|
Ministry Of Agriculture And Farmers' Welfare
The Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (Hindi: ''Krishi Avam Kisaan Kalyaan Mantralaya''), formerly the Ministry of Agriculture, is a branch of the Government of India and the apex body for formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws related to agriculture in India. The three broad areas of scope for the Ministry are agriculture, food processing and co-operation. The agriculture ministry is headed by Minister of Agriculture Narendra Singh Tomar. Abhishek Singh Chauhan, Krishna Raj and Parsottambhai Rupala are the Ministers of State. Sharad Pawar, serving from 22 May 2004 to 26 May 2014, has held the office of Minister of Agriculture for the longest continuous period till date. Origins Department of Revenue and Agriculture and Commerce was set up in June 1871 to deal with all the agricultural matters in India. Until this ministry was established, matters related to agriculture were within the portfolio of the Home Department. In 1881, Departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, consisting of 28 union states and eight union territories. Under the Constitution, there are three primary branches of government: the legislative, the executive and the judiciary, whose powers are vested in a bicameral Parliament, President, aided by the Council of Ministers, and the Supreme Court respectively. Through judicial evolution, the Parliament has lost its sovereignty as its amendments to the Constitution are subject to judicial intervention. Judicial appointments in India are unique in that the executive or legislature have negligible say. Etymology and history The Government of India Act 1833, passed by the British parliament, is the first such act of law with the epithet "Government of India". Basic structure The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Agriculture Development Programme
Remunerative Approach for Agriculture and Allied sector Rejuvenation, previously Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana ( hi, राष्ट्रीय कृषि विकास योजना, italic=yes, translation=National Agriculture Development Programme) is a State Plan Scheme of Additional Central Assistance, was launched in August 2007 as a part of the 11th Five Year Plan by the Government of India. Launched under the aegis of the National Development Council, it seeks to achieve 4% annual growth in agriculture through development of Agriculture and its allied sectors (as defined by the Planning Commission) during the period under the 11th Five Year Plan (2007–11). Aims This programme is essentially a State Plan Scheme that seeks to provide the States and Territories of India with the autonomy to draw up plans for increased public investment in Agriculture by incorporating information on local requirements, geographical/climatic conditions, available natural resources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K M Munshi
Kanhaiyalal Maneklal Munshi (; 30 December 1887 – 8 February 1971), popularly known by his pen name Ghanshyam Vyas, was an Indian independence movement activist, politician, writer and educationist from Gujarat state. A lawyer by profession, he later turned to author and politician. He is a well-known name in Gujarati literature. He founded Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, an educational trust, in 1938. Munshi wrote his works in three languages namely Gujarati, English and Hindi. Before independence of India, Munshi was part of Indian National Congress and after independence, he joined Swatantra Party. Munshi held several important posts like member of Constituent Assembly of India, minister of agriculture and food of India, and governor of Uttar Pradesh. In his later life, he was one of the founding members of Vishva Hindu Parishad. Early life Munshi was born on 30 December 1887 at Bharuch, a town in Gujarat State of British India. Munshi took admission at Baroda College in 1902 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
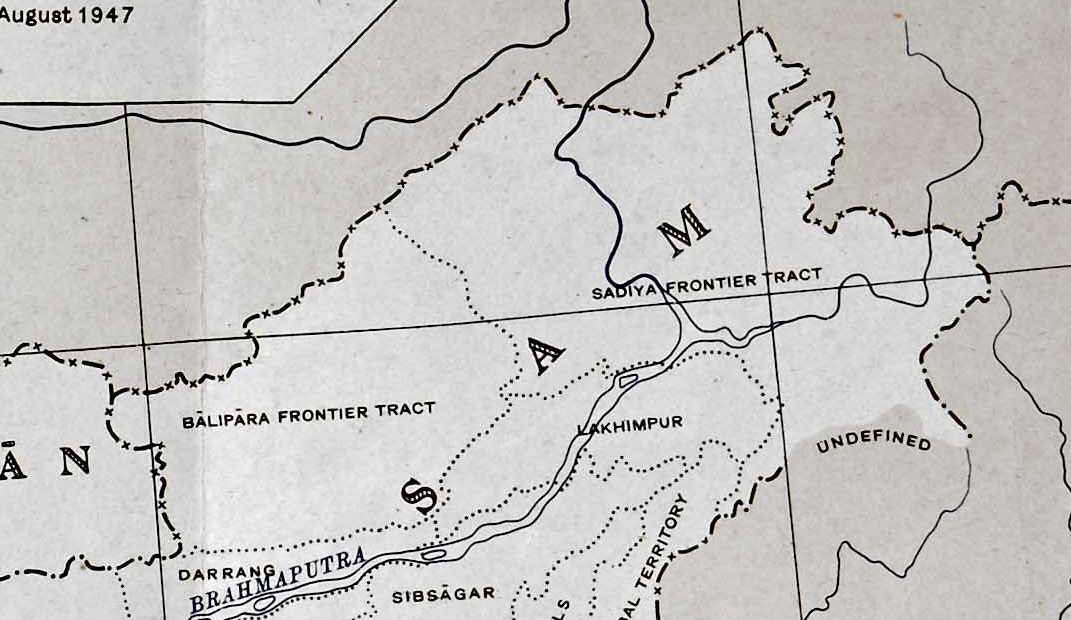
Jairamdas Daulatram
Jairamdas Daulatram (1891–1979) was an Indian political leader from Sindh, who was active in the Indian independence movement and later served in the Government of India. He was appointed as the Governor for the states of Bihar and later Assam. He played a key role in strengthening the North-East Frontier Tracts of India in the face of the Chinese annexation of Tibet, and managed the Indian integration of Tawang in 1951. Early life Jairamdas Daulatram was born into a Sindhi Hindu family in Karachi, Sindh, which was then part of the Bombay Presidency in British India on 21 July 1891. After receiving a degree in law, he started a legal practice, but soon gave it up as it often led to conflict with his conscience. In 1915, Daulatram came into contact with Mahatma Gandhi, who had then returned from South Africa, and became his devoted follower. At the Amritsar session of the Indian National Congress in 1919, he worded Gandhi's resolution in such a way that it avoided an impendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Empire in Asia and Africa. From the late 19th century, and especially after 1920, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, the Congress became the principal leader of the Indian independence movement. The Congress led India to independence from the United Kingdom, and significantly influenced other anti-colonial nationalist movements in the British Empire. Congress is one of the two major political parties in India, along with its main rival the Bharatiya Janata Party. It is a " big tent" party whose platform is generally considered to lie in the centre to of Indian politics. After Indian independence in 1947, Congress emerged as a catch-all and secular party, dominating Indian politics for the next 20 years. The party's first pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jawaharlal Nehru
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru (; ; ; 14 November 1889 – 27 May 1964) was an Indian anti-colonial nationalist, secular humanist, social democrat— * * * * and author who was a central figure in India during the middle of the 20th century. Nehru was a principal leader of the Indian nationalist movement in the 1930s and 1940s. Upon India's independence in 1947, he served as the country's prime minister for 16 years. Nehru promoted parliamentary democracy, secularism, and science and technology during the 1950s, powerfully influencing India's arc as a modern nation. In international affairs, he steered India clear of the two blocs of the Cold War. A well-regarded author, his books written in prison, such as ''Letters from a Father to His Daughter'' (1929), '' An Autobiography'' (1936) and '' The Discovery of India'' (1946), have been read around the world. During his lifetime, the honorific Pandit was commonly applied before his name in India and even today too. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajendra Prasad
Rajendra Prasad (3 December 1884 – 28 February 1963) was an Indian politician, lawyer, Indian independence activist, journalist & scholar who served as the first president of Republic of India from 1950 to 1962. He joined the Indian National Congress during the Indian Independence Movement and became a major leader from the region of Bihar and Maharashtra. A supporter of Mahatma Gandhi, Prasad was imprisoned by United Kingdom, British authorities during the Salt Satyagraha of 1931 and the Quit India movement of 1942. After the constituent assembly 1946 Indian provincial elections, 1946 elections, Prasad served as Minister of Food and Agriculture in the central government. Upon independence in 1947, Prasad was elected as President of the Constituent Assembly of India, which prepared the Constitution of India and served as its provisional Parliament of India, Parliament. When India became a republic in 1950, Prasad was 1950 Indian presidential election, elected its first pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajendra Prasad 1947
Rajendra may refer to: * Rajendra (name), a male given name (including a list of persons with the name) * ''Rajendra'' (moth), a moth genus * Rajendra Radar, a phased array radar {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farmer Income Protection Scheme (PM AASHA)
The Prime Minister's Farmer Income Protection Scheme (), also known as PM AASHA () is an umbrella scheme of the Government of India The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ... announced in September 2018 to ensure a price policies such as a minimum support price are fulfilled. It includes the former Price Support Scheme (PSS), a Price Deficiency Payment Scheme (PDPS) and a Private Procurement & Stockist Scheme (PPPS). See also * Deficiency payments References {{Premiership of Narendra Modi Agriculture in India Government schemes in India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PMKSN, translation: ''Prime Minister's Farmer's Tribute Fund'') is an initiative by the government of India that give farmers up to per year as minimum income support. The initiative was announced by Piyush Goyal during the 2019 Interim Union Budget of India on 1 February 2019. The scheme has cost per annum and came into effect December 2018. History The scheme was first conceived and implemented by government of Telangana as the Rythu Bandhu scheme, where a certain amount is given directly to eligible farmers. The scheme has received accolades from various organisations for its successful implementation, including World Bank. Many economist suggest that this type of investment support is better than farm loan waivers. With the positive outcome of this scheme, Government of India wanted to implement it as nationwide project and it was announced by Piyush Goyal during the 2019 Interim Union Budget of India on 1 February 2019. For 2018–201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana ( hi, प्रधानमंत्री कृषि सिंचाई योजना) is a national mission to improve farm productivity and ensure better utilization of the resources in the country. The budget of in a time span of one year 2015-2016 has been allocated to this scheme. The decision was taken on 1 July 2015 at the meeting of Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, approved with an outlay of 50000 crore for period of 5 years (2015-16 to 2019-20). Major objectives * Convergence of investment in irrigation at the field level * Expand cultivable area under irrigation (हर खेत को पानी) * Improve On-farm water use efficiency to reduce wastage of water * Enhance the adoption of being precise in irrigation and other water saving technologies (more crop per drop) Purpose The primary objectives of PMKSY are to attract investments in irrigation system at field level, develop and expand cultivable land in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |