|
Microporus Atrovillosus
''Microporus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Polyporaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution and, according to a 2008 estimate, contains 11 species. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek words ("small") and ("pore"). Species , Index Fungorum accepts 12 species in ''Microporus'': *'' M. affinis'' (Blume & T.Nees) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. affinis-microloma'' (Lloyd) T.Hatt. & Sotome (2013) *'' M. atroalbus'' (Henn.) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. atrovillosus'' Ryvarden (1975) *'' M. concinnus'' P.Beauv. (1804) *'' M. incomptus'' (Afzel. ex Fr.) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. internuntius'' (Corner) T. Hatt. (2005) *'' M. longisporus'' T.Hatt. (2000) *'' M. luteoceraceus'' D.A.Reid (1986) – Peninsular Malaysia *'' M. nipponicus'' (Yasuda) Imazeki (1943) *'' M. subvernicipes'' (Murrill) T.Hatt. & Sotome (2013) *'' M. xanthopus'' (Fr.) Kuntze (1898) Chemistry Seven novel diterpene molecules, microporenic acids A–G, were isolated from the cultures of an undescribed species of ''Microporus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microporus Incomptus
''Microporus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Polyporaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution and, according to a 2008 estimate, contains 11 species. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek words ("small") and ("pore"). Species , Index Fungorum accepts 12 species in ''Microporus'': *'' M. affinis'' (Blume & T.Nees) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. affinis-microloma'' (Lloyd) T.Hatt. & Sotome (2013) *'' M. atroalbus'' (Henn.) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. atrovillosus'' Ryvarden (1975) *'' M. concinnus'' P.Beauv. (1804) *'' M. incomptus'' (Afzel. ex Fr.) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. internuntius'' (Corner) T. Hatt. (2005) *'' M. longisporus'' T.Hatt. (2000) *'' M. luteoceraceus'' D.A.Reid (1986) – Peninsular Malaysia *'' M. nipponicus'' (Yasuda) Imazeki (1943) *'' M. subvernicipes'' (Murrill) T.Hatt. & Sotome (2013) *'' M. xanthopus'' (Fr.) Kuntze (1898) Chemistry Seven novel diterpene molecules, microporenic acids A–G, were isolated from the cultures of an undescribed species of ''Microporus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
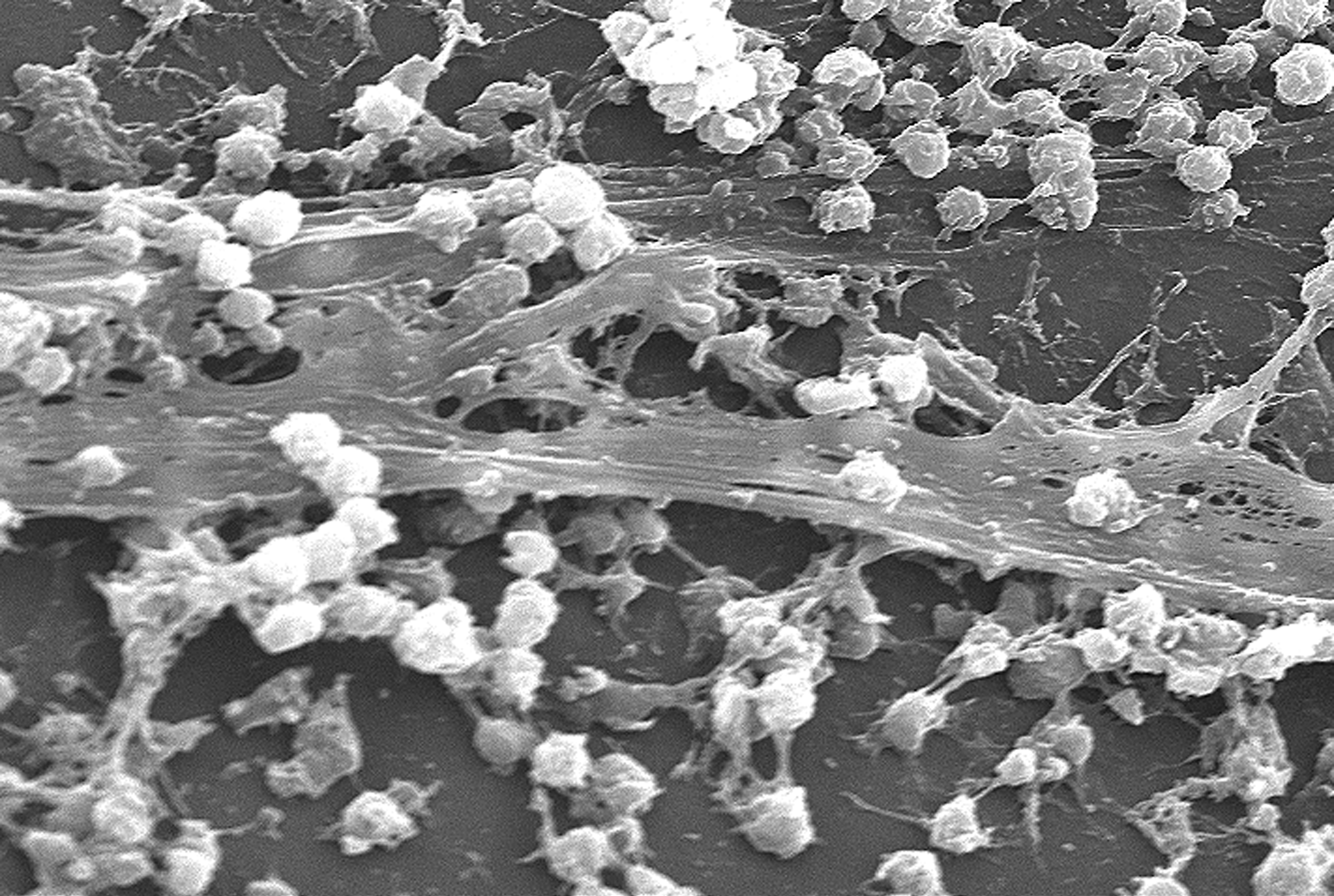
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureus'' (MRSA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive Bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain (sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals are used against fungi. They can also be classified according to their function. Agents that kill microbes are microbicides, while those that merely inhibit their growth are called bacteriostatic agents. The use of antimicrobial medicines to treat infection is known as antimicrobial chemotherapy, while the use of antimicrobial medicines to prevent infection is known as antimicrobial prophylaxis. The main classes of antimicrobial agents are disinfectants (non-selective agents, such as bleach), which kill a wide range of microbes on non-living surfaces to prevent the spread of illness, antiseptics (which are applied to living tissue and help reduce infection during surgery), and antibiotics (which destroy microorganisms within the body). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kakamega Forest
Kakamega Forest is a tropical rainforest situated in the Kakamega County, Kakamega and Nandi_County, Nandi County of Kenya, northwest of the capital Nairobi, and near to the border with Uganda. It is Kenya's only tropical rainforest and is said to be Kenya's last remnant of the ancient Guineo-Congolian region, Guineo-Congolian rainforest that once spanned the continent. Geography The forest lies on undulating terrain, mostly between 1500 and 1600 meters elevation. It is in the watershed of the Isiukhu and Yala rivers, which flow through the forest before emptying into Lake Victoria. The forest including reserves encloses about 238 square kilometers, a little less than half of which currently remains as indigenous forest. In the north of the forest is the Kakamega National Reserve, given national forest reserve status in 1985. Just to the north is the Kisere Forest Reserve. Throughout the forest are a series of grassy glades, ranging in size from about 1 to 50, with a few larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiological Culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as a research tool in molecular biology. The term ''culture'' can also refer to the microorganisms being grown. Microbial cultures are used to determine the type of organism, its abundance in the sample being tested, or both. It is one of the primary diagnostic methods of microbiology and used as a tool to determine the cause of infectious disease by letting the agent multiply in a predetermined medium. For example, a throat culture is taken by scraping the lining of tissue in the back of the throat and blotting the sample into a medium to be able to screen for harmful microorganisms, such as ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', the causative agent of strep throat. Furthermore, the term culture is more generally used informally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diterpene
Diterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being a primary intermediate. Diterpenes form the basis for biologically important compounds such as retinol, retinal, and phytol. They are known to be antimicrobial and antiinflammatory. Structures As with most terpenes a huge number of potential structures exists, which may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. Biosynthesis Diterpenes are derived from the addition of one IPP unit to FPP to form geranylgeranyl-pyrophosphate (GGPP). From GGPP, structural diversity is achieved mainly by two classes of enzymes; the diterpene synthases and cytochromes P450. Several diterpenes are produced by plants and cyanobacteria. GGPP is also the precursor for the synthesis of the phytane by the action of the enzyme geranylger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microporus Xanthopus
''Microporus xanthopus'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Microporus ''Microporus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Polyporaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution and, according to a 2008 estimate, contains 11 species. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek words ("small") and ("pore"). Species , In ...''. It is an inedible wood-decaying mushroom native to tropical areas. Gallery Microporus xanthopus, voet en ondersy, Krantzkloof Natuurreservaat.jpg, Yellow foot of fruiting body Microporus xanthopus, ondersy, Krantzkloof Natuurreservaat.jpg, Pores magnified by droplet Microporus xanthopus, Krantzkloof Natuurreservaat, f.jpg, Lateral view of fruiting bodies References Polyporaceae Fungus species {{Fungus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microporus Subvernicipes
''Microporus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Polyporaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution and, according to a 2008 estimate, contains 11 species. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek words ("small") and ("pore"). Species , Index Fungorum accepts 12 species in ''Microporus'': *'' M. affinis'' (Blume & T.Nees) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. affinis-microloma'' (Lloyd) T.Hatt. & Sotome (2013) *'' M. atroalbus'' (Henn.) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. atrovillosus'' Ryvarden (1975) *'' M. concinnus'' P.Beauv. (1804) *'' M. incomptus'' (Afzel. ex Fr.) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. internuntius'' (Corner) T. Hatt. (2005) *'' M. longisporus'' T.Hatt. (2000) *'' M. luteoceraceus'' D.A.Reid (1986) – Peninsular Malaysia *'' M. nipponicus'' (Yasuda) Imazeki (1943) *'' M. subvernicipes'' (Murrill) T.Hatt. & Sotome (2013) *'' M. xanthopus'' (Fr.) Kuntze (1898) Chemistry Seven novel diterpene molecules, microporenic acids A–G, were isolated from the cultures of an undescribed species of ''Microporus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microporus Nipponicus
''Microporus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Polyporaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution and, according to a 2008 estimate, contains 11 species. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek words ("small") and ("pore"). Species , Index Fungorum accepts 12 species in ''Microporus'': *'' M. affinis'' (Blume & T.Nees) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. affinis-microloma'' (Lloyd) T.Hatt. & Sotome (2013) *'' M. atroalbus'' (Henn.) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. atrovillosus'' Ryvarden (1975) *'' M. concinnus'' P.Beauv. (1804) *'' M. incomptus'' (Afzel. ex Fr.) Kuntze (1898) *'' M. internuntius'' (Corner) T. Hatt. (2005) *'' M. longisporus'' T.Hatt. (2000) *'' M. luteoceraceus'' D.A.Reid (1986) – Peninsular Malaysia *'' M. nipponicus'' (Yasuda) Imazeki (1943) *'' M. subvernicipes'' (Murrill) T.Hatt. & Sotome (2013) *'' M. xanthopus'' (Fr.) Kuntze (1898) Chemistry Seven novel diterpene molecules, microporenic acids A–G, were isolated from the cultures of an undescribed species of ''Microporus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |