|
Mullissu-mukannishat-Ninua
Mullissu-mukannishat-Ninua (Akkadian: ''Mullissu-mukannišat-Nīnua'') was a queen of the Neo-Assyrian Empire as the primary consort of Ashurnasirpal II (883–859 BC). She was probably also the mother of his son and successor Shalmaneser III (859–824 BC). Mullissu-mukannishat-Ninua is only known from her tomb, discovered in Nimrud in 1989. She was the daughter of the "great cupbearer" Ashur-nirka-da’’inni and as such probably belonged to the Assyrian aristocracy before she became queen. Life Queen of Ashurnasirpal II Mullissu-mukannishat-Ninua is known only from her tomb and its contents, found in 1989 among the Queens' tombs at Nimrud in the ruins of the Northwest Palace of the ancient Assyrian capital of Nimrud. As a result, little is known of her other than her name. Per the inscription on the lid of her sarcophagus, she was the queen of Ashurnasirpal II (883–859 BC). Mullissu-mukannishat-Ninua was probably the first person to be buried in the tombs in the North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queens Of The Neo-Assyrian Empire
The queen (Assyrian: ''issi ekalli'' or ''sēgallu'', ) of the Neo-Assyrian Empire was the consort of the Neo-Assyrian king. Though the queens derived their power and influence through their association with their husband, they were not pawns without political power. The queens oversaw their own, often considerable, finances and owned vast estates throughout the empire. To oversee their assets, the queens employed a large administrative staff headed by a set of female administrators called ''šakintu''. Among the duties of the queens were religious responsibilities and overseeing parts of the royal palaces; their role as "rulers of the domestic realm" is reflected in their title as "Women of the Palace". The power and influence of the queens was increased further under the Sargonid dynasty (722–609 BC), when they more frequently appear in artwork and large military units directly subservient to the queen were created. The most famous and powerful Neo-Assyrian queen was Shamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Of The Neo-Assyrian Empire
The queen (Assyrian: ''issi ekalli'' or ''sēgallu'', ) of the Neo-Assyrian Empire was the consort of the Neo-Assyrian king. Though the queens derived their power and influence through their association with their husband, they were not pawns without political power. The queens oversaw their own, often considerable, finances and owned vast estates throughout the empire. To oversee their assets, the queens employed a large administrative staff headed by a set of female administrators called ''šakintu''. Among the duties of the queens were religious responsibilities and overseeing parts of the royal palaces; their role as "rulers of the domestic realm" is reflected in their title as "Women of the Palace". The power and influence of the queens was increased further under the Sargonid dynasty (722–609 BC), when they more frequently appear in artwork and large military units directly subservient to the queen were created. The most famous and powerful Neo-Assyrian queen was Shamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
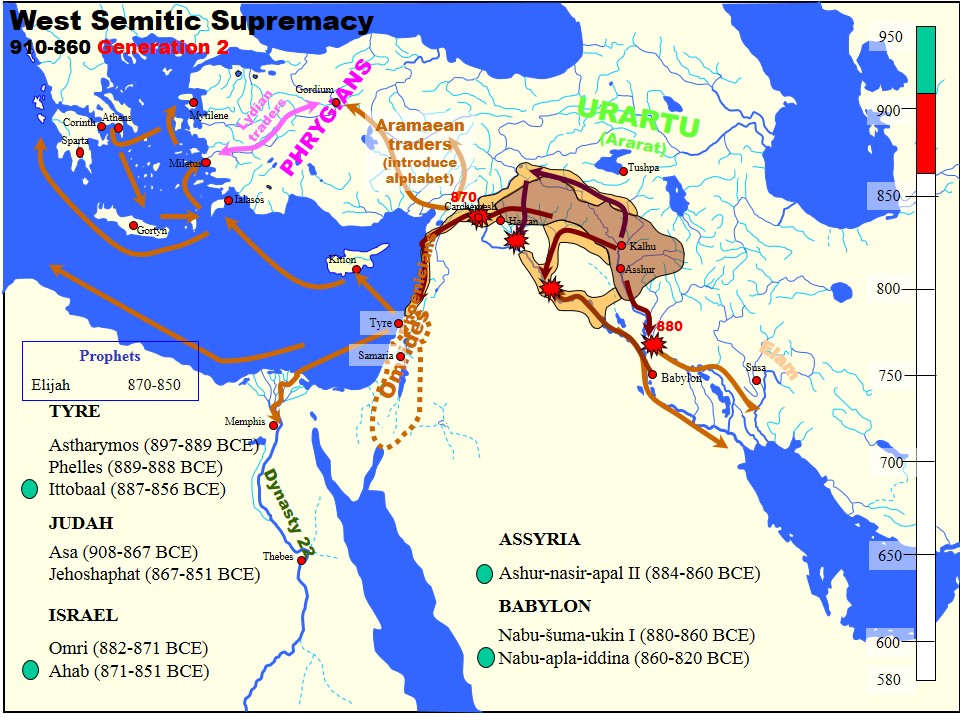
Ashurnasirpal II
Ashur-nasir-pal II (transliteration: ''Aššur-nāṣir-apli'', meaning " Ashur is guardian of the heir") was king of Assyria from 883 to 859 BC. Ashurnasirpal II succeeded his father, Tukulti-Ninurta II, in 883 BC. During his reign he embarked on a vast program of expansion, first conquering the peoples to the north in Asia Minor as far as Nairi and exacting tribute from Phrygia, then invading Aram (modern Syria) conquering the Aramaeans and Neo-Hittites between the Khabur and the Euphrates Rivers. His harshness prompted a revolt that he crushed decisively in a pitched, two-day battle. According to his monument inscription, while recalling this massacre he says: Following this victory, he advanced without opposition as far as the Mediterranean and exacted tribute from Phoenicia. On his return home, he moved his capital to the city of Kalhu (Nimrud). Family Ashurnasirpal II's father was Tukulti-Ninurta II. His son and successor was Shalmaneser III. His queen was Mullissu-muk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Ashurnasirpal II in 859 BC to his own death in 824 BC. His long reign was a constant series of campaigns against the eastern tribes, the Babylonians, the nations of Mesopotamia and Syria, as well as Kizzuwadna and Urartu. His armies penetrated to Lake Van and the Taurus Mountains; the Neo-Hittites of Carchemish were compelled to pay tribute, and the kingdoms of Hamath and Aram Damascus were subdued. It is in the annals of Shalmaneser III from the 850s BC that the Arabs and Chaldeans first appear in recorded history. Reign Campaigns Shalmaneser began a campaign against the Urartian Kingdom and reported that in 858 BC he destroyed the city of Sugunia and then in 853 BC also Araškun. Both cities are assumed to have been capitals of the Kingdom before Tushpa became a center for the Urartians. In 853 BC, a coalition was formed by 11 sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamshi-ilu
Shamshi-ilu (Šamši-ilu) was an influential court dignitary and commander in chief (turtanu) of the Assyrian army who rose in high prominence. He was active during the reigns of Assyrian kings Adad-nirari III (810–782 BC), Shalmaneser IV (782–772 BC), Ashur-dan III (771–754 BC) and Ashur-nirari V (754–746 BC). Three times, in 780, 770 and 752 BC, he held the office of limmu officials. He resided at Til Barsip, which is now in northern Syria, and where there are many inscriptions mentioning him. Origins Shamshi-ilu probably was not born in Assyria, though he was from noble lineage of the Bit-Adini tribe and was more than likely educated at the Assyrian court. Later, he rose in the ranks of the Assyrian army to become the commander in chief (turtanu) who had a high degree of influence over the kings of Assyria who lived in his time. He was probably made governor when Shalmaneser III annexed the territories of the Bit-Adini. Some scholars suggested that he might have been o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtanu
"Turtanu" or "Turtan" (Akkadian: 𒌉𒋫𒉡 ''tur-ta-nu''; he, תַּרְתָּן ''tartān''; el, Θαρθαν; la, Tharthan; arc, ܬܵܪܬܵܢ ''tartan'') is an Akkadian word/title meaning 'commander in chief' or 'prime minister'. In Assyria, the Turtanu ranked next to the king. The Assyrian king would assign the individual who was turtanu to go to battle for him, thus giving great power and influence to the turtanu. The office seems to have been duplicated, and there was a ''tartanu imni'' or 'tartan of the right', as well as a ''tartanu shumeli'' or 'tartan of the left'. In later times the title became territorial; we read of a tartan of 'Kummuh' (Commagene). The title is also applied to the commanders of foreign armies; thus Sargon speaks of the ''Tartan Musurai'', or 'Egyptian Tartan'.Assyria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Mesopotamian Women
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Assyrians
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the Assyrians from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC, then to a territorial state, and eventually an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian history into the Early Assyrian ( 2600–2025 BC), Old Assyrian ( 2025–1364 BC), Middle Assyrian ( 1363–912 BC), Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC) and post-imperial (609 BC– AD 630) periods, based on political events and gradual changes in language. Assur, the first Assyrian capital, was founded 2600 BC but there is no evidence yet discovered that the city was independent until the collapse of the Third Dynasty of Ur in the 21st century BC, when a line of independent kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala University
Uppsala University ( sv, Uppsala universitet) is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation. The university rose to significance during the rise of Swedish Empire, Sweden as a great power at the end of the 16th century and was then given a relative financial stability with a large donation from King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus in the early 17th century. Uppsala also has an important historical place in Swedish national culture, identity and for the Swedish establishment: in historiography, literature, politics, and music. Many aspects of Swedish academic culture in general, such as the white student cap, originated in Uppsala. It shares some peculiarities, such as the student nation system, with Lund University and the University of Helsinki. Uppsala belongs to the Coimbra Group of European universities a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ereshkigal
In Mesopotamian mythology, Ereshkigal ( sux, , lit. "Queen of the Great Earth") was the goddess of Kur, the land of the dead or underworld in Sumerian religion, Sumerian mythology. In later myths, she was said to rule Irkalla alongside her husband Nergal. Sometimes her name is given as Irkalla, similar to the way the name Hades was used in Greek mythology for both the underworld and its ruler, and sometimes it is given as Ninkigal, lit. "Lady of the Great Earth". Ereshkigal was only one of multiple deities regarded as rulers of the underworld in Mesopotamia. The main temple dedicated to her was located in Kutha, a city originally associated with Nergal, and her cult had a very limited scope. No personal names with "Ereshkigal" as a theophoric element are known. In the ancient Sumerian poem ''Inanna#Descent into the underworld, Inanna's Descent to the Underworld'', Ereshkigal is described as Inanna's older sister. However, they were not commonly associated with each other. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamash
Utu (dUD "Sun"), also known under the Akkadian name Shamash, ''šmš'', syc, ܫܡܫܐ ''šemša'', he, שֶׁמֶשׁ ''šemeš'', ar, شمس ''šams'', Ashurian Aramaic: 𐣴𐣬𐣴 ''š'meš(ā)'' was the ancient Mesopotamian sun god. He was believed to see everything that happened in the world every day, and was therefore responsible for justice and protection of travelers. As a divine judge, he could be associated with the underworld. Additionally, he could serve as the god of divination, typically alongside the weather god Adad. While he was universally regarded as one of the primary gods, he was particularly venerated in Sippar and Larsa. The moon god Nanna (Sin) and his wife Ningal were regarded as his parents, while his twin sister was Inanna (Ishtar). Occasionally other goddesses, such as Manzat and Pinikir, could be regarded as his sisters too. The dawn goddess Aya (Sherida) was his wife, and multiple texts describe their daily reunions taking place on a mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Dowager
A queen dowager or dowager queen (compare: princess dowager or dowager princess) is a title or status generally held by the widow of a king. In the case of the widow of an emperor, the title of empress dowager is used. Its full meaning is clear from the two words from which it is composed: queen indicates someone who served as queen consort (i.e. wife of a king), while dowager indicates a woman who holds the title from her deceased husband (a queen who rules in her own right instead of due to marriage to a king is a queen regnant). A queen mother is a former queen, often a dowager queen, who is the mother of the reigning monarch. Currently (2019) there are four queens dowager: Kesang Choden of Bhutan (who is the only living queen grandmother worldwide), Norodom Monineath of Cambodia (who is also queen mother), Lisa Najeeb Halaby (Noor Al'Hussein) of Jordan, and Sirikit Kitiyakara of Thailand (who is also queen mother). Queen Ratna of Nepal was queen dowager until the abolitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)