|
Mercury 3 (other)
Mercury 3 or variants may refer to: * Mercury 3, a spacecraft of Project Mercury * Mercury(III), an unknown compound of the element Mercury (element), Mercury * Mercury III, a version of the Blackburn Mercury early British aircraft * Mercury III, a 1929 version of the Bristol Mercury aircraft engine See also * Mercury (other) *Mercury-Redstone 3, the first U.S. human spaceflight, 1961 *Mercury-Atlas 3, a 1961 unmanned space flight {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Mercury
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbit and return him safely, ideally before the Soviet Union. Taken over from the US Air Force by the newly created civilian space agency NASA, it conducted 20 uncrewed developmental flights (some using animals), and six successful flights by astronauts. The program, which took its name from Roman mythology, cost $ (adjusted for inflation). The astronauts were collectively known as the "Mercury Seven", and each spacecraft was given a name ending with a "7" by its pilot. The Space Race began with the 1957 launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik 1. This came as a shock to the American public, and led to the creation of NASA to expedite existing US space exploration efforts, and place most of them under civilian control. After the successful launch of the Explorer 1 satellite in 1958, crewed spacef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver and was formerly named hydrargyrum ( ) from the Greek words, ''hydor'' (water) and ''argyros'' (silver). A heavy, silvery d-block A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-blo ... element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Mercury is used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackburn Mercury
The Blackburn Mercury was an early British aircraft designed as a pilot trainer for the Blackburn Flying School, Filey, in 1911. It was an enlarged, two-seat version of the Second Monoplane that flew earlier that year. It was a mid-wing monoplane of conventional configuration that accommodated pilot and student in tandem, open cockpits. This prototype was displayed at the Olympia Aero Show in March 1911, and led to orders being placed for two racers to participate in the ''Daily Mail'' Circuit of Britain race. The first of these crashed on takeoff, and the second was first rebuilt into a two-seat trainer, then into a single-seat trainer known as the Type B."The Blackburn School Monoplane", p.1051. Though ''Flight'' refers to this aircraft as the Blackburn School monoplane, it is the Type B. Another six Mercuries were built for various private buyers. A full-scale non-flying replica of Mercury II configuration was constructed for the Yorkshire Television series ''Flambards' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Mercury
The Bristol Mercury is a British nine-cylinder, air-cooled, single-row, piston radial engine. Designed by Roy Fedden of the Bristol Aeroplane Company it was used to power both civil and military aircraft of the 1930s and 1940s. Developed from the earlier Jupiter engine, later variants could produce 800 horsepower (600 kW) from its capacity of 1,500 cubic inches (25 L) by use of a geared supercharger. Almost 21,000 engines were produced, with a number also being built under license elsewhere in Europe. Several examples remain airworthy, with other preserved examples on public display in aviation museums. Design and development The Mercury was developed by the Bristol Aeroplane Company in 1925 as their Bristol Jupiter was reaching the end of its lifespan. Although the Mercury initially failed to attract much interest, the Air Ministry eventually funded three prototypes and it became another winner for the designer Roy Fedden. With the widespread introduction of superchar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (other)
Mercury commonly refers to: * Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun * Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg * Mercury (mythology), a Roman god Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to: Companies * Mercury (toy manufacturer), a brand of diecast toy cars manufactured in Italy * Mercury Communications, a British telecommunications firm set up in the 1980s * Mercury Drug, a Philippine pharmacy chain * Mercury Energy, an electricity generation and retail company in New Zealand * Mercury Filmworks, a Canadian independent animation studio * Mercury General, a multiple-line American insurance organization * Mercury Interactive, a software testing tools vendor * Mercury Marine, a manufacturer of marine engines, particularly outboard motors * Mercury Systems, a defense-related information technology company Computing * Mercury (programming language), a functional logic programming language * Mercury (metadata search system), a data search system f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
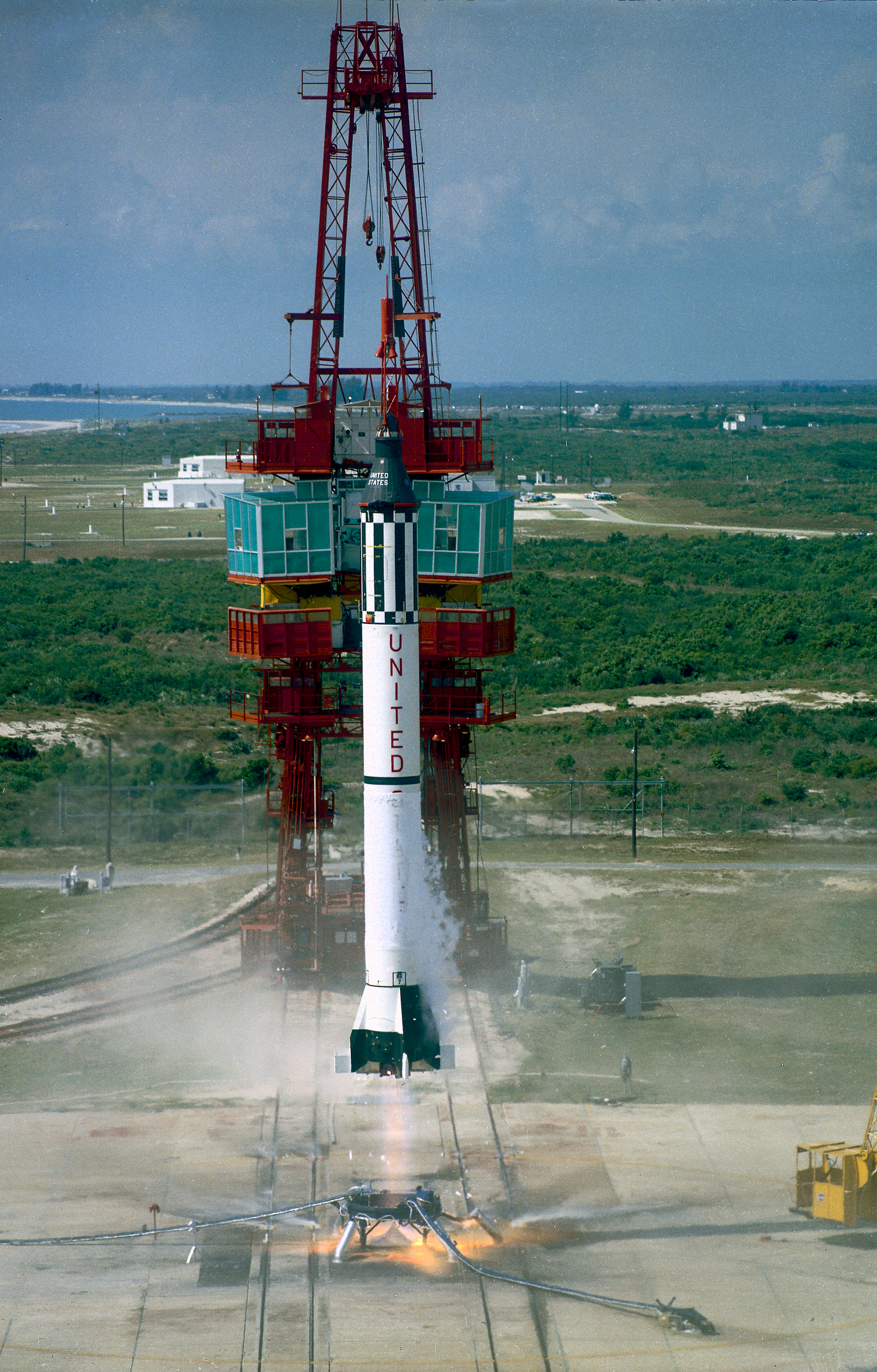
Mercury-Redstone 3
Mercury-Redstone 3, or ''Freedom 7'', was the first United States human spaceflight, on May 5, 1961, piloted by astronaut Alan Shepard. It was the first crewed flight of Project Mercury. The project had the ultimate objective of putting an astronaut into orbit around the Earth and returning him safely. Shepard's mission was a 15-minute suborbital flight with the primary objective of demonstrating his ability to withstand the high g-forces of launch and atmospheric re-entry. Shepard named his space capsule ''Freedom 7'', setting a precedent for the remaining six Mercury astronauts naming their spacecraft. The number 7 was included in all the crewed Mercury spacecraft names to honor NASA's first group of seven astronauts. His spacecraft reached an altitude of 101.2 nautical miles (116.5 statute miles, 187.5 km) and traveled a downrange distance of 263.1 nautical miles (302.8 statute miles, 487.3 km). It was the fourth Mercury flight launched with the Mercury-Redstone Launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
_Mercury.jpg)