|
Moonshine
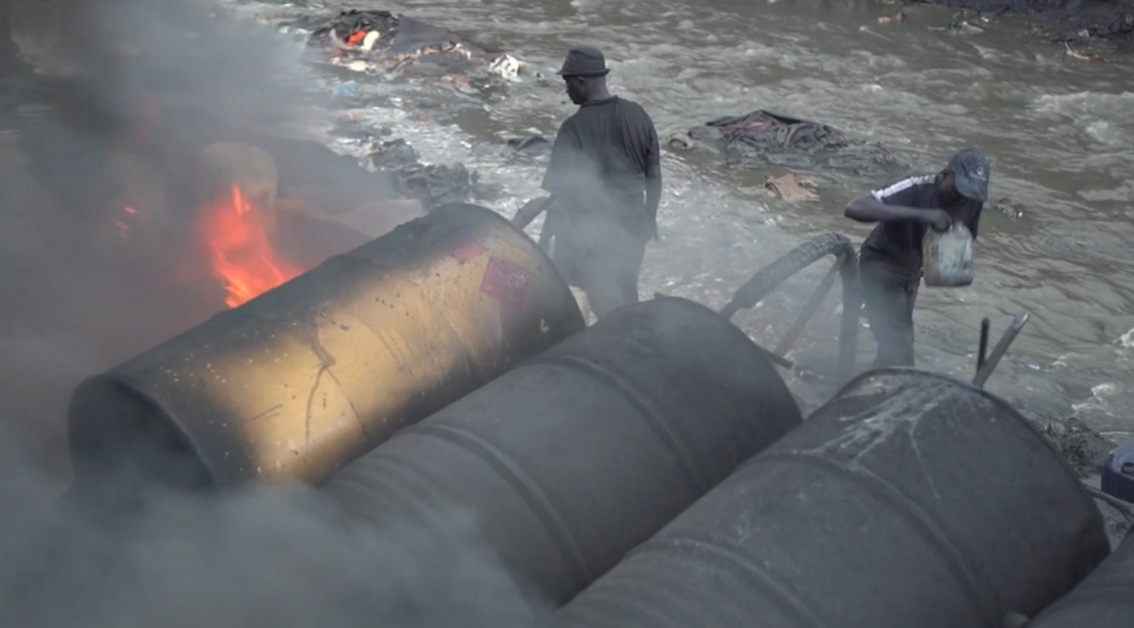
Moonshine is alcohol proof, high-proof liquor, traditionally made or distributed alcohol law, illegally. The name was derived from a tradition of distilling the alcohol (drug), alcohol at night to avoid detection. In the first decades of the 21st century, commercial distilleries have adopted the term for its outlaw cachet and have begun producing their own legal "moonshine", including many novelty flavored varieties, that are said to continue the tradition by using a similar method and/or locale of production. In 2013, moonshine accounted for about one-third of global alcohol consumption. Terminology Different languages and countries have their own terms for moonshine . Fractional crystallization The ethanol may be concentrated in fermented beverages by means of freezing. For example, the name ''Applejack (drink), applejack'' derives from the traditional method of producing the drink, ''wikt:jack#Verb, jacking'', the process of Freeze distillation#Freeze distillation, fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moonshine By Country
By contaminated moonshine Moonshine from various countries that have been known to be contaminated: * Africa ** Changaa (Kenya) ** Kumi Kumi (Kenya) ** Lotoko (Democratic Republic of the Congo) ** Waragi (Uganda) * America ** Guaro (drink), Guaro (Latin America) ** Jamaica ginger (United States) * Asia ** Desi daru (Indian subcontinent) *** Desi daru variant: Tharra (Indian subcontinent) ** Lambanog (Philippines) By type This is an alphabetic list of moonshine produced in various countries. Some moonshine types are produced in more than one country. The term bathtub gin refers to any style of homemade spirit made in amateur conditions. Some distilled drinks on the list below are flavored liquor, flavored, and some also List of national liquors, national liquors. By country Afghanistan Zarbali is a distilled alcoholic beverage supposedly made from fermented raisins. Albania In Albania, moonshine (Rakia, Raki) is the primary alcoholic beverage consumed on daily basis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moonshine
Moonshine is alcohol proof, high-proof liquor, traditionally made or distributed alcohol law, illegally. The name was derived from a tradition of distilling the alcohol (drug), alcohol at night to avoid detection. In the first decades of the 21st century, commercial distilleries have adopted the term for its outlaw cachet and have begun producing their own legal "moonshine", including many novelty flavored varieties, that are said to continue the tradition by using a similar method and/or locale of production. In 2013, moonshine accounted for about one-third of global alcohol consumption. Terminology Different languages and countries have their own terms for moonshine . Fractional crystallization The ethanol may be concentrated in fermented beverages by means of freezing. For example, the name ''Applejack (drink), applejack'' derives from the traditional method of producing the drink, ''wikt:jack#Verb, jacking'', the process of Freeze distillation#Freeze distillation, fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholic Beverage
Drinks containing alcohol (drug), alcohol are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and Distilled beverage, spirits—with alcohol content typically between 3% and 50%. Drinks with less than 0.5% are sometimes considered Non-alcoholic drink, non-alcoholic. Many societies have a distinct drinking culture, where alcoholic drinks are integrated into party, parties. Most countries have Alcohol law, laws regulating the production, sale, and consumption of alcoholic beverages. Some regulations require the labeling of the percentage alcohol content (as ABV or Alcohol proof, proof) and the use of a Alcohol warning label, warning label. List of countries with alcohol prohibition, Some countries Prohibition, ban the consumption of alcoholic drinks, but they are legal in most parts of the world. The temperance movement advocates against the consumption of alcoholic beverages. The global alcohol industry, alcoholic drink industry exceeded $1.5 trillion in 2017. Alcohol is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilju
Kilju () is the Finnish word for a mead-like homemade alcoholic beverage made from a source of carbohydrates (such as cane sugar or honey), yeast, and water, making it both affordable and cheap to produce. The ABV depends on the yeast that was used, and since it does not contain a sweet reserve it is completely dry. Crude product may be distilled into moonshine. Kilju intended for direct consumption is usually clarified and stabilized to avoid wine faults. It is a flax-colored alcoholic beverage with no discernible taste other than that of ethanol. It can be used as an ethanol base for drink mixers. Cultural aspects Kilju is commonly associated with the punk subculture. Kilju is a well-established part of the Finnish alcohol and counter-culture, as witnessed even in the leading engineer school's making-and-use-of video of yore. "Four thousand litres of gases are generated. They are led to the neighbours' delight." The drink tends to invite such black humour, of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol Law
Alcohol laws are laws relating to manufacture, Drinking alcohol, use, as Drunkeness, being under the influence of and sale of Alcohol (drug), alcohol (also known formally as ethanol) or alcoholic beverages. Common alcoholic beverages include beer, wine, (hard) cider, and distilled Spirits (alcohol), spirits (e.g., vodka, rum, gin). Definition of alcoholic beverage varies internationally, e.g., the United States defines an alcoholic beverage as "any beverage in liquid form which contains not less than one-half of one percent of alcohol by volume". Alcohol laws can restrict those who can produce alcohol, those who can buy it (often with Legal drinking age, minimum age restrictions and laws against selling to an already intoxicated person), when one can buy it (with hours of serving or days of selling set out), labelling and Alcohol advertising, advertising, the types of alcoholic beverage that can be sold (e.g., some stores can only sell beer and wine), where one can consume it (e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
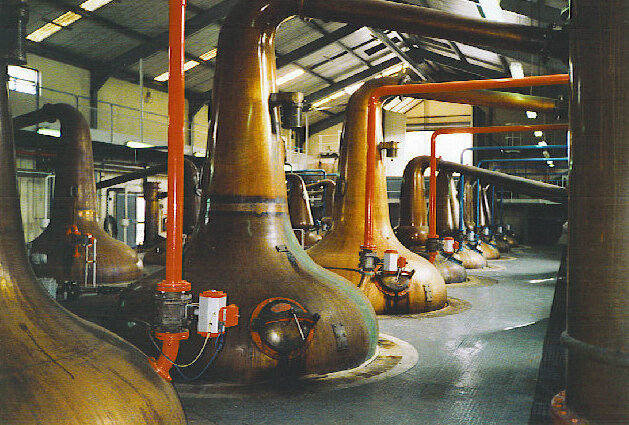
Still
A still is an apparatus used to distillation, distill liquid mixtures by heating to selectively Boiling, boil and then cooling to Condensation, condense the vapor. A still uses the same concepts as a basic Distillation#Laboratory_procedures, distillation apparatus, but on a much larger scale. Stills have been used to produce perfume and medicine, water for injection (WFI) for pharmaceutical use, generally to separate and purify different chemicals, and to produce distilled beverages containing ethanol. Application Since ethanol boiling point, boils at a much lower temperature than water, simple distillation can separate ethanol from water by applying heat to the mixture. Historically, a copper vessel was used for this purpose, since copper removes undesirable sulfur-based compounds from the alcohol. However, many modern stills are made of stainless steel pipes with copper linings to prevent erosion of the entire vessel and lower copper levels in the waste product (which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whisky
Whisky or whiskey is a type of liquor made from Fermentation in food processing, fermented grain mashing, mash. Various grains (which may be Malting, malted) are used for different varieties, including barley, Maize, corn, rye, and wheat. Whisky is typically Aging (food), aged in wooden casks, commonly of charred white oak. Uncharred white oak casks previously used for the aging of Port wine, port, rum or sherry may be employed during storage to impart a unique flavor and color. Whisky is a strictly regulated Alcoholic spirit, spirit worldwide with many classes and types. The typical unifying characteristics of the different classes and types are the fermentation of grains, distillation, and aging in Barrel, wooden barrels. Etymology The word ''whisky'' (or ''whiskey'') is an anglicisation of the Classical Gaelic word (or ) meaning "water" (now written as in Modern Irish, and in Scottish Gaelic). This Gaelic word shares its ultimate Indo-European_vocabulary#Natural_features, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectified Spirit
Rectified spirit, also known as neutral spirits, rectified alcohol or ethyl alcohol of agricultural origin, is highly concentrated ethanol that has been purified by means of repeated distillation in a process called rectification. In some countries, denatured alcohol or denatured rectified spirit may commonly be available as "rectified spirit", because in some countries (though not necessarily the same) the retail sale of rectified alcohol in its non-denatured form is prohibited. The purity of rectified spirit has a practical limit of 97.2% ABV (95.6% by mass) when produced using conventional distillation processes, as a mixture of ethanol and water becomes a minimum-boiling azeotrope at this concentration. However, rectified spirit is typically distilled in continuous multi-column stills at 96–96.5% ABV and diluted as necessary. Ethanol is a commonly used medical alcohol''spiritus fortis'' is a medical term for ethanol solutions with 95% ABV. Neutral spirits can be produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (drug)
Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ethanol, is the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits (hard liquor). Alcohol is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant, decreasing Action potential, electrical activity of neurons in the brain, which causes the characteristic effects of alcohol intoxication ("drunkenness"). Among other effects, alcohol produces euphoria, anxiolytic, decreased anxiety, increased sociability, sedation, and impairment of cognitive, memory, motor control, motor, and sense, sensory function. Alcohol has a variety of adverse effects. Short-term effects of alcohol consumption, Short-term adverse effects include generalized impairment of neurocognitive function, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and symptoms of hangover. Alcohol is addiction, addictive and can result in alcohol use disorder, Substance dependence, dependence, and Alcohol withdrawal syndrome, withdrawal upon cessation. The long-term effects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Heating
Electric heating is a process in which electrical energy is converted directly to heat energy. Common applications include space heating, cooking, water heating and industrial processes. An electric heater is an electricity, electrical device that converts an electric current into heat. The heating element inside every electric heater is an electrical resistor, and works on the principle of Joule heating: an electric current passing through a resistor will convert that electrical energy into heat energy. Most modern electric heating devices use nichrome wire as the active element; the heating element, depicted on the right, uses nichrome wire supported by ceramic insulators. Alternatively, a heat pump can achieve around 150% – 600% efficiency for heating, or COP 1.5 - 6.0 Coefficient of performance, because it uses electric power only for transferring existing thermal energy. The heat pump uses an electric motor to drive a reversed refrigeration cycle, that draws heat energy f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sous Vide
Sous vide (; French for 'under vacuum'), also known as low-temperature, long-time (LTLT) cooking, is a method of cooking invented by the French chef Georges Pralus in 1974, in which food is placed in a plastic pouch or a glass jar and cooked in a water bath for longer than usual cooking times (usually one to seven hours, and more than three days in some cases) at a precisely regulated temperature. The temperature is much lower than usually used for cooking, typically around for red meat, for poultry, and higher for vegetables. The intent is to cook the item evenly, ensuring that the inside is properly cooked without overcooking the outside, and to retain moisture. History Sous vide cooking is characterized by low-temperature cooking, a longer period of cooking than conventional cooking, a container (such as a plastic bag) that separates the food from its heating environment, and pressurized enclosure using full or partial vacuum. Low-temperature cooking was first described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
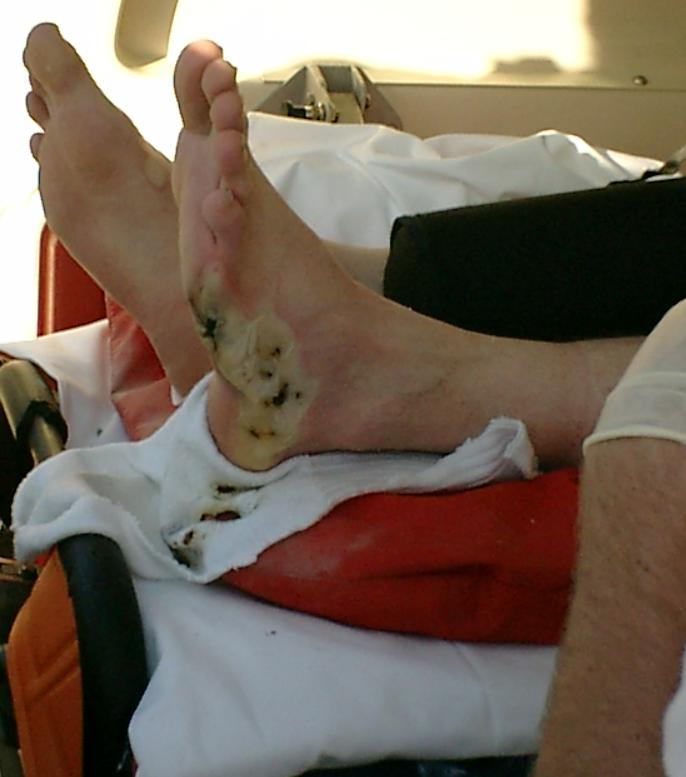
Electrical Injury
An electrical injury (electric injury) or electrical shock (electric shock) is damage sustained to the skin or internal organs on direct contact with an electric current. The injury depends on the density of the current, tissue resistance and duration of contact. Very small currents may be imperceptible or only produce a light tingling sensation. However, a shock caused by low and otherwise harmless current could startle an individual and cause injury due to jerking away or falling. A strong electric shock can often cause painful muscle spasms severe enough to dislocate joints or even to break bones. The loss of muscle control is the reason that a person may be unable to release themselves from the electrical source; if this happens at a height as on a power line they can be thrown off. Larger currents can result in tissue damage and may trigger ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest. If death results from an electric shock the cause of death is generally referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |