|
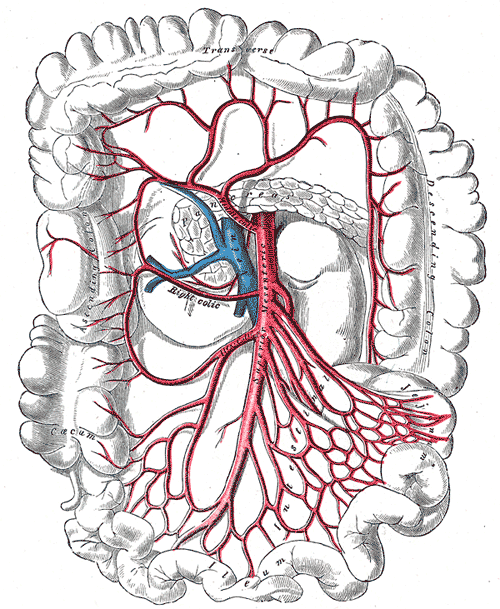
Mesenteric Arteries
The mesenteric arteries take blood from the aorta and distribute it to a large portion of the gastrointestinal tract. Both the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries arise from the abdominal aorta. Each of these arteries travel through the mesentery, within which they branch several times before reaching the gut. In humans, many of these branches are named, but in smaller animals the branches are more variable. In some animals, including humans, branches of these arteries join with the marginal artery of the colon, which means that occlusion of one of the main arteries does not necessarily lead to the death of the part of the gut that it usually supplies. The term mesenteric artery is also used to describe smaller branches of these vessels which, particularly in smaller animals, provide a significant source of vascular resistance. These branches have a dense innervation by sympathetic nerves, allowing the brain to control their diameter and hence the resistance to blood flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Mesenteric A
{{disambiguation ...
Inferior may refer to: * Inferiority complex * An anatomical term of location * Inferior angle of the scapula, in the human skeleton * ''Inferior'' (book), by Angela Saini * ''The Inferior'', a 2007 novel by Peadar Ó Guilín See also *Junior (other) Junior or Juniors may refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * ''Junior'' (Junior Mance album), 1959 * ''Junior'' (Röyksopp album), 2009 * ''Junior'' (Kaki King album), 2010 * ''Junior'' (LaFontaines album), 2019 Films * ''Junior'' (1994 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
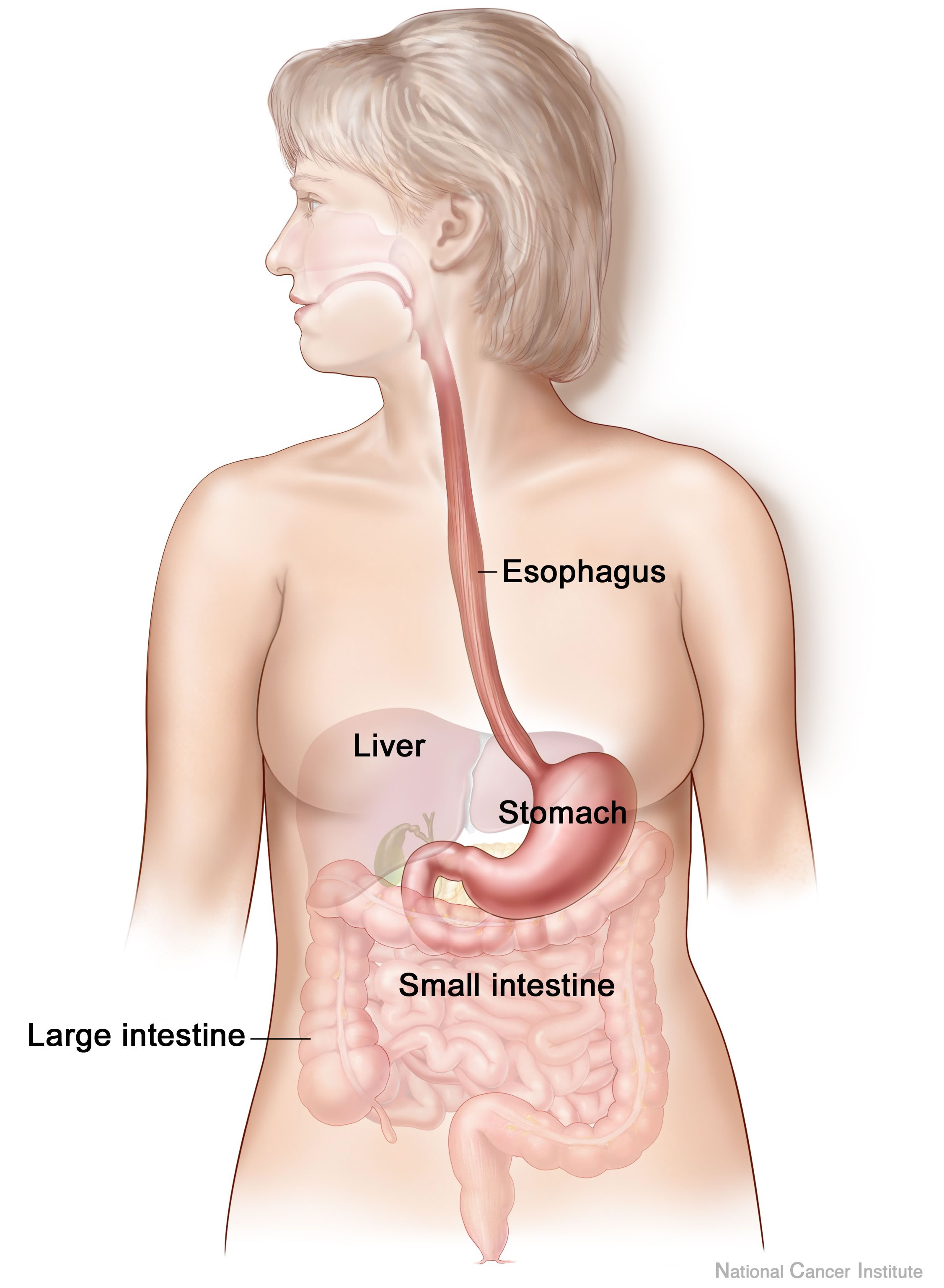
Gut (anatomy)
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Mesenteric Artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas. Structure It arises anterior to lower border of vertebra L1 in an adult. It is usually 1 cm lower than the celiac trunk. It initially travels in an anterior/inferior direction, passing behind/under the neck of the pancreas and the splenic vein. Located under this portion of the superior mesenteric artery, between it and the aorta, are the following: * left renal vein - travels between the left kidney and the inferior vena cava (can be compressed between the SMA and the abdominal aorta at this location, leading to nutcracker syndrome). * the third part of the duodenum, a segment of the small intestines (can be compressed by the SMA at this location, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric artery, often abbreviated as IMA, is the third main branch of the abdominal aorta and arises at the level of L3, supplying the large intestine from the distal transverse colon to the upper part of the anal canal. The regions supplied by the IMA are the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, and part of the rectum. Structure Proximally, its territory of distribution overlaps (forms a watershed) with the middle colic artery, and therefore the superior mesenteric artery. The SMA and IMA anastomose via the marginal artery of the colon (artery of Drummond) and via Riolan's arcade (also called the "meandering artery", an arterial connection between the left colic artery and the middle colic artery). The territory of distribution of the IMA is more or less equivalent to the embryonic hindgut. Branches The IMA branches off the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta below the renal artery branch points, 3-4 cm above the aortic bifurcation (into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Aorta
In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta (of the thorax). Structure The abdominal aorta begins at the level of the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, crossing it via the aortic hiatus, technically behind the diaphragm, at the vertebral level of T12. It travels down the posterior wall of the abdomen, anterior to the vertebral column. It thus follows the curvature of the lumbar vertebrae, that is, convex anteriorly. The peak of this convexity is at the level of the third lumbar vertebra (L3). It runs parallel to the inferior vena cava, which is located just to the right of the abdominal aorta, and becomes smaller in diameter as it gives off branches. This is thought to be due to the large size of its principal branches. At the 11th rib, the diameter is 122mm long and 55mm wide and this is because of the constant pressure. The abdominal aorta is clinically divided int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
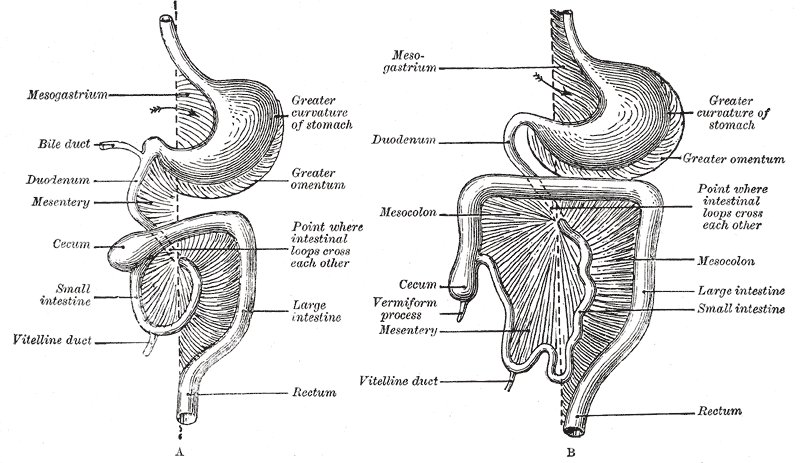
Mesentery
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions. The mesocolon was thought to be a fragmented structure, with all named parts—the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid mesocolons, the mesoappendix, and the mesorectum—separately terminating their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. However, in 2012, new microscopic and electron microscopic examinations showed the mesocolon to be a single structure derived from the duodenojejunal flexure and extending to the distal mesorectal layer. Thus, the mesentery is an internal organ. Structure The mesentery of the small intestine arises from the root of the mesentery (or mesenteric root) and is the part connected with the structures in front of the vertebral column. The root is narrow, about 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Artery Of The Colon
In human anatomy, the marginal artery of the colon, also known as the marginal artery of Drummond, the artery of Drummond, and simply as the marginal artery, is an artery that connects the inferior mesenteric artery with the superior mesenteric artery. It is sometimes absent, as an anatomical variant. Structure The marginal artery runs in the mesentery close to the large intestine as part of the vascular arcade that connects the superior mesenteric artery and the inferior mesenteric artery. It provides an effective anastomosis between these two arteries for the large intestine. Variation The marginal artery is almost always present, and its absence should be considered a variant. Clinical significance Removal of the inferior mesenteric artery Along with branches of the internal iliac arteries, it is usually sufficiently large to supply the oxygenated blood to the large intestine. This means that the inferior mesenteric artery does not have to be re-implanted (re-attached) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system. The autonomic nervous system functions to regulate the body's unconscious actions. The sympathetic nervous system's primary process is to stimulate the body's fight or flight response. It is, however, constantly active at a basic level to maintain homeostasis. The sympathetic nervous system is described as being antagonistic to the parasympathetic nervous system which stimulates the body to "feed and breed" and to (then) "rest-and-digest". Structure There are two kinds of neurons involved in the transmission of any signal through the sympathetic system: pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic. The shorter preganglionic neurons originate in the thoracolumbar division o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteries Of The Abdomen
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.gif)