|
Moment-area Theorem
The moment-area theorem is an engineering tool to derive the slope, rotation and deflection of beams and frames. This theorem was developed by Mohr and later stated namely by Charles Ezra Greene in 1873. This method is advantageous when we solve problems involving beams, especially for those subjected to a series of concentrated loadings or having segments with different moments of inertia The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular accelera .... Theorem 1 The change in slope between any two points on the elastic curve equals the area of the M/EI (moment) diagram between these two points. :\theta_=^B\left(\frac\right)dx where, * M = moment * EI = flexural rigidity * \theta_ = change in slope between points A and B * A, B = points on the elastic curve Theorem 2 The vertical deviation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Otto Mohr
Christian Otto Mohr (8 October 1835 – 2 October 1918) was a German civil engineer. He is renowned for his contributions to the field of structural engineering, such as Mohr's circle, and for his study of stress. Biography He was born on 8 October 1835 to a landowning family in Wesselburen in the Holstein region. At the age of 16 attended the Polytechnic School in Hannover. Starting in 1855, his early working life was spent in railroad engineering for the Hanover and Oldenburg state railways, designing some famous bridges and making some of the earliest uses of steel trusses. Even during his early railway years, Mohr had developed an interest in the theories of mechanics and the strength of materials. In 1867, he became professor of mechanics at Stuttgart Polytechnic, and in 1873 at Dresden Polytechnic. Mohr had a direct and unpretentious lecturing style that was popular with his students. In addition to a lone textbook, Mohr published many research papers on the theory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Ezra Greene
Charles Ezra Greene (February 12, 1842 – 1903) was an Americans, American civil engineer, born in Cambridge, Massachusetts. He graduated at Harvard University, Harvard in 1862 and at Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1863, served as quartermaster during the last two years of the American Civil War, Civil War, and was United States assistant engineer from 1870 to 1872, when, for part of a year, he was city engineer of Bangor, Maine. In the same year he became connected with the engineering department of the University of Michigan. In 1895, he became the first Dean (education), dean of the University of Michigan College of Engineering, a position he held until his death. He was an associate editor of the ''Engineering News-Record#History, Engineering News'' from 1876 - 1877. His publications include: * ''Graphical Method for the Analysis of Bridge Trusses'' (1876) * ''Trusses and Arches: Graphics for Engineers, Architects, and Builders'' (three volumes, 1876–79; third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moments Of Inertia
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rate of rotation. It is an extensive (additive) property: for a point mass the moment of inertia is simply the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis. For bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
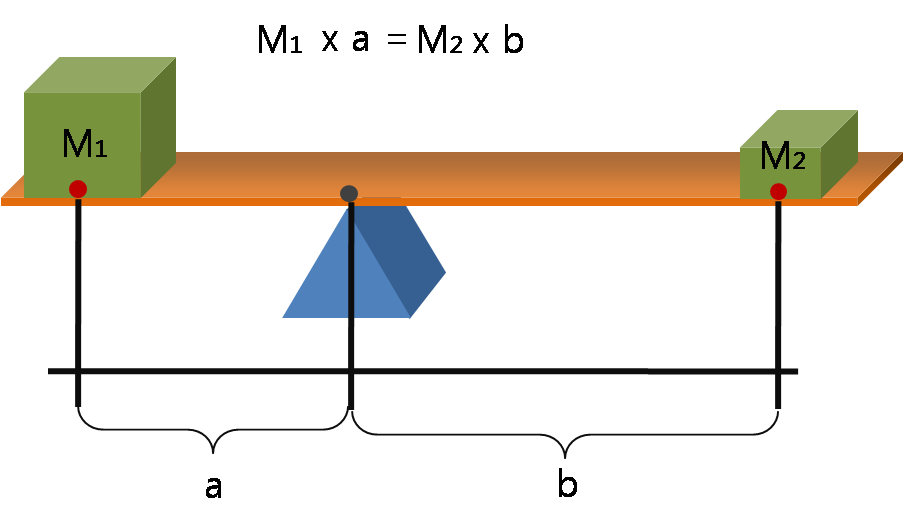
Moment (physics)
In physics, a moment is a mathematical expression involving the product of a distance and physical quantity. Moments are usually defined with respect to a fixed reference point and refer to physical quantities located some distance from the reference point. In this way, the moment accounts for the quantity's location or arrangement. For example, the moment of force, often called torque, is the product of a force on an object and the distance from the reference point to the object. In principle, any physical quantity can be multiplied by a distance to produce a moment. Commonly used quantities include forces, masses, and electric charge distributions. Elaboration In its most basic form, a moment is the product of the distance to a point, raised to a power, and a physical quantity (such as force or electrical charge) at that point: : \mu_n = r^n\,Q, where Q is the physical quantity such as a force applied at a point, or a point charge, or a point mass, etc. If the quantity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |