|
Mount Toondina Crater
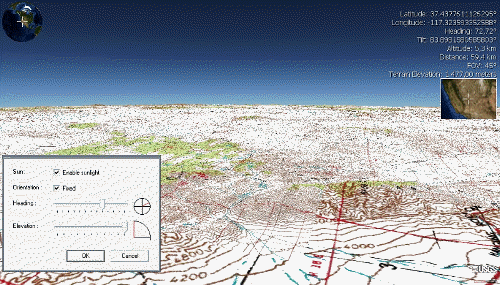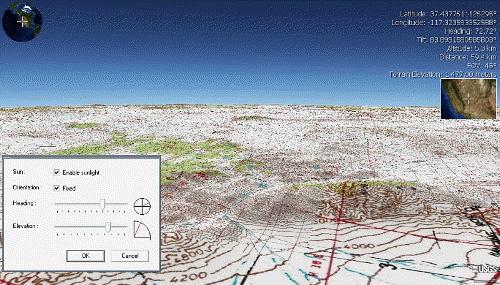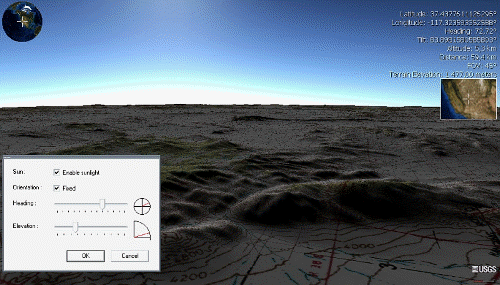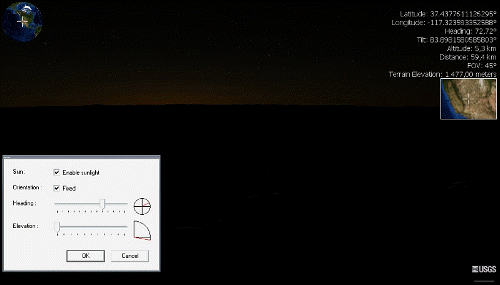
Mount Toondina crater is an impact structure (or astrobleme), the eroded remnant of a former impact crater, located in northern South Australia in the locality of Allandale Station about south of the town of Oodnadatta. Mount Toondina is the high point of a circular topographic feature rising out of an otherwise relatively flat desert area of the Eromanga Basin. An impact origin was first suggested in 1976, challenging the earlier diapir A diapir (; , ) is a type of igneous intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–T ... ( salt dome) hypothesis,Youles I.P. 1976. Mount Toondina impact structure. Geological Survey of South Australia Quarterly Geological Notes 60, 10–12. and strongly supported by subsequent studies.Shoemaker E.M. & Shoemaker C.S. 1988. Impact Structures of Australia (1987). Lunar and Planetary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsat
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery of Earth. It is a joint NASA / USGS program. On 23 July 1972, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite was launched. This was eventually renamed to Landsat 1 in 1975. The most recent, Landsat 9, was launched on 27 September 2021. The instruments on the Landsat satellites have acquired millions of images. The images, archived in the United States and at Landsat receiving stations around the world, are a unique resource for global change research and applications in agriculture, cartography, geology, forestry, regional planning, surveillance and education, and can be viewed through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) "EarthExplorer" website. Landsat 7 data has eight spectral bands with spatial resolutions ranging from ; the temporal resolution is 16 days. Landsat images are usually divided into scenes for easy downloading. Each Landsat scene is about 115 miles long and 115 miles wide (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oodnadatta, South Australia
Oodnadatta is a small, remote outback town and locality in the Australian state of South Australia, located north-north-west of the state capital of Adelaide by road or direct, at an altitude of . The unsealed Oodnadatta Track, an outback road popular with tourists, runs through the town. In the , there were 74 dwellings and the population was 318. Town facilities include a hotel, caravan park, post office, general stores, police station, hospital, fuel and minor mechanical repairs. The old railway station now serves as a museum. From the 1880s to the 1930s, Oodnadatta was a base for camel drivers and their animals, which provided cartage when the railway was under construction and along outback tracks before roads were established. After the railway line was lifted, Oodnadatta's role changed from that of a government service centre and supply depot for surrounding pastoral properties to a residential freehold town for Aboriginal families who, moving from cattle work, bought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous Impact Craters
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Craters Of South Australia
Impact may refer to: * Impact (mechanics), a high force or shock (mechanics) over a short time period * Impact, Texas, a town in Taylor County, Texas, US Science and technology * Impact crater, a meteor crater caused by an impact event * Impact event, the collision of a meteoroid, asteroid or comet with Earth * Impact factor, a measure of the citations to a science or social science journal Books and magazines * ''Impact'' (novel), a 2010 novel by Douglas Preston *''Impact Press'', a former Orlando, Florida-based magazine * Impact Magazines, a former UK magazine publisher * ''Impact'' (conservative magazine), a British political magazine * ''Impact'' (British magazine), a British action film magazine * ''Impact'', a French action film magazine spun off from ''Mad Movies'' * ''Impact'' (UNESCO magazine), a former UNESCO quarterly titled ''IMPACT of science on society'' * ''Impact'' (student magazine), a student magazine for the University of Nottingham, England * ''Bathimp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Geophysical Research
The ''Journal of Geophysical Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. It is the flagship journal of the American Geophysical Union. It contains original research on the physical, chemical, and biological processes that contribute to the understanding of the Earth, Sun, and Solar System. It has seven sections: A (Space Physics), B (Solid Earth), C (Oceans), D (Atmospheres), E (Planets), F (Earth Surface), and G (Biogeosciences). All current and back issues are available online for subscribers. History The journal was originally founded under the name ''Terrestrial Magnetism'' by the American Geophysical Union's president Louis Agricola Bauer in 1896. It was renamed to ''Terrestrial Magnetism and Atmospheric Electricity'' in 1899 and in 1948 it acquired its current name. In 1980, three specialized sections were established: ''A: Space Physics'', ''B: Solid Earth'', and ''C: Oceans''. Subsequently, further sections have been added: ''D: Atmospheres'' in 1984, ''E: Planets'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' sometimes refers only to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets. Gutenberg, B., 1929, Lehrbuch der Geophysik. Leipzig. Berlin (Gebruder Borntraeger). Runcorn, S.K, (editor-in-chief), 1967, International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar And Planetary Science Conference
The Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC), jointly sponsored by the Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI) and NASA Johnson Space Center (JSC), brings together international specialists in petrology, geochemistry, geophysics, geology, and astronomy to present the latest results of research in planetary science. Since its beginning in 1970, the LPSC has been a significant focal point for planetary science research, with more than 2000 planetary scientists and students attending from all over the world. History In a speech delivered at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in Houston, Texas in March 1968, President Lyndon B. Johnson announced the formation of the Lunar Science Institute (LSI). The creation of the LSI was the culmination of meetings and events involving the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the National Academy of Sciences, Universities Research Association, and several major universities. Initially operated by the National Academy of Sciences, the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Dome
A salt dome is a type of structural dome formed when salt (or other evaporite minerals) intrudes into overlying rocks in a process known as diapirism. Salt domes can have unique surface and subsurface structures, and they can be discovered using techniques such as seismic reflection. They are important in petroleum geology as they can function as petroleum traps. Formation Stratigraphically, salt basins developed periodically from the Proterozoic to the Neogene. The formation of a salt dome begins with the deposition of salt in a restricted basin. In these basins, the outflow of water exceeds inflow. More concretely, the basin loses water through evaporation, resulting in the precipitation and deposition of salt. While the rate of sedimentation of salt is significantly larger than the rate of sedimentation of clastics, it is recognized that a single evaporation event is rarely enough to produce the vast quantities of salt needed to form a layer thick enough for the formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapir
A diapir (; , ) is a type of igneous intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–Taylor-instability-type structures in regions with low tectonic stress such as in the Gulf of Mexico to narrow dikes of material that move along tectonically induced fractures in surrounding rock. The term was introduced by the Romanian geologist Ludovic Mrazek, who was the first to understand the principle of salt tectonics and plasticity. The term ''diapir'' may be applied to igneous structures, but it is more commonly applied to non-igneous, relatively cold materials, such as salt domes and mud diapirs. Occurrence Differential loading causes salt deposits covered by overburden (sediment) to rise upward toward the surface and pierce the overburden, forming diapirs (including salt domes), pillars, sheets, or other geological structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Lunar impact craters range from microscopic craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program and small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions in the lunar regolith to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury, Callisto, Ganymede and most small moons and asteroids. On other planets and moons that experience more active surface geological processes, such as Earth, Venus, Europa, Io and Titan, visible impact craters are less common because they become eroded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA World Wind
NASA WorldWind is an open-source (released under the NOSA license and the Apache 2.0 license) virtual globe. According to the website (https://worldwind.arc.nasa.gov/), "WorldWind is an open source virtual globe API. WorldWind allows developers to quickly and easily create interactive visualizations of 3D globe, map and geographical information. Organizations around the world use WorldWind to monitor weather patterns, visualize cities and terrain, track vehicle movement, analyze geospatial data and educate humanity about the Earth." It was first developed by NASA in 2003 for use on personal computers and then further developed in concert with the open source community since 2004. As of 2017, a web-based version of WorldWind is available online. An Android version is also available. The original version relied on .NET Framework, which ran only on Microsoft Windows. The more recent Java version, WorldWind Java, is cross platform, a software development kit (SDK) aime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrobleme
An impact structure is a generally circular or craterlike geologic structure of deformed bedrock or sediment produced by impact on a planetary surface, whatever the stage of erosion of the structure. In contrast, an impact crater is the surface expression of an impact structure. In many cases, on Earth, the impact crater has been destroyed by erosion, leaving only the deformed rock or sediment of the impact structure behind.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. This is the fate of almost all old impact craters on Earth, unlike the ancient pristine craters preserved on the Moon and other geologically inactive rocky bodies with old surfaces in the Solar System. Impact structure is synonymous with the less commonly used term astrobleme meaning "star wound". In an impact structure, the typical visible and topographic expressions of an impact crater are no longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)