|
Montol Language
Montol is an Afroasiatic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. Dialects are Baltap-Lalin and Montol. Roger Blench Roger Marsh Blench (born August 1, 1953) is a British linguist, ethnomusicologist and development anthropologist. He has an M.A. and a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge and is based in Cambridge, England. He researches, publishes, and work ... (2017) uses the name Tel or Tɛɛl for Montol.Blench, Roger. 2017Current research on the A3 West Chadic languages Notes West Chadic languages Languages of Nigeria {{WChadic-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, a population of more than 230 million, it is the List of African countries by population, most populous country in Africa, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in Niger–Nigeria border, the north, Chad in Chad–Nigeria border, the northeast, Cameroon in Cameroon–Nigeria border, the east, and Benin in Benin–Nigeria border, the west. Nigeria is a Federation, federal republic comprising 36 States of Nigeria, states and the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria, Federal Capital Territory, where its capital, Abuja, is located. The List of Nigerian cities by population, largest city in Nigeria by population is Lagos, one of the largest List of largest cities, metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plateau State
Plateau is a northern states of Nigeria, Nigerian state. It is located in the north-central geopolitical zone of Nigeria and includes a range of hills surrounding the Jos Plateau. Plateau State is described as "The Home of Peace and Tourism". The state has a population of around 4.7 million people. Its capital city is Jos. Geography Boundaries Plateau State is located in the north-central zone out of the six geopolitical zones of Nigeria. With an area of , the state has an estimated population of about three million people. It is located between latitude 8°24' N and 10°30' N and longitude 8°32' E and 10°38' E. The state is named after the Jos Plateau, a mountainous area in the north of the state with rock formations. Bare rocks are scattered across the grasslands, which cover the plateau. The altitude ranges from around to a peak of above sea level in the Shere Hills range near Jos. Years of tin and columbite mining have left the area strewn with deep gorges and lakes. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chadic Languages
The Chadic languages form a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken in parts of the Sahel. They include 196 languages spoken across northern Nigeria, southern Niger, southern Chad, and northern Cameroon. By far the most widely spoken Chadic language is Hausa, a lingua franca of much of inland Eastern West Africa, particularly Niger and the northern half of Nigeria. Hausa is the only Chadic language with more than 1 million speakers. Composition Paul Newman (1977) classified the languages into the four groups which have been accepted in all subsequent literature. Further subbranching, however, has not been as robust; Roger Blench (2006), for example, only accepts the A/B bifurcation of East Chadic. Subsequent work by Joseph Lovestrand argues strongly that Kujarge is a valid member of East Chadic. The placing of Luri as a primary split of West Chadic is erroneous. Bernard Caron (2004) shows that this language is South Bauchi and part of the Polci cluster. A sug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Chadic Languages
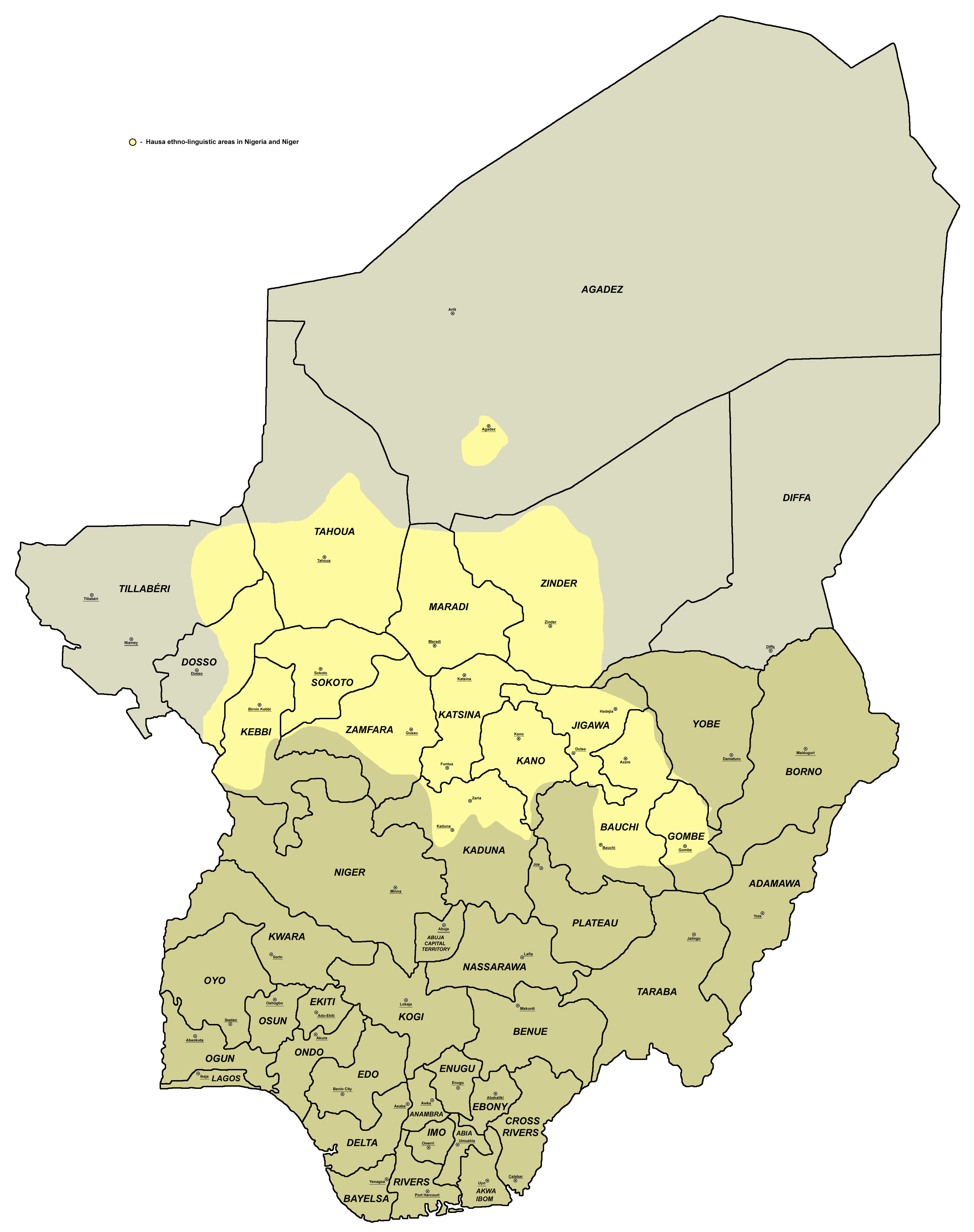
The West Chadic languages of the Afroasiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic family are spoken principally in Niger and Nigeria. They include Hausa language, Hausa, the most populous Chadic languages, Chadic language and a major language of West Africa. Languages The branches of West Chadic go either by names or by letters and numbers in an outline format. *West Chadic **Hausa–Gwandara languages, Hausa–Gwandara (A.1): Hausa language, Hausa, Gwandara language, Gwandara **Bole–Angas (?) ***Bole–Tangale languages, Bole–Tangale (A.2) ****North (Bole proper): Bure language, Bure, Karekare language, Karekare, Bole language, Bole, Gera language, Gera, Geruma language, Geruma, Deno language, Deno, Galambu language, Galambu, Giiwo language, Giiwo, Kubi language, Kubi, Ngamo language, Ngamo, Maaka language, Maaka (Maagha), Ɓeele language, Ɓeele, Dazawa language, Daza (Dazawa), ?Pali language (Chadic), Pali ****South (Tangale): Kwaami language, Kwaami, Pero language, Pero, Piya-Kw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bole–Angas Languages
The West Chadic languages of the Afro-Asiatic family are spoken principally in Niger and Nigeria. They include Hausa, the most populous Chadic language and a major language of West Africa. Languages The branches of West Chadic go either by names or by letters and numbers in an outline format. *West Chadic ** Hausa–Gwandara (A.1): Hausa, Gwandara **Bole–Angas (?) *** Bole–Tangale (A.2) ****North (Bole proper): Bure, Karekare, Bole, Gera, Geruma, Deno, Galambu, Giiwo, Kubi, Ngamo, Maaka (Maagha), Ɓeele, Daza (Dazawa), ?Pali ****South (Tangale): Kwaami, Pero, Piya-Kwonci, Kholok, Nyam, Kushi (Goji), Kutto (Kupto), Tangale, Dera (Kanakuru) *** Angas ( Central West Chadic) (A.3)Blench, Roger. 2017Current research on the A3 West Chadic languages ****Ngasic: Ngas (Angas), Belnəng ****Mwaghavulic: Mwaghavul, Mupun (Mapun), Takas (Toos); Cakfem-Mushere **** Miship (Chip) ****Pan cluster ***** Chakato/Jorto ***** Jipal, Mernyang (Mirriam), Kwagalla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
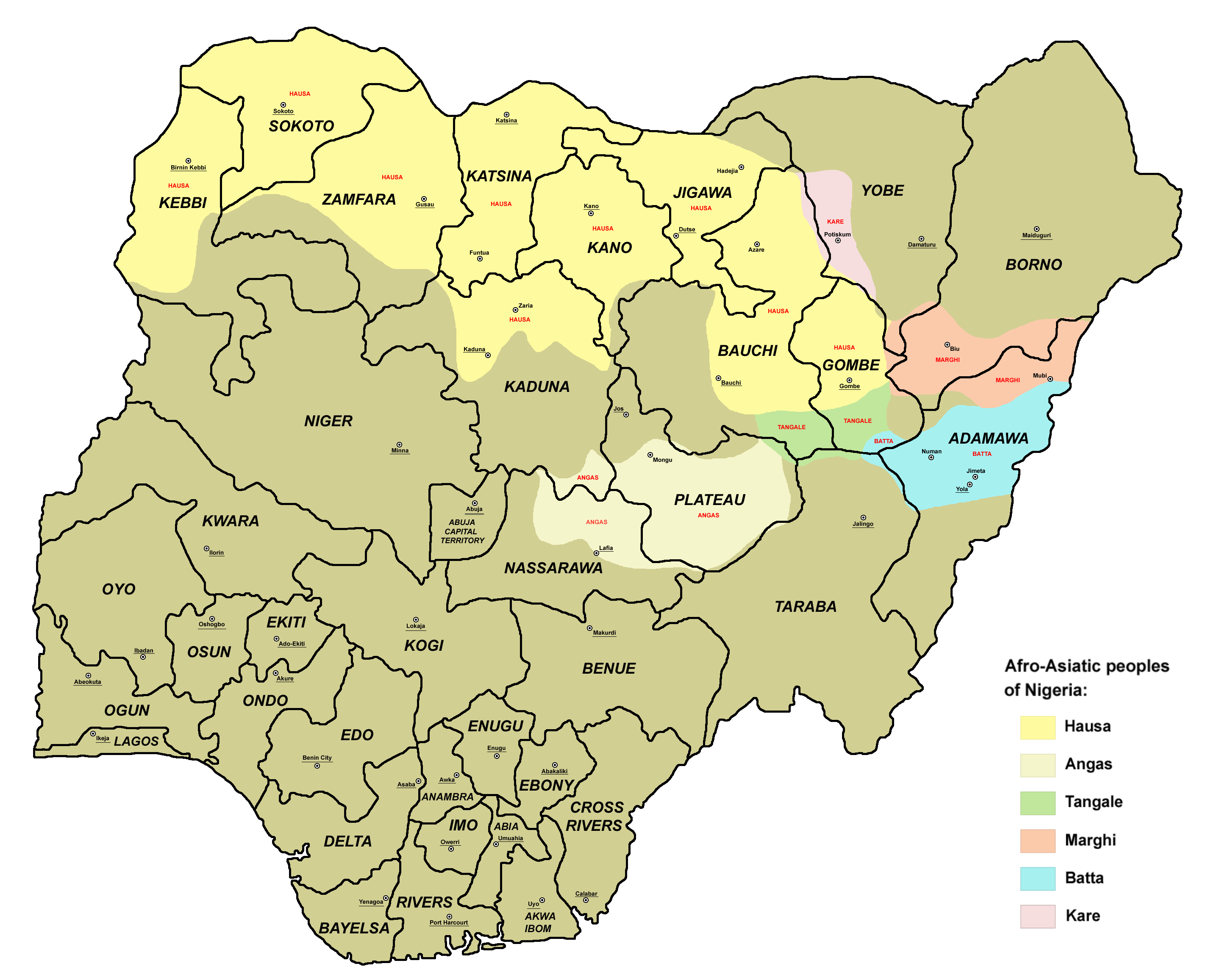
Angas Languages
The Angas, Angas–Sura, or Central West Chadic languages (also known as A.3 West Chadic) are a branch of West Chadic languages spoken in Plateau State, north-central Nigeria. Languages The Angas languages are:Blench, Roger. 2017Current research on the A3 West Chadic languages ;Angas *Ngasic: Ngas (Angas), Belnəng; ? Miler *Mwaghavulic: Mwaghavul, Mupun (Mapun), Takas (Toos); Cakfem-Mushere * Miship (Chip) *Pan cluster ** Chakato; Jorto (spurious) ** Jipal, Mernyang (Mirriam), Kwagallak, Kofyar (Doemak), Bwol, Goram, Jibyal * Nteng *Tel (Tɛɛl, Montol) *Talic: Tal, Pyapun, Koenoem *Goemaic: Goemai * Yiwom (Ywom, Gerka) Note that in the language names, orthographic '' oe'' stands for the mid central vowel ə, a practice that had been adopted by missionaries in the Shendam area during the 1930s, such as Father E. Sirlinger. Unlike many other West Chadic languages, Angas languages do not have complex nominal and verbal morphology. Ywom is the most divergent language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afroasiatic Languages
The Afroasiatic languages (also known as Afro-Asiatic, Afrasian, Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic) are a language family (or "phylum") of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara and Sahel. Over 500 million people are native speakers of an Afroasiatic language, constituting the fourth-largest language family after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo. Most linguists divide the family into six branches: Berber (Amazigh), Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Omotic, and Semitic. The vast majority of Afroasiatic languages are considered indigenous to the African continent, including all those not belonging to the Semitic branch (which originated in West Asia). The five most spoken languages are; Arabic (of all varieties) which is by far the most widely spoken within the family, with around 411 million native speakers concentrated primarily in West Asia and North Africa, the Chadic Hausa language w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Blench
Roger Marsh Blench (born August 1, 1953) is a British linguist, ethnomusicologist and development anthropologist. He has an M.A. and a Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge and is based in Cambridge, England. He researches, publishes, and works as a consultant. Career Blench is known for his wide-ranging interests and has made important contributions to African linguistics, Southeast Asian linguistics, anthropology, ethnomusicology, ethnobotany, and various other related fields. He has done significant research on the Niger–Congo, Nilo-Saharan, and Afroasiatic families, as well as the Arunachal languages. Additionally, Blench has published extensively on the relationship between linguistics and archaeology. Blench is currently engaged in a long-term project to document the languages of central Nigeria. He has also expressed concern about ranching in Nigeria. Blench collaborated with the late Professor Kay Williamson, who died in January 2005, and is now a trustee of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |