|
Muhammad Ibn Ibrahim Al-Mus'abi
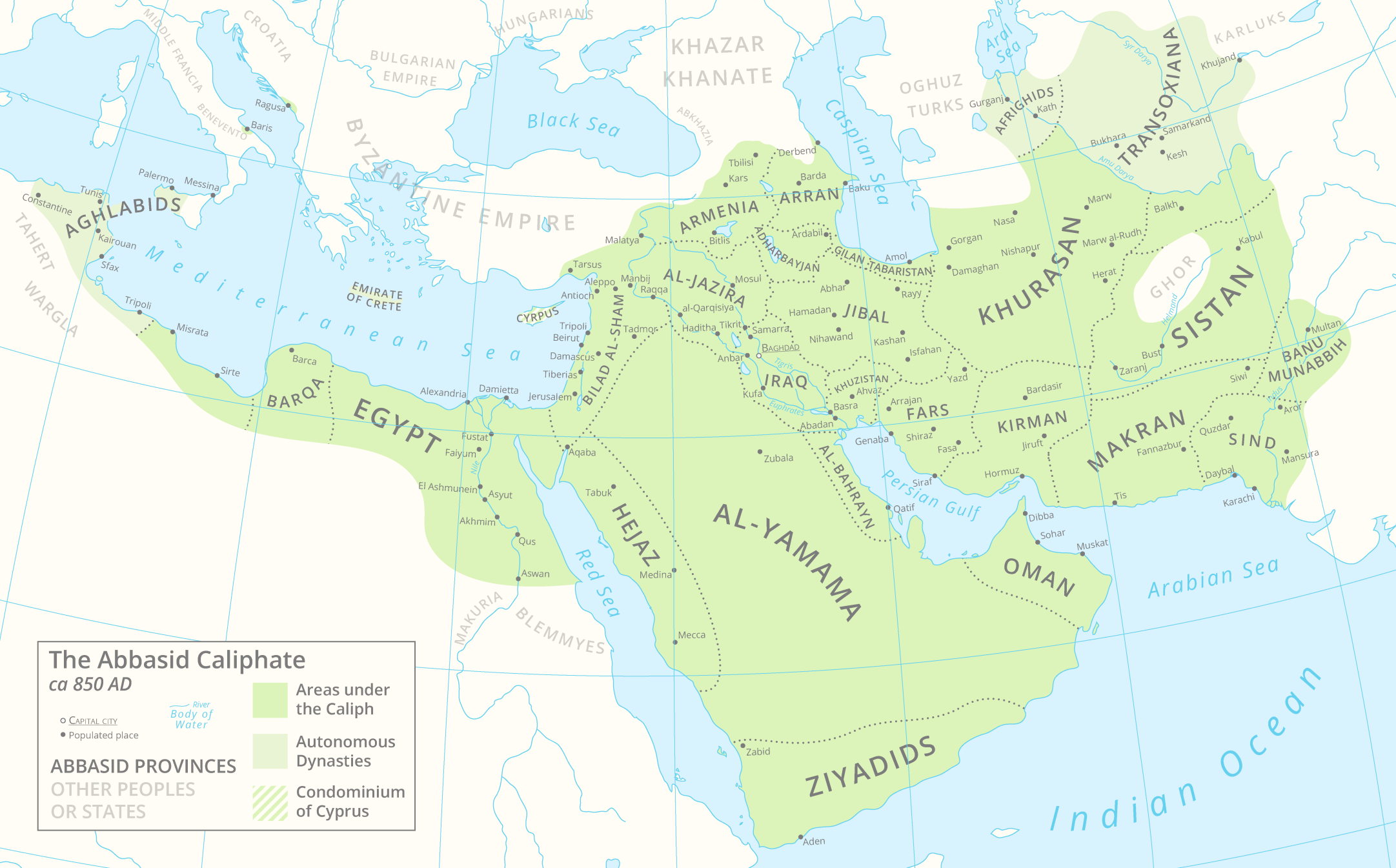
Abu Abdallah Muhammad ibn Ibrahim ibn Mus'ab ( ar, ابو عبد الله محمد بن إبراهيم بن مصعب, died c. 850) was a Mus'abid military commander and provincial official for the Abbasid Caliphate. He served as the governor of Fars from 846–7 until his death. Career A member of the Mus'abid family, Muhammad was the brother of Ishaq ibn Ibrahim, the long-running chief of security ('' shurtah'') of Baghdad, and first cousin to Abdallah ibn Tahir, the Tahirid governor of Khurasan. He participated in the caliph al-Mu'tasim's Amorium campaign of 838, during which he commanded the troops following the vanguard, and was shortly after responsible for putting to death Ujayf ibn Anbasah, who had participated in a failed conspiracy to assassinate the caliph. In the following year he led the caliphal troops that participated alongside Abdallah ibn Tahir's campaign against the rebel prince Mazyar in Tabaristan, and he fought a successful battle against Mazyar's lieut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Wathiq
Abū Jaʿfar Hārūn ibn Muḥammad ( ar, أبو جعفر هارون بن محمد المعتصم; 17 April 812 – 10 August 847), better known by his laqab, regnal name al-Wāthiq bi’llāh (, ), was an Abbasid caliph who reigned from 842 until 847 AD (227–232 AH in the Islamic calendar). Al-Wathiq is described in the sources as well-educated, intellectually curious, but also a poet and a drinker, who enjoyed the company of poets and musicians as well as scholars. His brief reign was one of continuity with the policies of his father, al-Mu'tasim, as power continued to rest in the hands of the same officials whom al-Mu'tasim had appointed. The chief events of the reign were the suppression of revolts: Bedouin rebellions occurred in Bilad al-Sham, Syria in 842, the Hejaz in 845, and the Yamamah in 846, Arminiya, Armenia had to be pacified over several years, and above all, an abortive uprising took place in Baghdad itself in 846, under Ahmad ibn Nasr al-Khuza'i. The latter w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
'Ujayf Ibn 'Anbasa
Ujayf ibn Anbasa () (died 838) was one of the senior-most military leaders of the Abbasid Caliphate under the caliphs al-Ma'mun and al-Mu'tasim. Biography Nothing is known of his family, but he was probably of native Greater Khorasan, Khurasani or Transoxianan origin. He appears in the early 9th century as a follower of the rebel governor Rafi ibn al-Layth, but quickly abandoned him along with most of the people of Fergana and Tashkent when Caliph Harun al-Rashid himself campaigned to Khurasan in 808.Bosworth (2000), p. 778'Ujayf probably belonged to the same social group as the other eastern Iranian generals who were later employed by al-Mu'tasim in his "Turkish" guard, and who were minor princes or drawn from the landed gentry (). Under al-Ma'mun (r. 813–833), Ujayf became a distinguished general, campaigning in northern Persia and suppressing the Kharijite revolt of Bilal al-Dibabi in 829. Ujayf maintained his position under Mu'tasim, Ma'mun's half-brother and successor, camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
850 Deaths
85 may refer to: * 85 (number) * one of the years 85 BC, AD 85, 1885, 1985, 2085 See also * * M85 (other), including "Model 85" * 1985 (other) 1985 was a year. 1985 may also refer to: Literature * ''1985'' (Burgess novel), a 1978 novel by Anthony Burgess * ''1985'' (Dalos novel), a 1983 novel by György Dalos * '' Marvel 1985'', a Marvel Comics mini-series Music * The 1985, a noise ... * List of highways numbered {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abel Pavet De Courteille
Abel Jean Baptiste Michel Pavet de Courteille (23 June 1821 – 12 December 1889) was a 19th-century French orientalist, who specialized in the study of Turkic languages. Career Through his mother, Sophie Silvestre (1793-1877), he was Antoine-Isaac Silvestre de Sacy's grandson. He taught Turkish at the Collège de France, as extraordinary professor in 1854 and then as holder of an ordinary chair in 1861. In 1873, he succeeded Emmanuel de Rougé at the Académie des inscriptions et belles-lettres. He was also a member of the Société asiatique. He led Turcology to the study of Central Asian languages and was the author of a dictionary of Eastern Turkish and of several editions and translations of texts. He is buried at Père Lachaise Cemetery (44th division). Publications * ''Dictionnaire turk-oriental, destiné principalement à faciliter la lecture des ouvrages de Babur, d' Aboul-Gâzi et de Ali-Shir Nava'i'', Paris, Imprimerie impériale, 1870 (562 pages). * (with A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Samarra
Samarra is a city in central Iraq, which served as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate from 836 to 892. Founded by the caliph al-Mu'tasim, Samarra was briefly a major metropolis that stretched dozens of kilometers along the east bank of the Tigris, but was largely abandoned in the latter half of the 9th century, especially following the return of the caliphs to Baghdad. Due to the relatively short period of occupation, extensive ruins of Abbasid Samarra have survived into modern times. The layout of the city can still be seen via aerial photography, revealing a vast network of planned streets, houses, palaces and mosques. Studies comparing the archeological evidence with information provided by Muslim historians have resulted in the identification of many of the toponyms within the former city. The archeological site of Samarra was named by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site in 2007, calling it "the best-preserved plan of an ancient large city." The modern city bearing the same nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Husayn Ibn Isma'il Al-Mus'abi
Al-Husayn ibn Isma'il ibn Ibrahim ibn Mus'ab ( ar, الحسين بن إسماعيل بن إبراهيم بن مصعب, died November 886) was a ninth century army commander in the service of the Abbasid Caliphate. He was particularly active during the period known as the Anarchy at Samarra (861–870). Career A member of the Mus'abid family, al-Husayn was a blood relation of the Tahirid family, and he is occasionally referred to in the sources by the ''nisba'' of "al-Tahiri." During the caliphate of al-Mutawakkil (r. 847–861) he was appointed as governor of Fars by his cousin Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Ibrahim in 850, and was responsible for putting to death his uncle Muhammad ibn Ibrahim al-Mus'abi, the previous holder of that position. In 858 he is mentioned as being a member of the al-Mutawakkil's bodyguard ('' haras'') when the caliph made his journey to Damascus, and in the following year he is reported to have been appointed as chamberlain (''hajib'') upon the death of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mutawakkil
Abū al-Faḍl Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad al-Muʿtaṣim bi-ʾllāh ( ar, جعفر بن محمد المعتصم بالله; March 822 – 11 December 861), better known by his regnal name Al-Mutawakkil ʿalā Allāh (, "He who relies on God") was the tenth Abbasid caliph. He succeeded his brother, al-Wathiq, and is known for expanding the empire to its maximum extent. He was deeply religious, and is remembered for discarding the Muʿtazila, ending the Mihna (a period of persecution of Islamic scholars), and releasing Ahmad ibn Hanbal. He is also known for his tough rule, especially with respect to non-Muslim subjects. He was assassinated on 11 December 861 by the Turkic guard with the support of his son, al-Muntasir, marking the beginning of the period of civil strife known as the "Anarchy at Samarra". Early life Al-Mutawakkil was born on February/March 822 to the Abbasid prince Abu Ishaq Muhammad (the future al-Mu'tasim) and a slave concubine from Khwarazm called Shuja. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mu'tazz
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Jaʿfar ( ar, أبو عبد الله محمد بن جعفر; 847 – 16 July 869), better known by his regnal title al-Muʿtazz bi-ʾllāh (, "He who is strengthened by God") was the Abbasid caliph from 866 to 869, during a period of extreme internal instability within the Abbasid Caliphate, known as the "Anarchy at Samarra". Originally named as the second in line of three heirs of his father al-Mutawakkil, al-Mu'tazz was forced to renounce his rights after the accession of his brother al-Muntasir, and was thrown in prison as a dangerous rival during the reign of his cousin al-Musta'in. He was released and raised to the caliphate in January 866, during the civil war between al-Musta'in and the Turkish military of Samarra. Al-Mu'tazz was capable and determined to reassert the authority of the caliph over the Turkish military, but had only limited success. Aided by the vizier Ahmad ibn Isra'il, he managed to remove and kill the leading Turkish genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Wathiq
Abū Jaʿfar Hārūn ibn Muḥammad ( ar, أبو جعفر هارون بن محمد المعتصم; 17 April 812 – 10 August 847), better known by his laqab, regnal name al-Wāthiq bi’llāh (, ), was an Abbasid caliph who reigned from 842 until 847 AD (227–232 AH in the Islamic calendar). Al-Wathiq is described in the sources as well-educated, intellectually curious, but also a poet and a drinker, who enjoyed the company of poets and musicians as well as scholars. His brief reign was one of continuity with the policies of his father, al-Mu'tasim, as power continued to rest in the hands of the same officials whom al-Mu'tasim had appointed. The chief events of the reign were the suppression of revolts: Bedouin rebellions occurred in Bilad al-Sham, Syria in 842, the Hejaz in 845, and the Yamamah in 846, Arminiya, Armenia had to be pacified over several years, and above all, an abortive uprising took place in Baghdad itself in 846, under Ahmad ibn Nasr al-Khuza'i. The latter w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmad Ibn Nasr Al-Khuza'i
Ahmad ( ar, أحمد, ʾAḥmad) is an Arabic male given name common in most parts of the Muslim world. Other spellings of the name include Ahmed and Ahmet. Etymology The word derives from the root (ḥ-m-d), from the Arabic (), from the verb (''ḥameda'', "to thank or to praise"), non-past participle (). Lexicology As an Arabic name, it has its origins in a Quranic prophecy attributed to Jesus in the Quran which most Islamic scholars concede is about Muhammad. It also shares the same roots as Mahmud, Muhammad and Hamed. In its transliteration, the name has one of the highest number of spelling variations in the world. Though Islamic scholars attribute the name Ahmed to Muhammed, the verse itself is about a Messenger named Ahmed, whilst Muhammed was a Messenger-Prophet. Some Islamic traditions view the name Ahmad as another given name of Muhammad at birth by his mother, considered by Muslims to be the more esoteric name of Muhammad and central to understanding his n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabaristan
Tabaristan or Tabarestan ( fa, طبرستان, Ṭabarestān, or mzn, تبرستون, Tabarestun, ultimately from Middle Persian: , ''Tapur(i)stān''), was the name applied to a mountainous region located on the Caspian coast of northern Iran. It corresponded to the present-day province of Mazandaran, which became the predominant name of the area from the 11th-century onwards. Pre-Islamic era Tabaristan was named after the Tapurians, who had been deported there from Parthia by the Parthian king Phraates I (). At the advent of the Sasanians, the region, along with Gilan and Daylam, was part of the Padishkhwargar kingdom of king Gushnasp, who is mentioned in the Letter of Tansar. He submitted to the first Sasanian King of Kings () Ardashir I () after being guaranteed to keep his kingdom. His line would continue ruling Padishkhwargar until the second reign of Kavad I (), who removed the dynasty from power and appointed his son Kawus in its stead. Under the Sasanians, Tabarist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazyar
Mazyar (Middle Persian: ''Māh-Izād''; Mazandarani/ fa, مازیار, Māzyār) was an Iranian prince from the Qarinvand dynasty, who was the ruler (''ispahbadh'') of the mountainous region of Tabaristan from 825/6 to 839. For his resistance to the Abbasid Caliphate, Mazyar is considered one of the national heroes of Iran by twentieth-century Iranian nationalist historiography. His name means "protected by the ''yazata'' of the moon". Origin Mazyar belonged to the Qarinvand dynasty, which was descended from Sukhra, a powerful magnate from the House of Karen, who was the ''de facto'' ruler of the Sasanian Empire from 484 to 493. However, due to his great influence and power, he was exiled and executed by the Sasanian king Kavadh I (r. 488–496 & 498–531). Sukhra was survived by eight sons, one of them being Karin, who in return for aiding Kavadh I's son and successor Khosrow I (r. 531–579) against the Western Turkic Khaganate in the 550s, received land to the south of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |