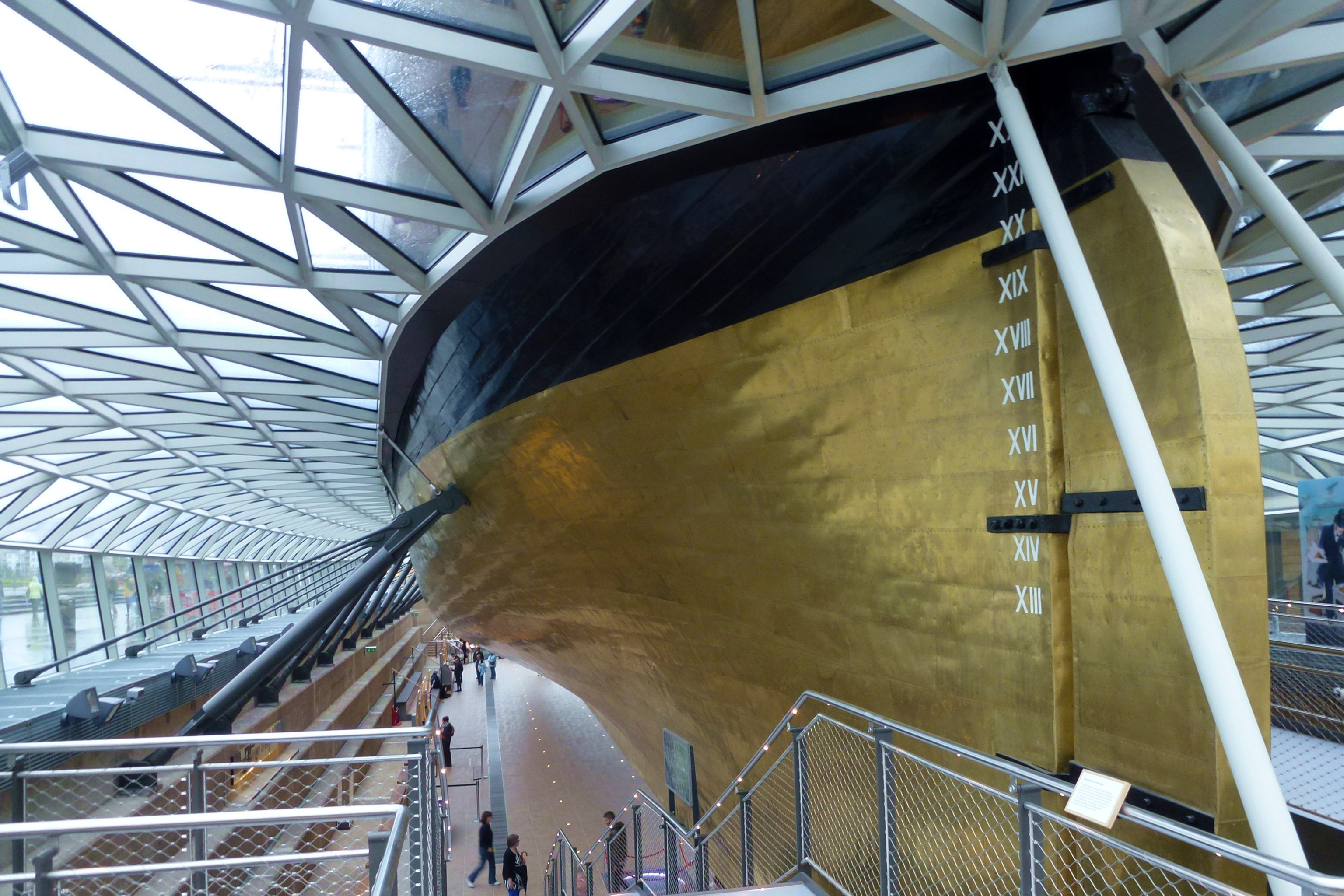
Cutty Sark
''Cutty Sark'' is a British clipper ship. Built on the River Leven, Dumbarton, Scotland in 1869 for the Jock Willis Shipping Line, she was one of the last tea clippers to be built and one of the fastest, coming at the end of a long period of design development for this type of vessel, which halted as steamships took over their routes. She was named after the apparel (short shirt) of the fictional witch in the Robert Burns poem: Tam o’ Shanter. After the big improvement in the fuel efficiency of steamships in 1866, the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 gave them a shorter route to China, so ''Cutty Sark'' spent only a few years on the tea trade before turning to the trade in wool from Australia, where she held the record time to Britain for ten years. Continuing improvements in steam technology meant that gradually steamships also came to dominate the longer sailing route to Australia, and the ship was sold to the Portuguese company Ferreira and Co. in 1895 and renamed ''Fer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
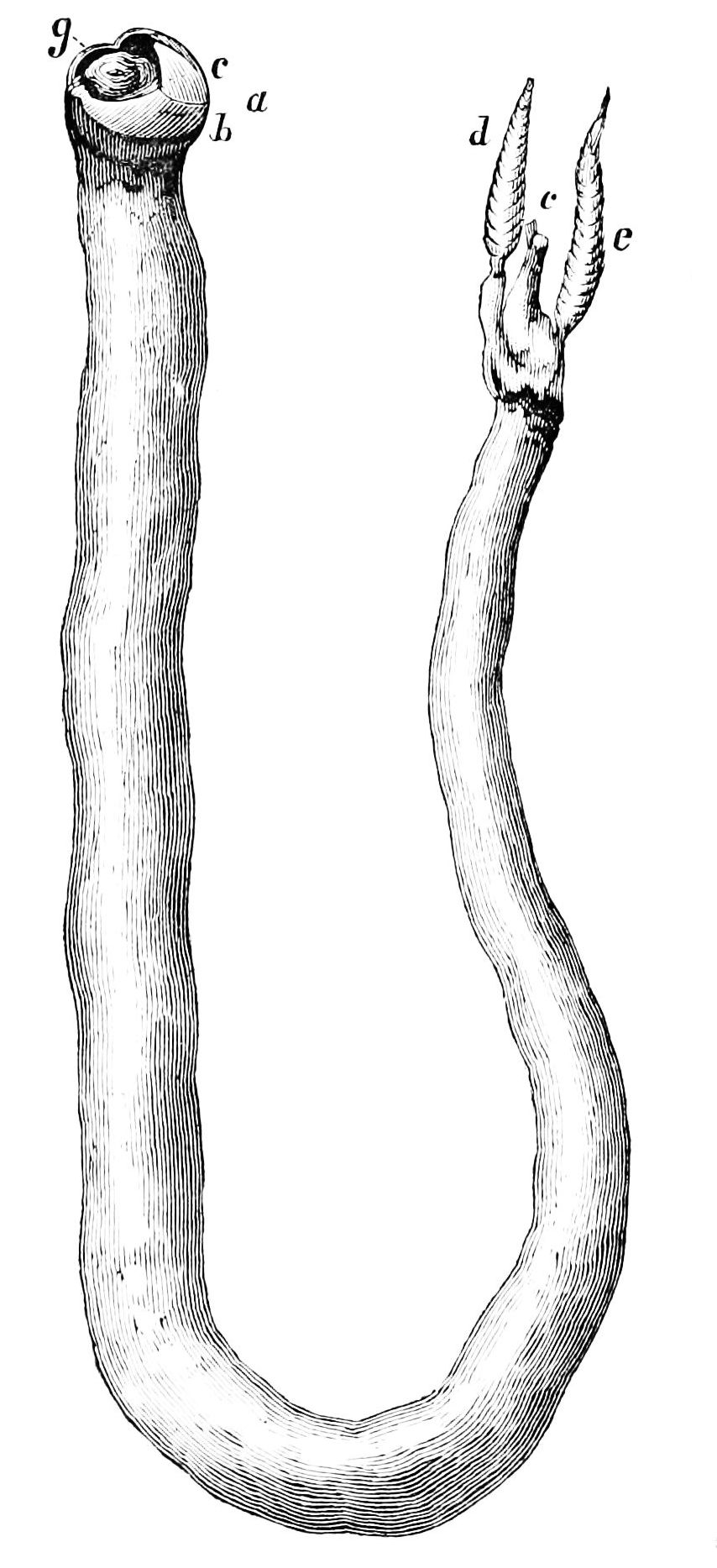
Shipworm
The shipworms are marine bivalve molluscs in the family Teredinidae: a group of saltwater clams with long, soft, naked bodies. They are notorious for boring into (and commonly eventually destroying) wood that is immersed in sea water, including such structures as wooden piers, docks and ships; they drill passages by means of a pair of very small shells (“valves”) borne at one end, with which they rasp their way through. Sometimes called "termites of the sea", they also are known as " Teredo worms" or simply Teredo (from grc, τερηδών, , translit=terēdṓn, lit=wood-worm via ). Carl Linnaeus assigned the common name '' Teredo'' to the best-known genus of shipworms in the 10th edition of his taxonomic ''magnum opus'', '' Systema Naturæ'' (1758). Description Removed from its burrow, the fully grown teredo ranges from several centimetres to about a metre in length, depending on the species. The body is cylindrical, slender, naked and superficially vermiform, meaning "w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-fouling
Biofouling or biological fouling is the accumulation of microorganisms, plants, algae, or small animals where it is not wanted on surfaces such as ship and submarine hulls, devices such as water inlets, pipework, grates, ponds, and rivers that cause degradation to the primary purpose of that item. Such accumulation is referred to as '' epibiosis'' when the host surface is another organism and the relationship is not parasitic. Since biofouling can occur almost anywhere water is present, biofouling poses risks to a wide variety of objects such as boat hulls and equipment, medical devices and membranes, as well as to entire industries, such as paper manufacturing, food processing, underwater construction, and desalination plants. Anti-fouling is the ability of specifically designed materials (such as toxic biocide paints, or non-toxic paints) to remove or prevent biofouling. The buildup of biofouling on marine vessels poses a significant problem. In some instances, the hull struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body-centered Cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc, and alternatively called ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp) Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais lattices in the cubic crystal system are: The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of one lattice point on each corner of the cube; this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one lattice point. Each atom at a lattice point is then shared equally between eight adjacent cubes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutty Sark Stern
Cutty may refer to: People * Cutty Cutshall, American jazz trombonist Robert Cutshall (1911–1968) * Cutty Ranks, Jamaican dancehall musician Philip Thomas (born 1965) * Cutty (rapper), a rapper featured on T.O.K.'s ''Bombrush Hour'' Other uses * Cutty grass, a common name for several grasses * Dennis "Cutty" Wise, a fictional character on the HBO drama ''The Wire'' See also * Cuddy (other) * Cuttie stool A cuttie-stool, or cutty-stool (also -stuil), was a type of three-legged chair used in Scotland. It was a short stool, often having a round seat on the top, but the word also designates a larger piece of furniture associated with public penance in ..., an inexpensive Scottish stool used in milking, and also for church penance * Cutty Sark (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_-_SLV_H91.250-164.jpg)