|
Midgut Carcinoid
The midgut is the portion of the embryo from which most of the intestines develop. After it bends around the superior mesenteric artery, it is called the "midgut loop". It comprises the portion of the alimentary canal from the end of the foregut at the opening of the bile duct to the hindgut, about two-thirds of the way through the transverse colon. In the embryo During development, the human midgut undergoes a rapid phase of growth in which the loop of midgut herniates outside of the abdominal cavity of the fetus and protrudes into the umbilical cord. This herniation is physiological (occurs normally). Later in development, the fetus's body catches up in size relative to the midgut and creates adequate room in the abdominal cavity for the entirety of the midgut to reside. The midgut loops slip back out of the umbilical cord and the physiological hernia ceases to exist. This change coincides with the termination of the yolk sac and the counterclockwise rotation of the two limb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo. Vertebrates Structure Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. Mesenchymal cells can migrate easily (in contrast to epithelial cells, which lack mobility), are organized into closely adherent sheets, and are polarized in an apical-basal orientation. Development The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. From the mesoderm, the mesenchyme appears as an embryologically primitive "soup". This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascending Colon
''Ascending'' is a science fiction novel by the Canadian writer James Alan Gardner, published in 2001 by HarperCollins Publishers under its various imprints.HarperCollins, Avon, HarperCollins Canada, SFBC/Avon; paperback edition 2001, Eos Books. It is the fifth novel in Gardner's "League of Peoples" series. It is a direct sequel to the first novel in the series, ''Expendable'', in that it picks up the dual story of Festina Ramos, Explorer turned admiral, and the transparent glass woman Oar, where the earlier novel left off. Backstory Through the course of ''Ascending'', Gardner adds depth, detail, and perspective to the conceptual background he has established for the "League of Peoples" series. In particular, he explains how human beings and other species in the galaxy are contacted by, and become a part of, the larger galactic community. Sometime in the middle of the 21st century, humanity encounters a mysterious group of beings who call themselves merely "citizens of the Leag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omphalocele
Omphalocele or omphalocoele also called exomphalos, is a rare abdominal wall defect. Beginning at the 6th week of development, rapid elongation of the gut and increased liver size reduces intra abdominal space, which pushes intestinal loops out of the abdominal cavity. Around 10th week, the intestine returns to the abdominal cavity and the process is completed by the 12th week. Persistence of intestine or the presence of other abdominal viscera (e.g. stomach, liver) in the umbilical cord results in an omphalocele. Omphalocele occurs in 1 in 4,000 births and is associated with a high rate of mortality (25%) and severe malformations, such as cardiac anomalies (50%), neural tube defect (40%), exstrophy of the bladder and Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome. Approximately 15% of live-born infants with omphalocele have chromosomal abnormalities. About 30% of infants with an omphalocele have other congenital abnormalities. Signs and symptoms The sac, which is formed from an outpouching of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volvulus
A volvulus is when a loop of intestine twists around itself and the mesentery that supports it, resulting in a bowel obstruction. Symptoms include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, vomiting, constipation, and bloody stool. Onset of symptoms may be rapid or more gradual. The mesentery may become so tightly twisted that blood flow to part of the intestine is cut off, resulting in ischemic bowel. In this situation there may be fever or significant pain when the abdomen is touched. Risk factors include a birth defect known as intestinal malrotation, an enlarged colon, Hirschsprung disease, pregnancy, and abdominal adhesions. Long term constipation and a high fiber diet may also increase the risk. The most commonly affected part of the intestines in adults is the sigmoid colon with the cecum being second most affected. In children the small intestine is more often involved. The stomach can also be affected. Diagnosis is typically with medical imaging such as plain X-rays, a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Mesenteric Plexus
The superior mesenteric plexus is a continuation of the lower part of the celiac plexus, receiving a branch from the junction of the right vagus nerve with the plexus. It surrounds the superior mesenteric artery, accompanies it into the mesentery, and divides into a number of secondary plexuses, which are distributed to all the parts supplied by the artery, viz., pancreatic branches to the pancreas; intestinal branches to the small intestine; and ileocolic, right colic, and middle colic branches, which supply the corresponding parts of the great intestine. The nerves composing this plexus are white in color and firm in texture; in the upper part of the plexus close to the origin of the superior mesenteric artery is the superior mesenteric ganglion. Additional images File:Gray838.png, The right sympathetic chain and its connections with the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic plexuses. File:Gray839.png, Diagram of efferent sympathetic nervous system. File:Gray849.png, Lower half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innervation
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisterna Chyli
The cisterna chyli (or cysterna chyli, and etymologically more correct, receptaculum chyli) is a dilated sac at the lower end of the thoracic duct in most mammals into which lymph from the intestinal trunk and two lumbar lymphatic trunks flow. It receives fatty chyle from the intestines and thus acts as a conduit for the lipid products of digestion. It is the most common drainage trunk of most of the body's lymphatics. The cisterna chyli is a retro-peritoneal structure. Structure In humans, the cisterna chyli is located posterior to the abdominal aorta on the anterior aspect of the bodies of the first and second lumbar vertebrae (L1 and L2). There it forms the beginning of the primary lymph vessel, the thoracic duct, which transports lymph and chyle from the abdomen via the aortic opening of the diaphragm up to the junction of left subclavian vein and internal jugular veins. Other animals In dogs, the cisterna chyli is located to the left and often ventral to the aorta; in cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chyle
Chyle (from the Ancient Greek, Greek word χυλός ''chylos'', "juice") is a milky bodily fluid consisting of lymph and emulsified fats, or free fatty acids (FFAs). It is formed in the small intestine during digestion of fatty foods, and taken up by lymph vessels specifically known as lacteals. The lipids in the chyle are colloidally suspended in chylomicrons. Clinical significance A chyle fistula occurs when defect(s) of lymphatic vessel(s) result in leakage of lymphatic fluid, typically accumulating in the thoracic (pleural) or abdominal (peritoneal) cavities, leading to a chylous pleural effusion (chylothorax) or chylous ascites, respectively. Diagnosis of a chyle fistula may be accomplished by analysis of pleural/peritoneal fluid. Identifying the source (localizing the lymphatic defect) is often challenging, but may be accomplished with lymphangiography, which is occasionally associated with a serendipitous therapeutic effect (resolution of the leak), thought to be secondar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the origin of the fluid-return process, interstitial fluid—the fluid between the cells in all body tissues—enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood. Because it is derived from interstitial fluid, with which blood and surrounding cells continually exchange substances, lymph undergoes continual change in composition. It is generally similar to blood plasma, which is the fluid component of blood. Lymph returns pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
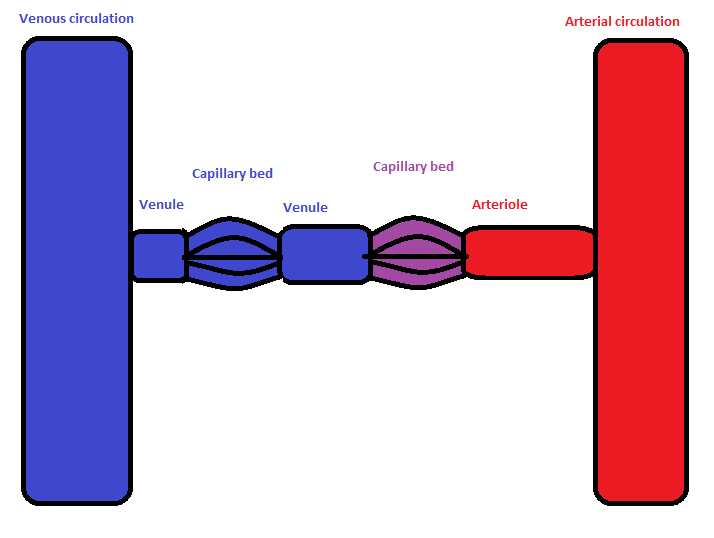
Portal Venous System
In the circulatory system of animals, a portal venous system occurs when a capillary bed pools into another capillary bed through veins, without first going through the heart. Both capillary beds and the blood vessels that connect them are considered part of the portal venous system. They are relatively uncommon as the majority of capillary beds drain into veins which then drain into the heart, not into another capillary bed. Portal venous systems are considered venous because the blood vessels that join the two capillary beds are either veins or venules. Examples of such systems include the hepatic portal system, the hypophyseal portal system, and (in non-mammals) the renal portal system. Unqualified, ''portal venous system'' often refers to the hepatic portal system. For this reason, ''portal vein'' most commonly refers to the hepatic portal vein. The functional significance of such a system is that it transports products of one region directly to another region in relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Structure Sections In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections. One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation. Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this system, the aorta starts as the ascending aorta, travels superiorly from the heart, and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |