|
Morison's Pouch
The hepatorenal recess (subhepatic recess, pouch of Morison or Morison's pouch) is the subhepatic space that separates the liver from the right kidney. As a potential space, the recess is not normally filled with fluid. However, fluid can collect here in circumstances where the abdomen fills with fluid, such as hemoperitoneum. This fluid may be seen on ultrasound or computed tomography (CT scan). Clinical importance Since it is a potential space, the hepatorenal recess is not normally filled with fluid. However, this space becomes significant in conditions in which fluid collects within the abdomen (most commonly ascites and hemoperitoneum). The intraperitoneal fluid, be it blood, ascites, or dialysate, collects in this space and may be visualized, most commonly via ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) scanning. As little as 30 or 40 ml of fluid in the abdominal cavity may be visualized in this space. Early visualization of fluid in the hepatorenal recess on FAST scan may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequency, frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomic Space
{{set index article In anatomy, a spatium or anatomic space is a space (cavity or gap). Anatomic spaces are often landmarks to find other important structures. When they fill with gases (such as air) or liquids (such as blood) in pathological ways, they can suffer conditions such as pneumothorax, edema, or pericardial effusion. Many anatomic spaces are potential spaces, which means that they are potential rather than realized (with their realization being dynamic according to physiologic or pathophysiologic events). In other words, they are like an empty plastic bag that has not been opened (two walls collapsed against each other; no interior volume until opened) or a balloon that has not been inflated. Examples of anatomic spaces (or potential spaces) include: *Axillary space *Buccal space * Canine space *Cystohepatic triangle * Deep perineal space * Deep temporal space *Epidural space * Extraperitoneal space *Fascial spaces of the head and neck *Infratemporal space *Intercostal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential Space
In anatomy, a potential space is a space between two adjacent structures that are normally pressed together (directly apposed). Many anatomic spaces are potential spaces, which means that they are potential rather than realized (with their realization being dynamic according to physiologic or pathophysiologic events). In other words, they are like an empty plastic bag that has not been opened (two walls collapsed against each other; no interior volume until opened) or a balloon that has not been inflated. The pleural space, between the visceral and parietal pleura of the lung, is a potential space. Though it only contains a small amount of fluid normally, it can sometimes accumulate fluid or air that widens the space. The pericardial space is another potential space that may fill with fluid (effusion) in certain disease states (e.g. pericarditis; a large pericardial effusion may result in cardiac tamponade. Examples * costodiaphragmatic recess * pericardial cavity *epidural space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoperitoneum
Hemoperitoneum (also haemoperitoneum, sometimes also hematoperitoneum) is the presence of blood in the peritoneal cavity. The blood accumulates in the space between the inner lining of the abdominal wall and the internal abdominal organs. Hemoperitoneum is generally classified as a surgical emergency; in most cases, urgent laparotomy is needed to identify and control the source of the bleeding. In selected cases, careful observation may be permissible. The abdominal cavity is highly distensible and may easily hold greater than five liters of blood, or more than the entire circulating blood volume for an average-sized individual. Therefore, large-scale or rapid blood loss into the abdomen will reliably induce hemorrhagic shock and, if untreated, may rapidly lead to death. Causes Causes of hemoperitoneum include: * Penetrating trauma * Blunt trauma, most commonly injuries to solid organs such as the liver and spleen. * Vascular accidents, such as rupture of an abdominal aortic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 Hertz, kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating Predation, prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pyth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computed Tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 Nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascites
Ascites is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, abdominal discomfort, and shortness of breath. Complications can include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. In the developed world, the most common cause is liver cirrhosis. Other causes include cancer, heart failure, tuberculosis, pancreatitis, and blockage of the hepatic vein. In cirrhosis, the underlying mechanism involves high blood pressure in the portal system and dysfunction of blood vessels. Diagnosis is typically based on an examination together with ultrasound or a CT scan. Testing the fluid can help in determining the underlying cause. Treatment often involves a low-salt diet, medication such as diuretics, and draining the fluid. A transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) may be placed but is associated with co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
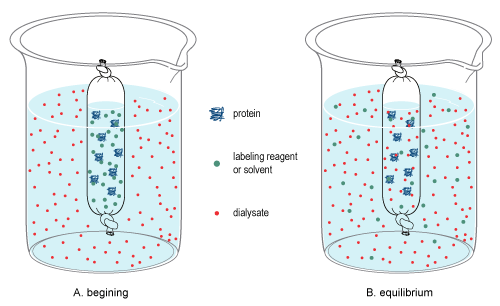
Dialysate
In chemistry, dialysis is the process of separating molecules in solution by the difference in their rates of diffusion through a semipermeable membrane, such as dialysis tubing. Dialysis is a common laboratory technique that operates on the same principle as medical dialysis. In the context of life science research, the most common application of dialysis is for the removal of unwanted small molecules such as salts, reducing agents, or dyes from larger macromolecules such as proteins, DNA, or polysaccharides. Dialysis is also commonly used for buffer exchange and drug binding studies. The concept of dialysis was introduced in 1861 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Graham. He used this technique to separate sucrose (small molecule) and gum Arabic solutes (large molecule) in aqueous solution. He called the diffusible solutes crystalloids and those that would not pass the membrane colloids. From this concept dialysis can be defined as a spontaneous separation process of suspen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focused Assessment With Sonography For Trauma
Focused assessment with sonography in trauma (commonly abbreviated as FAST) is a rapid bedside ultrasound examination performed by surgeons, emergency physicians, and paramedics as a screening test for blood around the heart (pericardial effusion) or abdominal organs (hemoperitoneum) after trauma. There is also the extended FAST (eFAST) which includes some additional ultrasound views to assess for pneumothorax. The four classic areas that are examined for free fluid are the perihepatic space (including Morison's pouch or the hepatorenal recess), perisplenic space, pericardium, and the pelvis. With this technique it is possible to identify the presence of intraperitoneal or pericardial free fluid. In the context of traumatic injury, this fluid will usually be due to bleeding. Indications Reasons a FAST or eFAST would be performed would be: #Blunt abdominal trauma #Penetrating abdominal trauma #Blunt thoracic trauma #Penetrating thoracic trauma #Undifferentiated shock (low blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |