|
Montenegrin Parliamentary Election, 2016
Parliamentary elections were held in Montenegro on 16 October 2016. The ruling Democratic Party of Socialists (DPS) remained the largest party, winning 36 of the 81 seats, and subsequently formed a coalition government with the new Social Democrats of Montenegro, Social Democrats and national minority parties. The elections were held in the midst of an Montenegrin coup plot, alleged coup d'état attempt. Background Protests against incumbent Prime Minister Milo Djukanovic occurred in the preceding year over issues ranging from NATO membership to electoral fraud. A split in Coalition for a European Montenegro, the ruling coalition followed in January 2016, leaving the government functioning as a de facto minority government. The provisional government of electoral trust was elected on May 12, 2016, by the parliament of Montenegro. The provisional governing coalition was formed by DPS and several opposition parties. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2012 Montenegrin Parliamentary Election
Snap parliamentary elections were held in Montenegro on 14 October 2012. The parliamentary elections were the ninth since the reintroduction of multi-party system in 1990, and the third since regaining full independence in 2006. The result was a victory for the ruling European Montenegro alliance (based around the Democratic Party of Socialists) led by Milo Đukanović, which won 39 of the 81 seats, remaining without the majority by itself for the first time since the 2001 election, and subsequently forming a majority coalition government with the ethnic minority Bosniak Party (BS) and Croatian Civic Initiative (HGI) parties. Electoral system The 81 members of Parliament were elected by proportional representation from a single nationwide constituency with an electoral threshold of 3%, although the threshold was reduced to 0.7% for ethnic minority parties in districts where ethnic minorities accounted for at least 15% of the population. For ethnic Croats, the electoral l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegro
, image_flag = Flag of Montenegro.svg , image_coat = Coat of arms of Montenegro.svg , coa_size = 80 , national_motto = , national_anthem = () , image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Podgorica , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Montenegrin language, Montenegrin , languages2_type = Languages in official use , languages2 = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_ref = , ethnic_groups_year = 2023 census , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2023 census , demonym = Montenegrins, Montenegrin , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President of Montenegro, President , leader_name1 = Jakov Milatović , leader_title2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Serb Party
The Democratic Serb Party () is a minor conservative political party in Montenegro, representing the Serbs of Montenegro. History The Democratic Serb Party was formed in 2003 following a split from the Serb People's Party led by Božidar Bojović, who was the first party president, and Ranko Kadić, first vice president and his subsequent successor. At the legislative elections held in March 2009, DSS formed a pre-election coalition with the People's Party, but the coalition failed to gain parliamentary status, winning 2,9% of the votes, just below the 3% electoral threshold. At the next election DSS participated in a nationalist coalition ''Serb National Alliance'' along with Party of Serb Radicals Party of Serb Radicals (, SSR), formerly Serbian Radical Party of Montenegro (SRS CG), was a minor far-right and Serbian nationalist political party, active in Montenegro. History The SSR was formed by the former members of Serbian Radical Party, ... and Serb National Alliance, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
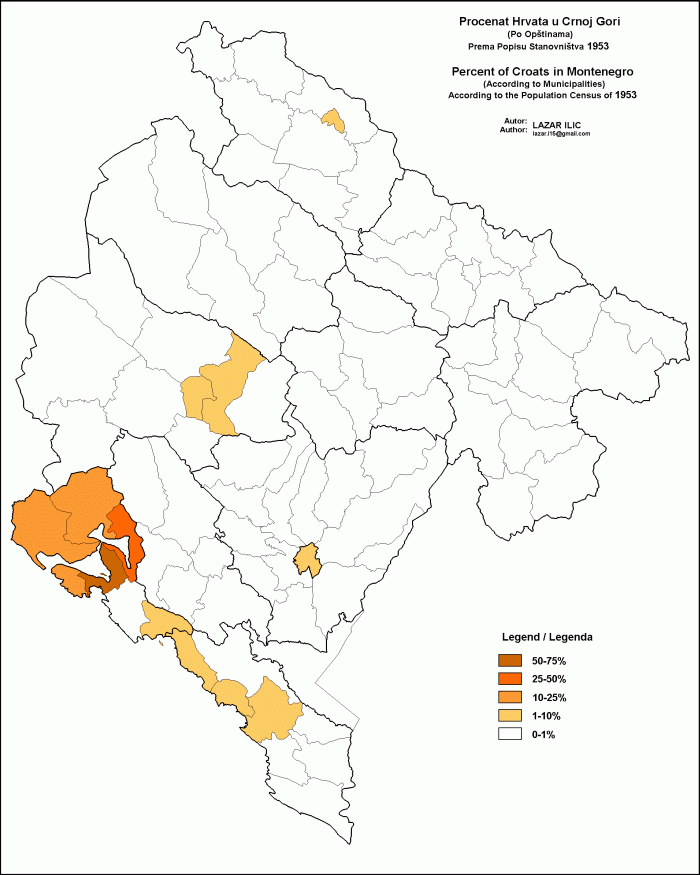
Croats Of Montenegro
The Croats have a minority in Boka Kotorska (''Bay of Kotor''), a coastal region in Montenegro, the largest of their kind in Tivat. The three Municipalities of Montenegro, municipalities making up the Bay of Kotor (Tivat, Kotor and Herceg-Novi) include 4,519 Croats or 6.70%. They are also known as Bokelji, a common name for all inhabitants for of Boka Kotorska. Tivat is home to the minority political party Croatian Civic Initiative, and to the ''National Council of Croats in Montenegro''. Kotor is home to Croatian Civic Society of Montenegro. Religion Croats of Montenegro are mainly Catholic. According to the 2011 census, 5,527 (91.80%) Croats declared as such. Since most of them live in the Bay of Kotor, the vast majority of them fall under the Roman Catholic Diocese of Kotor, Diocese of Kotor. ;Places of worship *Our Lady of the Rocks *Cathedral of Saint Tryphon Demographics Settlements in Montenegro with significant Croatian minority (10 percent or more) include (2011) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Montenegro
The ''municipalities'' ( cnr-Latn-Cyrl, opštine, општине, separator=" / ", singular: cnr-Latn-Cyrl, opština, општина, separator=" / ", label=none) are the first level administrative subdivisions of Montenegro. The country is divided into 25 municipalities including the Old Royal Capital Cetinje and the Podgorica Capital City. Podgorica is divided into one subdivision called ''city municipality'' ( cnr-Latn-Cyrl, gradska opština, градска општина, separator=" / ", link=no, plural: cnr-Latn-Cyrl, gradske opštine, градске општине, separator=" / ", label=none), forming the most basic level of local government. Recently created: *Petnjica Municipality (2013) *Gusinje Municipality (2014) *Tuzi Municipality (2018) *Zeta Municipality (2022) ** The ''Union of Municipalities of Montenegro'' is a national association of local authorities of Montenegro. List Source: Politics List of current mayors and local governments (4) (3) (3) (2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral Threshold
The electoral threshold, or election threshold, is the minimum share of votes that a candidate or political party requires before they become entitled to representation or additional seats in a legislature. This limit can operate in various ways; for example, in party-list proportional representation systems where an electoral threshold requires that a party must receive a specified minimum percentage of votes (e.g. 5%), either nationally or in a particular electoral district, to obtain seats in the legislature. In single transferable voting, the election threshold is called the quota, and it is possible to achieve it by receiving first-choice votes alone or by a combination of first-choice votes and votes transferred from other candidates based on lower preferences. In mixed-member-proportional (MMP) systems, the election threshold determines which parties are eligible for top-up seats in the legislative chamber. Some MMP systems still allow a party to retain the seats the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D'Hondt Method
The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is an apportionment method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in proportional representation among political parties. It belongs to the class of highest-averages methods. Compared to ideal proportional representation, the D'Hondt method reduces somewhat the political fragmentation for smaller electoral district sizes, where it favors larger political parties over small parties. The method was first described in 1792 by American Secretary of State and later President of the United States Thomas Jefferson. It was re-invented independently in 1878 by Belgian mathematician Victor D'Hondt, which is the reason for its two different names. Motivation Proportional representation systems aim to allocate seats to parties approximately in proportion to the number of votes received. For example, if a party wins one-third of the votes then it should gain about one-third of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions (Political party, political parties) among voters. The aim of such systems is that all votes cast contribute to the result so that each representative in an assembly is mandated by a roughly equal number of voters, and therefore all votes have equal weight. Under other election systems, a bare Plurality (voting), plurality or a scant majority in a district are all that are used to elect a member or group of members. PR systems provide balanced representation to different factions, usually defined by parties, reflecting how votes were cast. Where only a choice of parties is allowed, the seats are allocated to parties in proportion to the vote tally or ''vote share'' each party receives. Exact proportionality is never achieved under PR systems, except by chance. The use of elector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed List
Closed list describes the variant of party-list systems where voters can effectively vote for only political parties as a whole; thus they have no influence on the party-supplied order in which party candidates are elected. If voters had some influence, that would be called an open list. Closed list systems are still commonly used in party-list proportional representation, and most mixed electoral systems also use closed lists in their party list component. Many countries, however have changed their electoral systems to use open lists to incorporate personalised representation to their proportional systems. In closed list systems, each political party has pre-decided who will receive the seats allocated to that party in the elections, so that the candidates positioned highest on this list tend to always get a seat in the parliament while the candidates positioned very low on the closed list will not. However, the candidates "at the water mark" of a given party are in the positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Montenegro
The Parliament of Montenegro () is the unicameral legislature of Montenegro. The Parliament currently has 81 members, with each member elected to a four-year term. Following the 2006 independence referendum, the Parliament declared and ratified the independence of Montenegro on 3 June 2006. Members of the Parliament are elected using proportional representation. History The Parliament of Montenegro was initially established by the Constitution of the Principality of Montenegro in 1905 and was called the Popular Assembly (''Narodna skupština''). It had a limited legislative role, limited by the authority of the Knjaz (Prince). The first parliament was constituted in 1906. Following the incorporation of the Kingdom of Montenegro into the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1918, the Parliament of Montenegro was disbanded until World War II. The Parliament was reinstated in 1944, in the form of the ''Montenegrin Anti-Fascist Assembly of National Liberation (CASNO)'', which changed its name to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coalition For A European Montenegro
The European Montenegro (, ; abbr. ECG) was the ruling political alliance in Montenegro headed by Milo Đukanović's Democratic Party of Socialists (DPS). Following the internal turmoil within the DPS during late 1996 and early 1997 when the party's most prominent members Đukanović and Momir Bulatović bitterly fought behind the scenes for the control of the party, Đukanović emerged as the clear winner of the year-long power struggle. Under his leadership, DPS began entering pre-election alliances with smaller parties under the coalition banner that had a different name ahead of each parliamentary election. Besides the leading DPS, it was also consisted of two main political parties, the SDP and the LPCG. The coalition was formally dissolved in 2016. The first version of the coalition was formed ahead of the 1998 parliamentary elections in Montenegro under the name So that we live better (/). Before the 2001 elections the coalition was rebranded as Victory is Montenegro's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member states—30 European and 2 North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact, and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa. The organization's motto is . The organization's strategic concepts include Deterrence theory, deterrence. NATO headquarters, NATO's main headquarter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |