|
Mi'kmaw
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Mi'kmaw'' or ''Mi'gmaw''; ; , and formerly Micmac) are an Indigenous group of people of the Northeastern Woodlands, native to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces, primarily Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland, and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as Native Americans in the northeastern region of Maine. The traditional national territory of the Mi'kmaq is named Mi'kma'ki (or Mi'gma'gi). There are 66,748 Mi'kmaq people in the region as of 2023 (including 25,182 members in the more recently formed Qalipu First Nation in Newfoundland). According to the Canadian 2021 census, 9,245 people claim to speak Mi'kmaq, an Eastern Algonquian language. Once written in Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing, it is now written using most letters of the Latin alphabet. The Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and Pasamaquoddy nations signed a series of treaties known as the Covenant Chain of Peace and Friendship Treaties with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikmaq State Flag
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Mi'kmaw'' or ''Mi'gmaw''; ; , and formerly Micmac) are an Indigenous group of people of the Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, Northeastern Woodlands, native to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Canada, Atlantic Provinces, primarily Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland, and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans in the northeastern region of Maine. The traditional national territory of the Mi'kmaq is named Mi'kma'ki (or Mi'gma'gi). There are 66,748 Mi'kmaq people in the region as of 2023 (including 25,182 members in the more recently formed Qalipu First Nation in Newfoundland). According to the Canadian 2021 census, 9,245 people claim to speak Mi'kmaq language, Mi'kmaq, an Eastern Algonquian languages, Eastern Algonquian language. Once written in Mi'kmaw hieroglyphs, Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing, it is now wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mi'kmaw Hieroglyphs
Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing or Suckerfish script ( Mi'kmawi'sit: ) was a writing system for the Mi'kmaw language, later superseded by various Latin scripts which are currently in use. Mi'kmaw are a Canadian First Nation whose homeland, called Mi'kma'ki, overlaps much of the Atlantic provinces, specifically all of Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and parts of New Brunswick and Newfoundland and Labrador. These glyphs, or , although unrelated, followed a prior pictograph and petroglyph tradition, and are logograms, with phonetic elements used alongside, including logographic, alphabetic, and ideographic information. As petroglyphs and pictographs were the writing system of Hand Talk, a sign language that was the historically most spoken language on the continent, it is unknown to academia what, if any, connection there is between sign language and Suckerfish script. The take their name from the (plural: ) or sucker fish whose tracks are visibly left on the muddy river bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
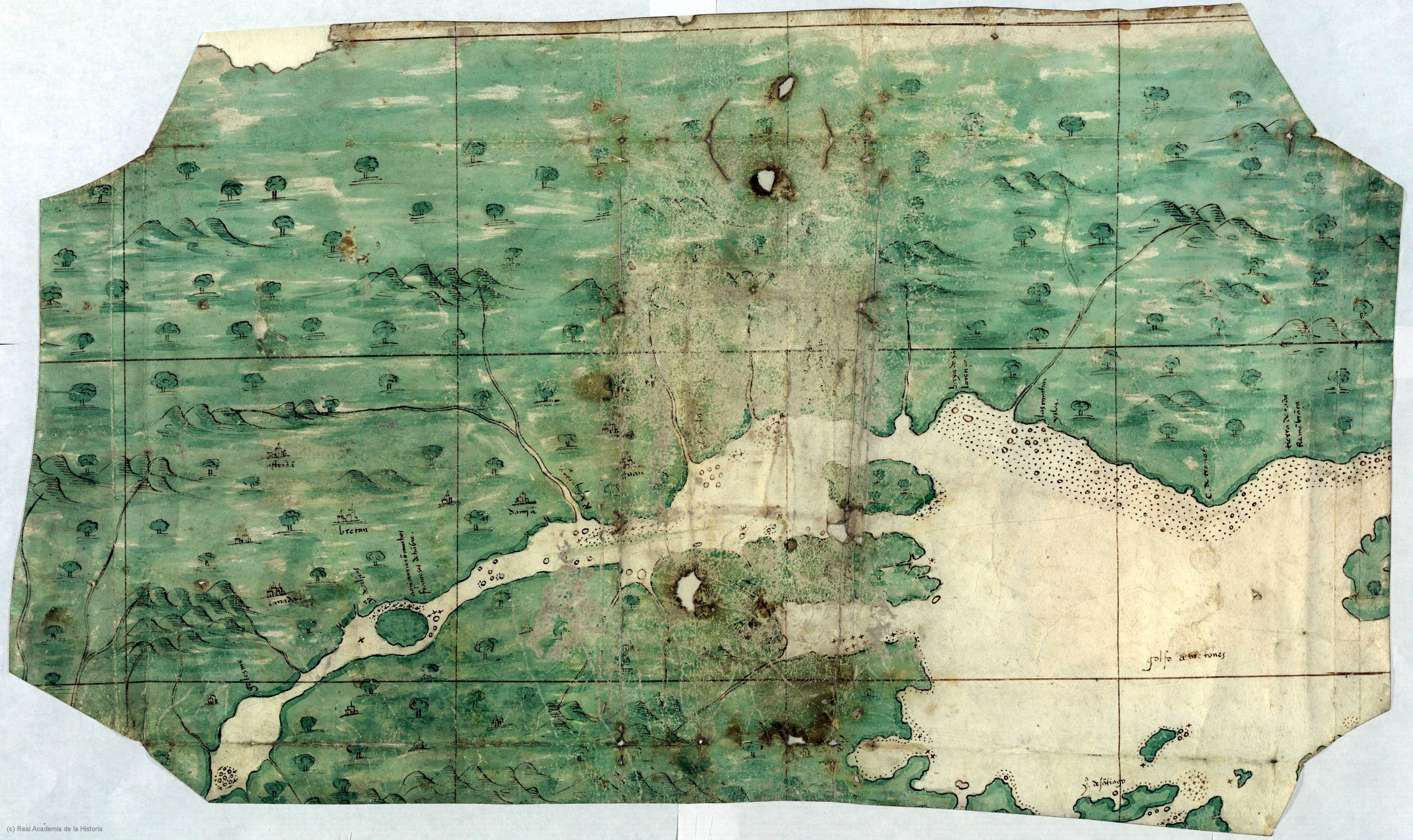
Mi'kma'ki
Mi'kma'ki or Mi'gma'gi is composed of the traditional and current territories, or country, of the Mi'kmaq people, in what is now Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and eastern Quebec, Canada. It is shared by an Non-governmental organization, inter-Nation forum among Mi'kmaq First Nations in Canada, First Nations and is divided into seven geographical and traditional districts with Newfoundland (island), ''Taqamkuk'' being separately represented as an eighth district, formerly joined with Cape Breton Island, ''Unama'ki'' (Cape Breton). Mi'kma'ki and the Mi'kmaq, Mi'kmaw Nation are one of the confederated entities within the Wabanaki Confederacy. History Each district was autonomous, headed by a ''Sachem, Sagamaw''. He would meet with Wampum readers and knowledge keepers called ''turkey keepers'', a women's council, and the ''Kji Sagamaw'', or Grand Chief, to form the Grand Council (Mi'kmaq), ''Sante'Mawio'mi'' (or ''Mi'kmawey Mawio'mi''), the Grand Council. The se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Council (Mi'kmaq)
The Grand Council (Santé Mawiómi or Mi'kmawey Mawio'mi) is the normal senior level of government for the Mi'kmaq, based in present-day Canada, until passage of the Indian Act in 1876, requiring elected governments. After the Indian Act, the Grand Council adopted a more spiritual function. The Grand Council was made up of representatives from the seven district councils in Mi'kma'ki and ''Keptinaq'' ("captains"), who were the district chiefs. There were also elders, the ''putús'', the women's council, and the Grand Chief. The ''putús'' recorded the Mi'kmaq Grand Council meetings by stories and the creation of wampum belts, a kind of visual history, and dealt with the treaties with other native tribes and non-native groups. The hereditary chiefs of the traditional Grand Council continue to have a role, but the legal authority to govern has been largely transferred by the Indian Act to the elected chiefs and councils. Establishment The Grand Council was created following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlantic Canada, with an estimated population of over 1 million as of 2024; it is also the second-most densely populated province in Canada, and second-smallest province by area. The province comprises the Nova Scotia peninsula and Cape Breton Island, as well as 3,800 other coastal islands. The province is connected to the rest of Canada by the Isthmus of Chignecto, on which the province's land border with New Brunswick is located. Nova Scotia's Capital city, capital and largest municipality is Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, which is home to over 45% of the province's population as of the 2021 Canadian census, 2021 census. Halifax is the List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, twelfth-largest census metropolitan area in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tufts Cove, Nova Scotia
Tufts Cove is an urban neighbourhood in the community of Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, Canada. It is situated on the eastern shore of Halifax Harbour in the North End of Dartmouth. The neighbourhood boundaries of Tufts Cove are approximately from Albro Lake Road in the south to Highway 111 in the north, and from Victoria Road in the east with the harbour to the west. History The cove was the site of a Mi'kmaq community called Turtle Grove, first recorded in the 18th century and likely inhabited for generations. A painting from the 1790s shows a Mi'kmaq family at the cove, while an oil painting from around 1837 by William Eager shows a Mi'kmaq encampment. A notable resident in later years was the Mi'kmaw leader and ethnologist Jerry Lonecloud. The cove was named for Gersham Tufts, who was living in Halifax by 1752. He later received a Crown land grant for a large tract of land in Dartmouth. The farms of the early settler community grew in the early 19th century as industry spread n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wabanaki Confederacy
The Wabanaki Confederacy (''Wabenaki, Wobanaki'', translated to "People of the Dawn" or "Easterner"; also: Wabanakia, "Dawnland") is a North American First Nations and Native American confederation of five principal Eastern Algonquian nations: the Abenaki, Mi'kmaq, Wolastoqiyik, Passamaquoddy (''Peskotomahkati'') and Penobscot. There were more tribes, along with many bands, that were once part of the Confederation. Native tribes such as the Nanrantsouak, Alemousiski, Pennacook, Sokoki, and Canibas, through massacres, tribal consolidation, and ethnic label shifting were absorbed into the five larger national identities. Members of the Wabanaki Confederacy, the Wabanakiyak, are located in and named for the area which they call Wabanaki ("Dawnland"), roughly the area that became the French colony of Acadia. The territory boundaries encompass present-day Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, in the United States, and New Brunswick, mainland Nova Scotia, Cape Breton Island, Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miꞌkmaq Language
The Miꞌkmaq language ( ; ), or , is an Eastern Algonquian language spoken by nearly 11,000 Miꞌkmaq in Canada and the United States; the total ethnic Miꞌkmaq population is roughly 20,000. The native name of the language is , or (in some dialects). The word is a plural word meaning 'my friends' (singular Micmac Teaching Grammar. Delisle / Metallic 1976.); the adjectival form is . Phonology The phonemic inventory of Miꞌkmaq is shown below. Vowels Consonants The sounds of Miꞌkmaq can be divided into two groups: obstruents () and sonorants ( and all vowels). The obstruents have a wide variety of pronunciations. When they are located word-initially or next to another obstruent, they are voiceless . However, when they are located between sonorants, they are voiced, and appear as . When the plosives and affricate (namely ) are located word-finally, they may be aspirated and appear as . An example of each kind of pronunciation is given below. Miꞌkmaq distinguish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qalipu First Nation
The Qalipu First Nation (Phonetics, phon: /xa.li.bu/, [xalibu]; Mi'kmaq language, Mi'kmaq for 'caribou') is a Mi'kmaq band government based on the eastern Canadian island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland. The landless band was created by order-in-council in 2011, pursuant to the Agreement for the Recognition of the Qalipu Mi'kmaq Band. Following their approval as a First Nation, around 100,000 people applied for membership, while a total of 23,000 were, ultimately, approved. In 2018, the Qalipu First Nation was accepted as a member of the Canadian Assembly of First Nations. History prior to recognition Pre-contact Prior to the time of European Canadians, European contact, the Mi'kmaq people inhabited Mi'kma'ki, Miꞌkmaꞌki, their vast territories which encompassed much of modern-day Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island, as well as portions of northeastern New Brunswick and Quebec's Gaspé Peninsula. By the Timeline of Canadian history, 17th century, the Mi'kmaq would of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mi'kmaq Language
The Miꞌkmaq language ( ; ), or , is an Eastern Algonquian language spoken by nearly 11,000 Miꞌkmaq in Canada and the United States; the total ethnic Miꞌkmaq population is roughly 20,000. The native name of the language is , or (in some dialects). The word is a plural word meaning 'my friends' (singular Micmac Teaching Grammar. Delisle / Metallic 1976.); the adjectival form is . Phonology The phonemic inventory of Miꞌkmaq is shown below. Vowels Consonants The sounds of Miꞌkmaq can be divided into two groups: obstruents () and sonorants ( and all vowels). The obstruents have a wide variety of pronunciations. When they are located word-initially or next to another obstruent, they are voiceless . However, when they are located between sonorants, they are voiced, and appear as . When the plosives and affricate (namely ) are located word-finally, they may be aspirated and appear as . An example of each kind of pronunciation is given below. Miꞌkmaq distinguish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", "Birthplace of Canadian Confederation, Confederation" and "Cradle of Confederation". Its capital and largest city is Charlottetown. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Part of the traditional lands of the Mi'kmaq, it was colonized by the French in 1604 as part of the colony of Acadia. The island, known as Isle St-Jean (St. John's Island), was ceded to the British at the conclusion of the Seven Years' War in 1763 and became part of the colony of Nova Scotia. In 1769, St. John's Island became its own British colony and its name was changed to Prince Edward Island (PEI) in 1798. PEI hosted the Charlottetown Conference in 1864 to discuss a Maritime Union, union of the Maritime provinces; however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penobscot
The Penobscot (Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewi'') are an Indigenous people in North America from the Northeastern Woodlands region. They are organized as a federally recognized tribe in Maine and as a First Nations band government in the Atlantic provinces and Quebec. The ''Penobscot Nation'', formerly known as the ''Penobscot Tribe of Maine,'' is the federally recognized tribe of Penobscot in the United States."Tribal Directory" ''National Congress of American Indians''. Retrieved 30 August 2012. They are part of the , along with the , |