|
Movement Paradox
A movement paradox is a phenomenon of grammar that challenges the transformational approach to syntax. The importance of movement paradoxes is emphasized by those theories of syntax (e.g. lexical functional grammar, head-driven phrase structure grammar, construction grammar, most dependency grammars) that reject movement, i.e. the notion that discontinuities in syntax are explained by the movement of constituents. Syntactic movement Given a transformational approach to syntax, the following related sentences are explained in terms of movement: ::a. We talked about the fact that he was sick for days. ::b. The fact that he was sick, we talked about ___ for days. - Example of topicalization The underlined noun phrase, which contains a clause, is taken to have moved leftward in the second sentence, the blank marking its starting position. A transformational approach to syntax will explain all sorts of discontinuities (e.g. wh-fronting, topicalization, extraposition, scrambl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformational Grammar
In linguistics, transformational grammar (TG) or transformational-generative grammar (TGG) is part of the theory of generative grammar, especially of natural languages. It considers grammar to be a system of rules that generate exactly those combinations of words that form grammatical sentences in a given language and involves the use of defined operations (called transformations) to produce new sentences from existing ones. The method is commonly associated with American linguist Noam Chomsky. Generative algebra was first introduced to general linguistics by the structural linguist Louis Hjelmslev although the method was described before him by Albert Sechehaye in 1908. Chomsky adopted the concept of transformations from his teacher Zellig Harris, who followed the American descriptivist separation of semantics from syntax. Hjelmslev's structuralist conception including semantics and pragmatics is incorporated into functional grammar. Historical context Transformational analys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topicalization
Topicalization is a mechanism of syntax that establishes an expression as the sentence or clause topic by having it appear at the front of the sentence or clause (as opposed to in a canonical position further to the right). This involves a phrasal movement of determiners, prepositions, and verbs to sentence-initial position. Topicalization often results in a discontinuity and is thus one of a number of established discontinuity types, the other three being ''wh''-fronting, scrambling, and extraposition. Topicalization is also used as a constituency test; an expression that can be topicalized is deemed a constituent. The topicalization of arguments in English is rare, whereas circumstantial adjuncts are often topicalized. Most languages allow topicalization, and in some languages, topicalization occurs much more frequently and/or in a much less marked manner than in English. Topicalization in English has also received attention in the pragmatics literature. Examples Typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Linguistics
Generative grammar, or generativism , is a linguistic theory that regards linguistics as the study of a hypothesised innate grammatical structure. It is a biological or biologistic modification of earlier structuralist theories of linguistics, deriving ultimately from glossematics. Generative grammar considers grammar as a system of rules that generates exactly those combinations of words that form grammatical sentences in a given language. It is a system of explicit rules that may apply repeatedly to generate an indefinite number of sentences which can be as long as one wants them to be. The difference from structural and functional models is that the object is base-generated within the verb phrase in generative grammar. This purportedly cognitive structure is thought of as being a part of a universal grammar, a syntactic structure which is caused by a genetic mutation in humans. Generativists have created numerous theories to make the NP VP (NP) analysis work in natural l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copula (linguistics)
In linguistics, a copula (plural: copulas or copulae; abbreviated ) is a word or phrase that links the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, such as the word ''is'' in the sentence "The sky is blue" or the phrase ''was not being'' in the sentence "It was not being co-operative." The word ''copula'' derives from the Latin noun for a "link" or "tie" that connects two different things. A copula is often a verb or a verb-like word, though this is not universally the case. A verb that is a copula is sometimes called a copulative or copular verb. In English primary education grammar courses, a copula is often called a linking verb. In other languages, copulas show more resemblances to pronouns, as in Classical Chinese and Guarani, or may take the form of suffixes attached to a noun, as in Korean, Beja, and Inuit languages. Most languages have one main copula, although some (like Spanish, Portuguese and Thai) have more than one, while others have none. In the case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-finite Verb
A nonfinite verb is a derivative form of a verb unlike finite verbs. Accordingly, nonfinite verb forms are inflected for neither number nor person, and they cannot perform action as the root of an independent clause. In English, nonfinite verbs include infinitives, participles and gerunds. Nonfinite verb forms in some other languages include converbs, gerundives and supines. Formally, nonfinite verb forms lack the three grammatical features (mood, tense and voice) that are "associated, independently or relatively, with ... the act of predication." Generally, they also lack a subject dependent. One or more nonfinite verbs may be associated with a finite verb in a finite clause: the elements of a verb catena, or verb chain. Because English lacks most inflectional morphology, the finite and the nonfinite forms of a verb may appear the same in a given context. Examples The following sentences each contain one finite verb (underlined) and multiple nonfinite verbs (in bold): ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shifting (syntax)
In syntax, shifting occurs when two or more constituents appearing on the same side of their common head exchange positions in a sense to obtain non-canonical order. The most widely acknowledged type of shifting is heavy NP shift, but shifting involving a heavy NP is just one manifestation of the shifting mechanism. Shifting occurs in most if not all European languages, and it may in fact be possible in all natural languages including sign languages. Shifting is not inversion, and inversion is not shifting, but the two mechanisms are similar insofar as they are both present in languages like English that have relatively strict word order. The theoretical analysis of shifting varies in part depending on the theory of sentence structure that one adopts. If one assumes relatively flat structures, shifting does not result in a discontinuity. Shifting is often motivated by the relative weight of the constituents involved. The weight of a constituent is determined by a number of factors: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversion (linguistics)
In linguistics, inversion is any of several grammatical constructions where two expressions switch their canonical order of appearance, that is, they invert. There are several types of subject-verb inversion in English: ''locative inversion'', ''directive inversion'', ''copular inversion'', and ''quotative inversion''. The most frequent type of inversion in English is subject–auxiliary inversion in which an auxiliary verb changes places with its subject; it often occurs in questions, such as ''Are you coming?'', with the subject ''you'' is switched with the auxiliary ''are''. In many other languages, especially those with a freer word order than English, inversion can take place with a variety of verbs (not just auxiliaries) and with other syntactic categories as well. When a layered constituency-based analysis of sentence structure is used, inversion often results in the discontinuity of a constituent, but that would not be the case with a flatter dependency-based analysis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrambling (linguistics)
Scrambling is a syntactic phenomenon wherein sentences can be formulated using a variety of different word orders without any change in meaning. Scrambling often results in a discontinuity since the scrambled expression can end up at a distance from its head. Scrambling does not occur in English, but it is frequent in languages with freer word order, such as German, Russian, Persian and Turkic languages. The term was coined by Haj Ross in his 1967 dissertation and is widely used in present work, particularly with the generative tradition. Examples The following examples from German illustrate typical instances of scrambling: : These examples illustrate typical cases of scrambling in the midfield of a subordinate clause in German. All six clauses are acceptable, whereby the actual order that appears is determined by pragmatic considerations such as emphasis. If one takes the first clause (clause a) as the basic order, then scrambling has occurred in clauses b–f. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraposition
Extraposition is a mechanism of syntax that alters word order in such a manner that a relatively "heavy" constituent appears to the right of its canonical position. Extraposing a constituent results in a discontinuity and in this regard, it is unlike shifting, which does not generate a discontinuity. The extraposed constituent is separated from its governor by one or more words that dominate its governor. Two types of extraposition are acknowledged in theoretical syntax: standard cases where extraposition is optional and ''it''-extraposition where extraposition is obligatory. Extraposition is motivated in part by a desire to reduce center embedding by increasing right- branching and thus easing processing, center-embedded structures being more difficult to process. Extraposition occurs frequently in English and related languages. Examples Standard cases of extraposition are optional, although at times the extraposed version of the sentence is strongly preferred. The followin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wh-fronting
In linguistics, wh-movement (also known as wh-fronting, wh-extraction, or wh-raising) is the formation of syntactic dependencies involving interrogative words. An example in English is the dependency formed between ''what'' and the object position of ''doing'' in "What are you doing?" Interrogative forms are sometimes known within English linguistics as ''wh-words'', such as ''what, when, where, who'', and ''why'', but also include other interrogative words, such as ''how''. This dependency has been used as a diagnostic tool in syntactic studies as it can be observed to interact with other grammatical constraints. In languages with wh- movement, sentences or clauses with a wh-word show a non-canonical word order that places the wh-word (or phrase containing the wh-word) at or near the front of the sentence or clause ("''Who'' are you thinking about?") instead of the canonical position later in the sentence ("I am thinking about ''you''"). Leaving the wh-word in its canonical positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning ( semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
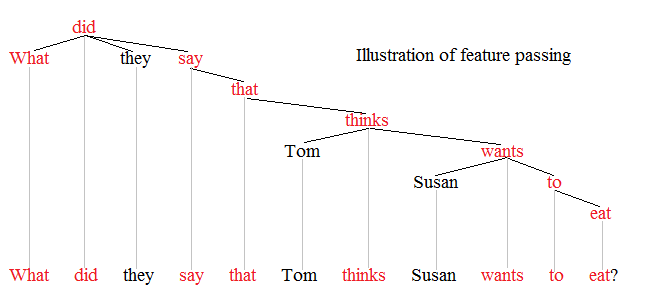
Syntactic Movement
Syntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of ''discontinuous constituents'' or ''displacement''. Some constituents appear to have been displaced from the position in which they receive important features of interpretation. The concept of movement is controversial and is associated with so-called ''transformational'' or ''derivational'' theories of syntax (such as transformational grammar, government and binding theory, minimalist program). Representational theories (such as head-driven phrase structure grammar, lexical functional grammar, construction grammar, and most dependency grammars), in contrast, reject the notion of movement and often instead address discontinuities with other mechanisms including graph reentrancies, feature passing, and type shifters. Illustration Movement is the traditional means of explaining discontinuities such as wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)